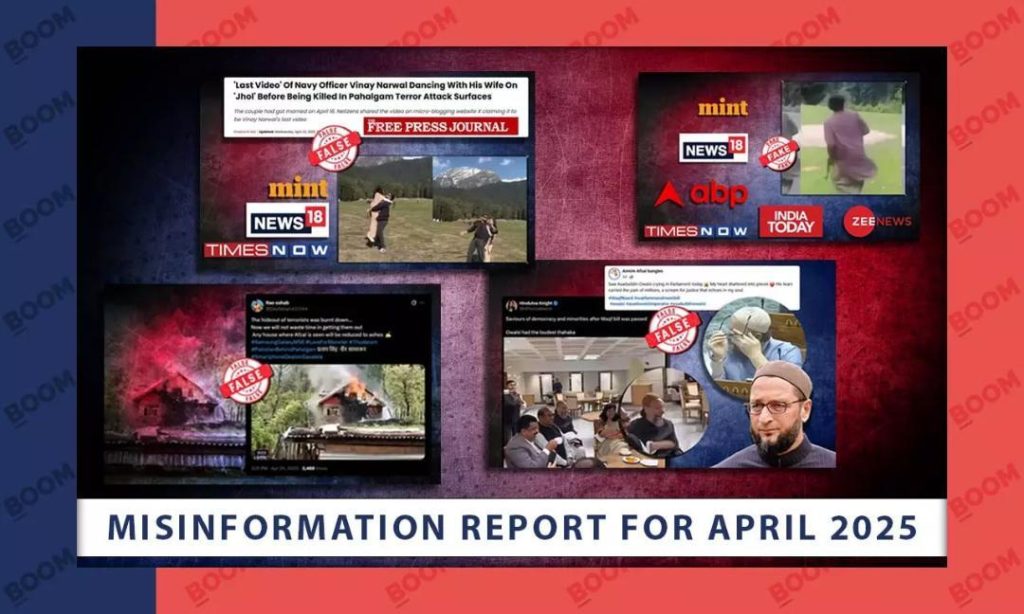
Pahalgam Attack Drove Misinformation Surge in April: BOOM
The month of April 2025 witnessed a surge in misinformation online, particularly after the Pahalgam terror attack on April 22. The attack, which left several injured and killed, triggered a wave of false claims, old videos, and AI-generated images that spread like wildfire on social media. In its latest report, BOOM, a fact-checking organization, revealed that nearly a quarter of its April fact-checks focused on the Pahalgam terror attack, highlighting the devastating impact of misinformation on communal tensions and online discourse.
According to BOOM’s research, 97% of the flagged content was sensational in nature, with most circulating via video. The surge in misinformation was a result of a combination of factors, including old videos, AI-generated images, and media misreporting. The report highlights the urgent need for fact-checking and media literacy to counter the spread of misinformation, which can have severe consequences on society.
The Pahalgam terror attack, which targeted both Indian and Pakistani forces, sparked a wave of false claims and conspiracy theories online. BOOM’s fact-checking efforts revealed that many of these claims were baseless and lacked any factual basis. The organization received over 1,000 requests to fact-check content related to the attack, with around 200 instances of misinformation identified.
One of the most common forms of misinformation was the sharing of old videos, which were presented as new footage of the attack. These videos often showed graphic content, such as explosions and gunfire, which further amplified the sensational nature of the misinformation. BOOM identified several instances of old videos being shared with altered audio or captions, which were designed to create a false narrative about the attack.
AI-generated images were another tool used to spread misinformation. These images, which were designed to look like real news footage, showed scenes of destruction and chaos, with captions and audio claiming to be from the Pahalgam attack. BOOM identified several instances of AI-generated images being shared on social media, often accompanied by sensational headlines and captions.
Media misreporting also played a significant role in the spread of misinformation. Many news outlets reported on the attack without verifying the facts, leading to the spread of false information. BOOM found several instances of news articles and TV channels reporting on the attack without providing credible sources or evidence to support their claims.
The consequences of misinformation were severe, with many social media users being misled into believing false information about the attack. The spread of misinformation further amplified communal tensions, with many online users engaging in heated debates and arguments about the attack. BOOM’s research found that many online users were unaware of the fact that the information they were sharing was false, highlighting the need for media literacy and fact-checking.
In light of the Pahalgam terror attack and the subsequent surge in misinformation, BOOM’s report emphasizes the need for fact-checking and media literacy. The organization urges social media platforms and news outlets to take a proactive approach in identifying and removing misinformation, as well as educating users about the dangers of false information.
BOOM’s report also highlights the need for governments and institutions to take a proactive approach in combating misinformation. The organization recommends that governments establish fact-checking units and media literacy programs to educate citizens about the importance of verifying information before sharing it online.
In conclusion, the Pahalgam terror attack and the subsequent surge in misinformation highlight the urgent need for fact-checking and media literacy. BOOM’s report emphasizes the devastating impact of misinformation on communal tensions and online discourse, and urges social media platforms, news outlets, and governments to take a proactive approach in combating false information.