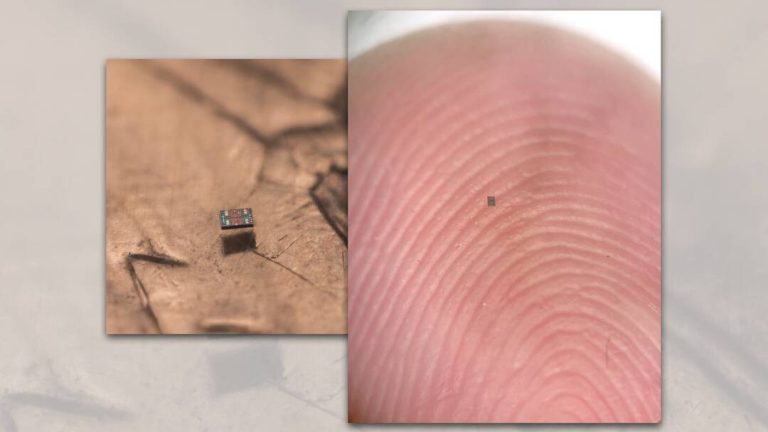
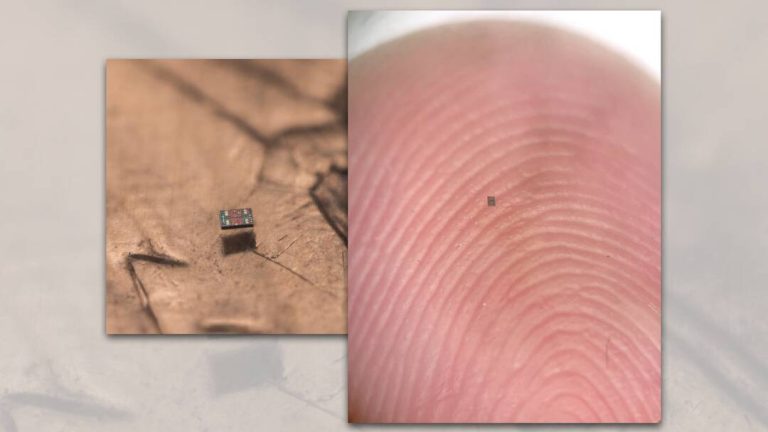
Scientists create world’s smallest programmable robots, share pics
In a groundbreaking achievement, researchers from the Universities of Pennsylvania and Michigan have successfully created the world’s smallest fully programmable and autonomous robots. These microscopic swimming machines are capable of independently sensing and responding to their surroundings, paving the way for a new era of miniature robotics. The robots, which are barely visible to the naked eye, measure a mere 0.2 by 0.3 by 0.05 millimeters and can be produced at a cost of just one penny per unit.
The development of these tiny robots is a significant breakthrough in the field of robotics, as it enables the creation of machines that can operate in tight spaces and interact with their environment in ways that were previously impossible. The robots are equipped with a range of sensors and actuators that allow them to navigate and respond to their surroundings, making them ideal for applications such as search and rescue, environmental monitoring, and medical research.
One of the most significant advantages of these robots is their ability to be programmed and controlled remotely. This allows researchers to tailor the behavior of the robots to specific tasks and environments, making them highly versatile and adaptable. The robots can also be equipped with a range of sensors, including cameras, microphones, and chemical detectors, which enable them to gather data and respond to their surroundings in real-time.
The creation of these tiny robots is the result of a collaboration between researchers from the Universities of Pennsylvania and Michigan, who used advanced manufacturing techniques to produce the robots. The team used a combination of 3D printing and microfabrication to create the robots, which are made from a range of materials including metals, plastics, and ceramics.
The robots are powered by a small electric motor that is capable of generating a significant amount of torque relative to their size. This allows the robots to move and maneuver with ease, even in tight spaces. The robots are also equipped with a range of communication systems, including wireless radio transceivers and optical communication systems, which enable them to communicate with other robots and with external controllers.
The potential applications of these tiny robots are vast and varied. They could be used to search for survivors in rubble or debris, to monitor environmental pollutants, or to deliver drugs or other treatments to specific locations within the body. They could also be used to explore and map tight spaces, such as pipes or ducts, and to inspect and maintain complex systems, such as aircraft or industrial equipment.
The researchers behind the project are excited about the potential of these tiny robots and are already exploring new applications and uses. “These microscopic swimming machines can independently sense and respond to their surroundings,” they stated. “We believe that this technology has the potential to revolutionize a range of fields, from medicine to environmental monitoring, and we are eager to see where it will take us.”
The development of these tiny robots is also significant because of their low cost. At just one penny per unit, they are highly affordable and could be produced in large quantities for a range of applications. This could enable the widespread adoption of robotic technology in fields where it was previously too expensive or impractical.
In addition to their potential applications, the creation of these tiny robots is also significant because of the technological advancements that it represents. The development of these robots required the creation of new manufacturing techniques, new materials, and new control systems, all of which have the potential to be used in a range of other applications.
The researchers have shared pictures of the robots, which provide a glimpse into the tiny world of miniature robotics. The pictures show the robots in action, swimming and maneuvering through tight spaces with ease. They also show the robots’ components, including their sensors, actuators, and communication systems, which are all packed into a tiny package.
In conclusion, the creation of the world’s smallest fully programmable and autonomous robots is a significant breakthrough in the field of robotics. These tiny machines have the potential to revolutionize a range of fields, from medicine to environmental monitoring, and could enable the widespread adoption of robotic technology in fields where it was previously too expensive or impractical. With their low cost, high versatility, and advanced capabilities, these robots are set to make a big impact in the world of robotics and beyond.