Scientists create world’s smallest programmable robots, share pics
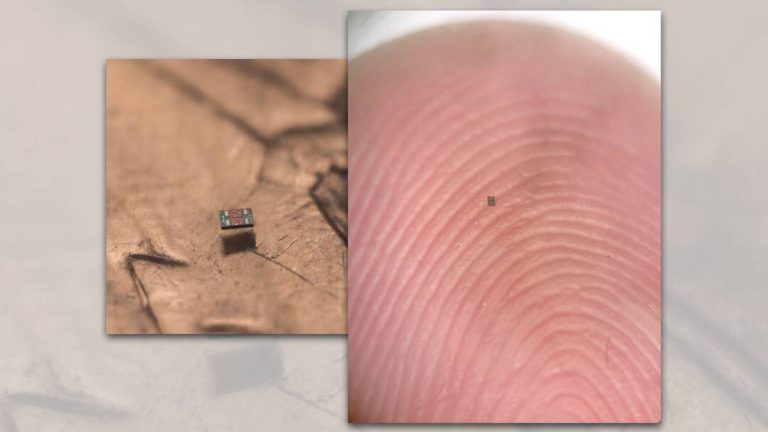
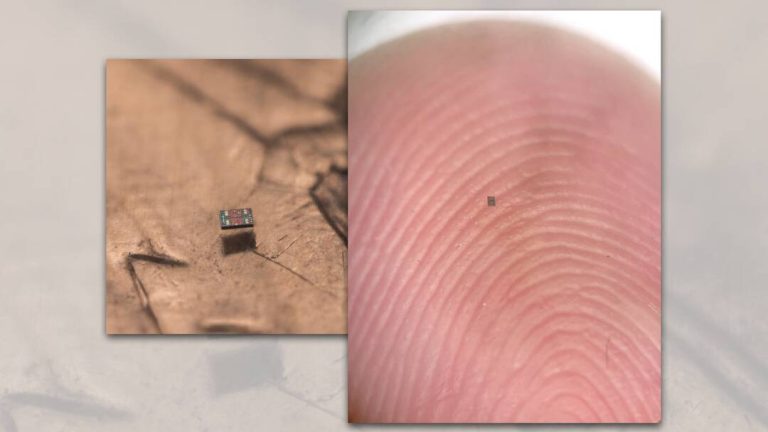
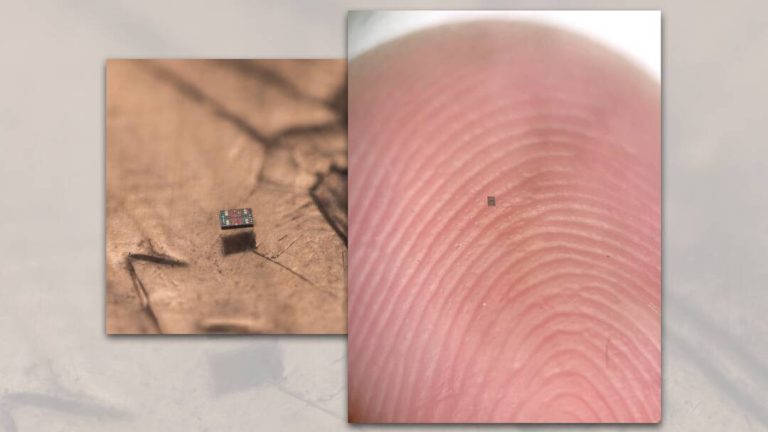
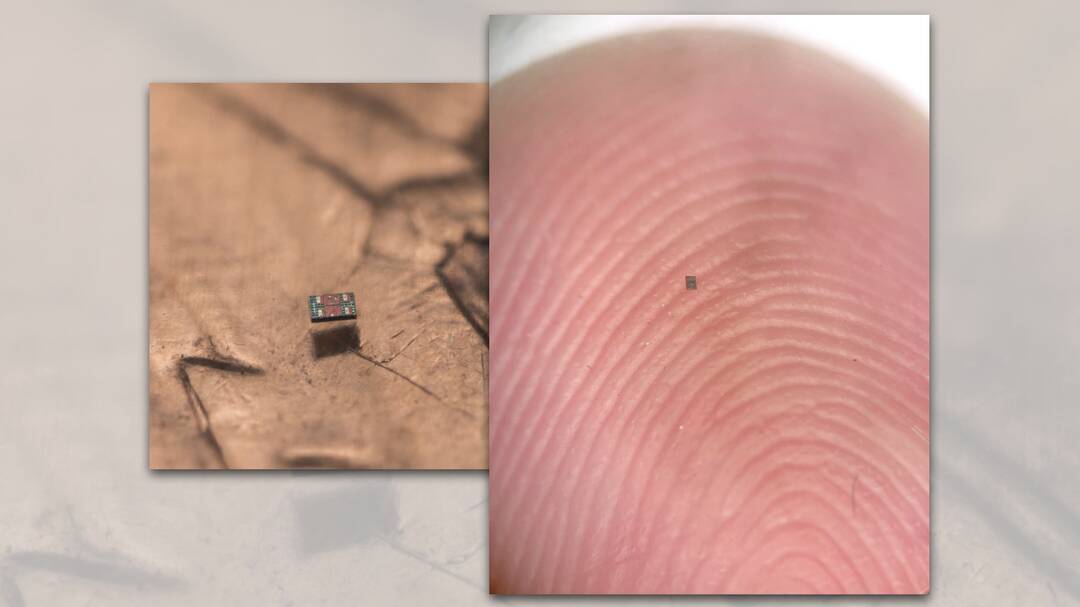
In a groundbreaking achievement, researchers from the Universities of Pennsylvania and Michigan have successfully created the world’s smallest fully programmable and autonomous robots. These microscopic swimming machines are capable of independently sensing and responding to their surroundings, paving the way for a new era in robotics and microtechnology. The robots, which are barely visible to the naked eye, measure a mere 0.2 by 0.3 by 0.05 millimeters, making them smaller than a grain of salt.
The creation of these tiny robots is a significant milestone in the field of robotics, as it demonstrates the possibility of designing and building machines that can operate at the microscale. According to the researchers, the robots are not only small but also incredibly inexpensive, with a production cost of just one penny per unit. This affordability makes them an attractive option for a wide range of applications, from medical devices to environmental monitoring systems.
The robots are equipped with a sophisticated propulsion system that allows them to swim through liquids with ease. They are also capable of sensing their surroundings, including changes in temperature, pH, and other environmental factors. This ability to sense and respond to their environment makes them ideal for tasks such as searching for specific cells or molecules in a sample.
One of the most significant advantages of these robots is their ability to operate independently. They do not require any external control or power source, making them perfect for applications where traditional robots would be impractical or impossible to use. For example, they could be used to explore tight spaces, such as inside the human body, or to monitor environmental conditions in remote or hard-to-reach areas.
The researchers behind the project have shared pictures of the robots, which are truly remarkable. The images show the robots in various configurations, including a swarm of robots working together to achieve a common goal. The pictures also demonstrate the robots’ ability to navigate through complex environments, such as mazes and obstacles.
The creation of the world’s smallest programmable robots is a testament to the ingenuity and creativity of the researchers involved. It is a significant achievement that has the potential to revolutionize a wide range of fields, from medicine to environmental science. As the researchers continue to develop and refine their technology, we can expect to see even more exciting applications and innovations in the future.
The potential applications of these robots are vast and varied. They could be used to develop new medical devices, such as tiny surgical tools or implantable sensors. They could also be used to monitor environmental conditions, such as water quality or air pollution. Additionally, they could be used to explore tight spaces, such as inside buildings or bridges, to detect potential hazards or damage.
The researchers have also noted that the robots could be used to study complex systems, such as the behavior of cells or the movement of molecules. By using the robots to interact with these systems, scientists could gain a deeper understanding of how they work and how they respond to different stimuli.
In conclusion, the creation of the world’s smallest programmable robots is a significant achievement that has the potential to revolutionize a wide range of fields. The robots’ ability to sense and respond to their surroundings, combined with their independence and affordability, make them an attractive option for a wide range of applications. As the researchers continue to develop and refine their technology, we can expect to see even more exciting innovations and applications in the future.
News Source: https://www.seas.upenn.edu/stories/penn-and-umich-create-worlds-smallest-programmable-autonomous-robots/