Safer method boosts gas capture for clean energy
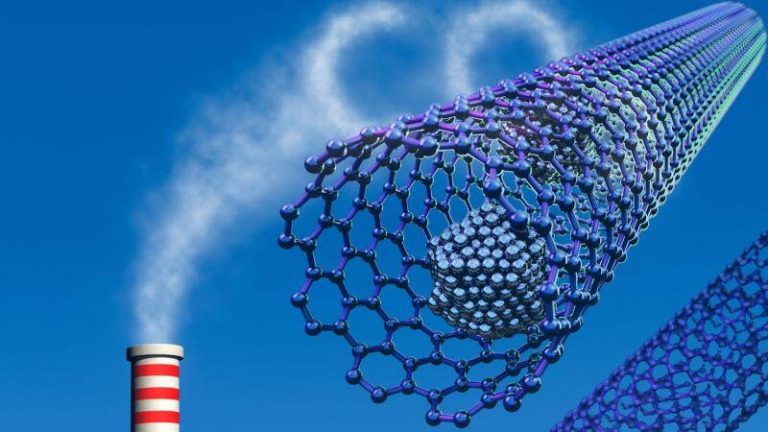
The world is shifting towards cleaner energy sources to combat climate change, and one crucial aspect of this transition is the development of efficient technologies for capturing and storing greenhouse gases. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have emerged as promising materials for this purpose, owing to their high surface area and tunable properties. However, the traditional synthesis methods for MOFs often involve the use of toxic hydrofluoric acid, which poses significant environmental and health risks. In a breakthrough, researchers have now developed a fluoride-free synthesis method for MOFs, replacing hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators. This innovative approach not only simplifies the production process but also yields superior crystals that can trap greenhouse gases and store hydrogen more efficiently at room temperature.
The new method has significant implications for the development of affordable carbon scrubbers and advanced atmospheric water harvesting systems, which are essential for mitigating climate change globally. By providing a safer and more efficient way to synthesize MOFs, this research paves the way for the widespread adoption of these materials in various applications, from environmental remediation to energy storage. In this blog post, we will delve into the details of this groundbreaking research and explore its potential impact on the clean energy landscape.
The challenges of traditional MOF synthesis
Metal-organic frameworks are a class of porous materials composed of metal nodes connected by organic linkers. Their unique structure allows them to absorb and store large amounts of gases, making them ideal for applications such as carbon capture and hydrogen storage. However, the traditional synthesis methods for MOFs often involve the use of hydrofluoric acid, a highly toxic and corrosive substance that requires specialized handling and equipment.
The use of hydrofluoric acid in MOF synthesis poses significant risks to human health and the environment. Exposure to this acid can cause severe burns, respiratory problems, and even death. Moreover, the disposal of hydrofluoric acid waste is a major concern, as it can contaminate soil and water sources. The need for safer and more environmentally friendly synthesis methods has been a major hurdle in the widespread adoption of MOFs for clean energy applications.
The fluoride-free synthesis method
The researchers’ new method replaces hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators, such as benzoic acid or acetic acid, which are commonly used in food and pharmaceutical industries. These modulators facilitate the formation of MOF crystals by controlling the reaction kinetics and thermodynamics. The resulting crystals have superior properties, including higher surface areas, improved thermal stability, and enhanced gas adsorption capacities.
The fluoride-free synthesis method is not only safer but also more efficient and cost-effective. It eliminates the need for specialized equipment and handling procedures, making it more accessible to researchers and industries. The simplified process also reduces the production time and cost, paving the way for the large-scale manufacture of MOFs for various applications.
Improved gas capture and storage
The MOFs synthesized using the new method have shown remarkable gas capture and storage capabilities. They can absorb large amounts of carbon dioxide, methane, and other greenhouse gases at room temperature, making them ideal for carbon capture and storage applications. The MOFs can also store hydrogen more efficiently, which is essential for the development of fuel cell technologies and other clean energy systems.
The improved gas capture and storage properties of the MOFs are attributed to their high surface areas and tunable pore sizes. The researchers can design the MOFs to have specific pore sizes and shapes, allowing them to target specific gases and applications. This versatility makes MOFs an attractive material for a wide range of clean energy applications, from carbon capture and storage to hydrogen fuel cells and beyond.
Implications for climate change mitigation
The development of safer and more efficient MOF synthesis methods has significant implications for climate change mitigation. By providing a cost-effective and environmentally friendly way to produce MOFs, this research paves the way for the widespread adoption of these materials in various applications. The improved gas capture and storage capabilities of the MOFs can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions from power plants, industrial processes, and transportation systems.
The MOFs can also be used to develop advanced atmospheric water harvesting systems, which can provide clean drinking water for millions of people around the world. By capturing and condensing water vapor from the air, these systems can help alleviate water scarcity and support sustainable agriculture, industry, and urbanization.
Conclusion
The development of a fluoride-free synthesis method for metal-organic frameworks is a significant breakthrough in the field of clean energy research. By replacing toxic hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators, this method simplifies the production process and yields superior crystals that can trap greenhouse gases and store hydrogen more efficiently at room temperature. The improved gas capture and storage capabilities of the MOFs have significant implications for climate change mitigation, from carbon capture and storage to hydrogen fuel cells and atmospheric water harvesting.
As the world transitions towards cleaner energy sources, the development of efficient and environmentally friendly technologies is crucial. The research on MOFs and their applications is an exciting area of study, with the potential to make a significant impact on the clean energy landscape. We look forward to seeing the further development and implementation of these innovative materials in the fight against climate change.
News source: https://researchmatters.in/news/greener-path-synthesising-metal-organic-frameworks-carbon-capture-and-storage