Safer method boosts gas capture for clean energy
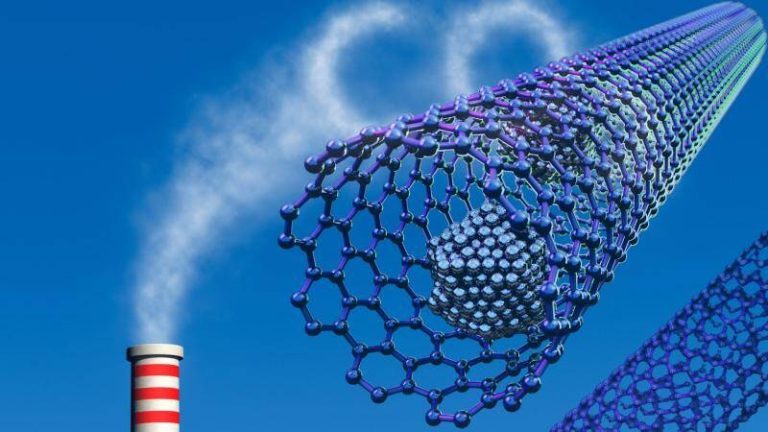
The world is shifting towards cleaner and more sustainable forms of energy to combat climate change, and researchers are working tirelessly to develop innovative solutions to reduce our carbon footprint. One such breakthrough has been made in the field of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), which are highly porous materials that can trap greenhouse gases and store hydrogen more efficiently. Recently, a team of researchers has developed a fluoride-free synthesis method for MOFs, replacing toxic hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators. This simplified method produces superior crystals that can capture and store gases at room temperature, paving the way for affordable carbon scrubbers and advanced atmospheric water harvesting systems to fight climate change globally.
Metal-organic frameworks are a class of materials that have gained significant attention in recent years due to their unique properties. They are composed of metal ions or clusters connected by organic linkers, which create a porous structure that can trap and store gases. MOFs have a wide range of applications, including gas storage, separation, and catalysis, as well as carbon capture and storage. However, the traditional synthesis method for MOFs involves the use of hydrofluoric acid, which is highly toxic and corrosive. This has limited the widespread adoption of MOFs, particularly in industrial settings.
The new synthesis method developed by the researchers uses safer modulators, such as amino acids or peptides, to facilitate the formation of MOF crystals. This approach eliminates the need for hydrofluoric acid, making the synthesis process much safer and more environmentally friendly. The resulting MOF crystals are also superior in terms of their structure and properties, with higher surface areas and pore volumes that enable more efficient gas capture and storage.
One of the most significant advantages of this new synthesis method is its ability to produce MOFs that can capture and store gases at room temperature. This is a major breakthrough, as most MOFs require high temperatures and pressures to function effectively. The new MOFs can also capture a wide range of gases, including carbon dioxide, methane, and hydrogen, making them highly versatile and useful for a variety of applications.
The potential applications of this new synthesis method are vast and varied. One of the most exciting possibilities is the development of affordable carbon scrubbers that can remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Carbon scrubbers are devices that use MOFs or other materials to capture and store carbon dioxide, which can then be converted into useful products such as fuels or chemicals. The new synthesis method could make it possible to produce carbon scrubbers that are more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly.
Another potential application of this technology is the development of advanced atmospheric water harvesting systems. These systems use MOFs or other materials to capture and condense water vapor from the air, providing a sustainable source of clean water for drinking, irrigation, and other uses. The new synthesis method could enable the production of more efficient and effective water harvesting systems, which could have a major impact on global water security and sustainability.
In addition to these applications, the new synthesis method could also have a significant impact on the development of hydrogen fuel cells and other clean energy technologies. Hydrogen is a highly promising alternative to fossil fuels, but it is difficult to store and transport due to its low density and high reactivity. The new MOFs could provide a safe and efficient way to store and transport hydrogen, making it possible to use this clean energy source more widely.
Overall, the development of a fluoride-free synthesis method for metal-organic frameworks is a major breakthrough that could have a significant impact on our ability to combat climate change. The new method is safer, more environmentally friendly, and more efficient than traditional synthesis methods, and it could enable the production of a wide range of clean energy technologies, from carbon scrubbers to hydrogen fuel cells. As the world continues to transition towards cleaner and more sustainable forms of energy, innovations like this will be critical to our success.
In conclusion, the new synthesis method for metal-organic frameworks is a game-changer for the field of clean energy. Its potential applications are vast and varied, and it could have a major impact on our ability to reduce our carbon footprint and combat climate change. As researchers continue to develop and refine this technology, we can expect to see new and innovative solutions emerge that will help us to create a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future.
News source: https://researchmatters.in/news/greener-path-synthesising-metal-organic-frameworks-carbon-capture-and-storage