Safer method boosts gas capture for clean energy
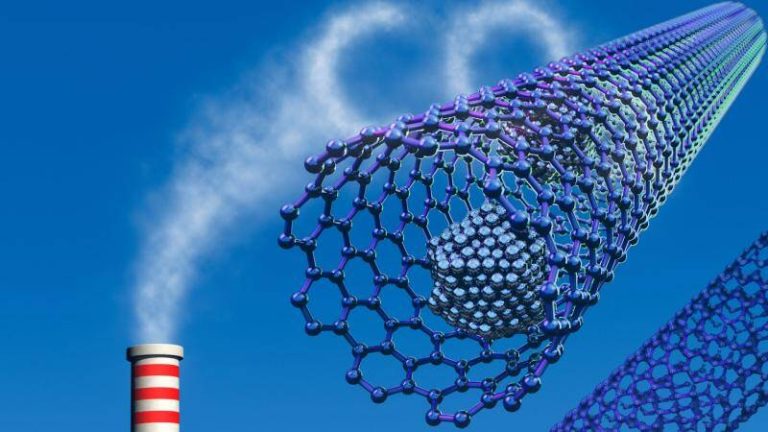
As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change, researchers are working tirelessly to develop innovative solutions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote clean energy. One promising area of research involves the development of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), which are highly porous materials that can capture and store gases, including carbon dioxide and hydrogen. However, the traditional synthesis methods for MOFs often rely on toxic chemicals, such as hydrofluoric acid, which poses significant safety risks. Recently, a team of researchers has made a breakthrough by developing a fluoride-free synthesis method for MOFs, replacing toxic hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators. This simplified method produces superior crystals that trap greenhouse gases and store hydrogen more efficiently at room temperature, paving the way for affordable carbon scrubbers and advanced atmospheric water harvesting systems to fight climate change globally.
The traditional synthesis method for MOFs involves the use of hydrofluoric acid, a highly toxic and corrosive chemical that requires specialized handling and equipment. The use of hydrofluoric acid also generates significant amounts of waste, which can be hazardous to the environment. In contrast, the new fluoride-free synthesis method uses safer modulators, such as organic acids or bases, to control the growth of MOF crystals. This approach not only eliminates the need for toxic chemicals but also simplifies the synthesis process, making it more efficient and cost-effective.
The new method produces MOF crystals with superior properties, including higher surface areas and more uniform pore sizes. These characteristics enable the MOFs to capture and store gases more efficiently, including carbon dioxide and hydrogen. The researchers have demonstrated that their MOFs can capture carbon dioxide at room temperature, which is a significant advantage over traditional carbon capture methods that require high temperatures and pressures. Additionally, the MOFs can store hydrogen at room temperature, which is a crucial step towards developing hydrogen fuel cells and other clean energy technologies.
The potential applications of this breakthrough are vast and varied. One of the most significant implications is the development of affordable carbon scrubbers, which can be used to remove carbon dioxide from power plant emissions and other industrial sources. Currently, carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies are expensive and energy-intensive, which limits their widespread adoption. The new MOF synthesis method could help to reduce the cost and complexity of CCS technologies, making them more viable for large-scale deployment.
Another potential application is the development of advanced atmospheric water harvesting systems. These systems use MOFs to capture water vapor from the air, which can then be condensed and used for drinking, irrigation, or other purposes. The new MOF synthesis method could enable the development of more efficient and cost-effective atmospheric water harvesting systems, which could help to address global water scarcity challenges.
The breakthrough also has significant implications for the development of hydrogen fuel cells and other clean energy technologies. Hydrogen is a clean-burning fuel that can be used to power vehicles, generate electricity, and provide heat. However, the storage and transportation of hydrogen are significant challenges due to its low energy density and high reactivity. The new MOF synthesis method could help to address these challenges by enabling the development of more efficient and cost-effective hydrogen storage systems.
In conclusion, the development of a fluoride-free synthesis method for metal-organic frameworks is a significant breakthrough with far-reaching implications for clean energy and climate change mitigation. The new method produces superior MOF crystals that can capture and store gases more efficiently, including carbon dioxide and hydrogen. The potential applications of this breakthrough are vast and varied, ranging from affordable carbon scrubbers to advanced atmospheric water harvesting systems and hydrogen fuel cells. As researchers continue to develop and refine this technology, we can expect to see significant advances in the field of clean energy and climate change mitigation.
The development of this technology is a testament to the power of innovation and collaboration in addressing global challenges. As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change, it is clear that we need to develop new and innovative solutions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote clean energy. The breakthrough in MOF synthesis is a significant step in this direction, and it highlights the importance of continued investment in research and development to address the global energy and environmental challenges.
As we move forward, it is essential to continue to develop and refine this technology, as well as to explore new and innovative applications for MOFs. By working together, we can unlock the full potential of this breakthrough and create a more sustainable and equitable energy future for all.