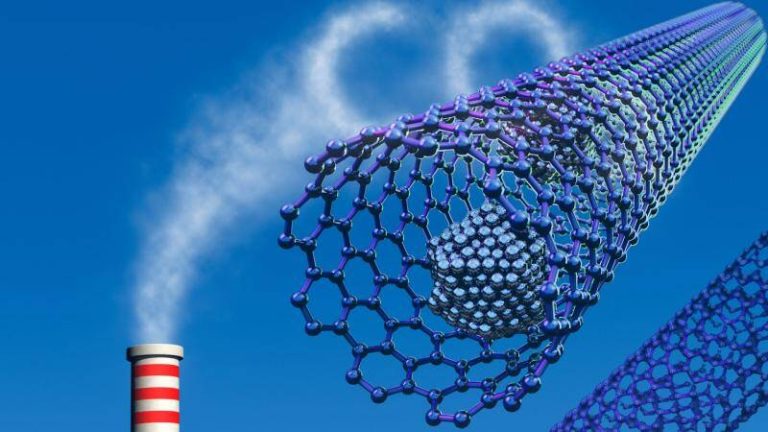
Safer method boosts gas capture for clean energy
The world is shifting towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources to combat climate change. One crucial aspect of this transition is the development of efficient technologies for capturing and storing greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have emerged as promising materials for this purpose, owing to their high surface area and tunable properties. However, the traditional synthesis methods for MOFs often involve the use of toxic hydrofluoric acid, which poses significant environmental and health risks. Recently, researchers have made a breakthrough by developing a fluoride-free synthesis method for MOFs, replacing hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators. This innovative approach not only simplifies the production process but also yields superior crystals that can trap greenhouse gases and store hydrogen more efficiently at room temperature.
The new synthesis method has significant implications for the development of affordable carbon scrubbers and advanced atmospheric water harvesting systems. Carbon scrubbers are devices that capture carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, which can then be utilized or stored, reducing the amount of greenhouse gases in the environment. Atmospheric water harvesting systems, on the other hand, extract water from air, even in arid regions, providing a sustainable source of clean drinking water. The improved MOFs produced through the fluoride-free method can enhance the performance of these systems, making them more efficient and cost-effective.
The traditional synthesis of MOFs involves the use of hydrofluoric acid, which is highly corrosive and toxic. This acid is used as a modulator to control the size and shape of the MOF crystals, but it poses significant risks to the environment and human health. The fluoride-free synthesis method replaces hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators, such as benzoic acid or acetic acid, which are more environmentally friendly and less hazardous to handle. This approach not only reduces the risks associated with the synthesis process but also simplifies the production of MOFs, making them more accessible for various applications.
The researchers who developed the fluoride-free synthesis method demonstrated its effectiveness by producing high-quality MOF crystals with superior properties. The resulting MOFs exhibited higher surface areas and more uniform pore sizes, which are essential for efficient gas capture and storage. The team also tested the MOFs for their ability to trap greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, and found that they performed better than MOFs produced through traditional methods. Additionally, the fluoride-free MOFs showed improved hydrogen storage capacity at room temperature, which is a critical aspect of developing efficient hydrogen fuel cells.
The implications of this breakthrough are far-reaching, with potential applications in various fields, including energy, environment, and water management. The development of more efficient carbon scrubbers and atmospheric water harvesting systems can help mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and providing sustainable sources of clean energy and water. The improved MOFs can also be used in other applications, such as catalysis, drug delivery, and sensing, where their high surface area and tunable properties can be leveraged.
The fluoride-free synthesis method is a significant step forward in the development of sustainable technologies for a cleaner and more environmentally friendly future. By replacing toxic hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators, researchers can produce high-quality MOFs with superior properties, which can be used to capture and store greenhouse gases more efficiently. As the world continues to transition towards cleaner energy sources and more sustainable practices, innovations like the fluoride-free synthesis method will play a crucial role in addressing the challenges of climate change and ensuring a more livable future for generations to come.
In conclusion, the development of a fluoride-free synthesis method for metal-organic frameworks is a groundbreaking achievement that can boost gas capture for clean energy applications. The safer and more efficient production of MOFs can lead to the development of more effective carbon scrubbers and atmospheric water harvesting systems, which are essential for mitigating climate change. As researchers continue to explore the properties and applications of MOFs, it is likely that we will see significant advancements in the field of clean energy and sustainable technologies.
News Source: https://researchmatters.in/news/greener-path-synthesising-metal-organic-frameworks-carbon-capture-and-storage