NASA’s Perseverance rover completes 1st AI-planned drive on Mars
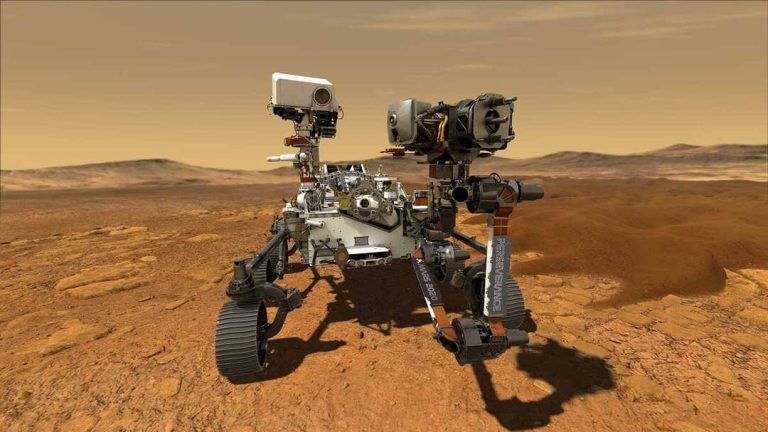
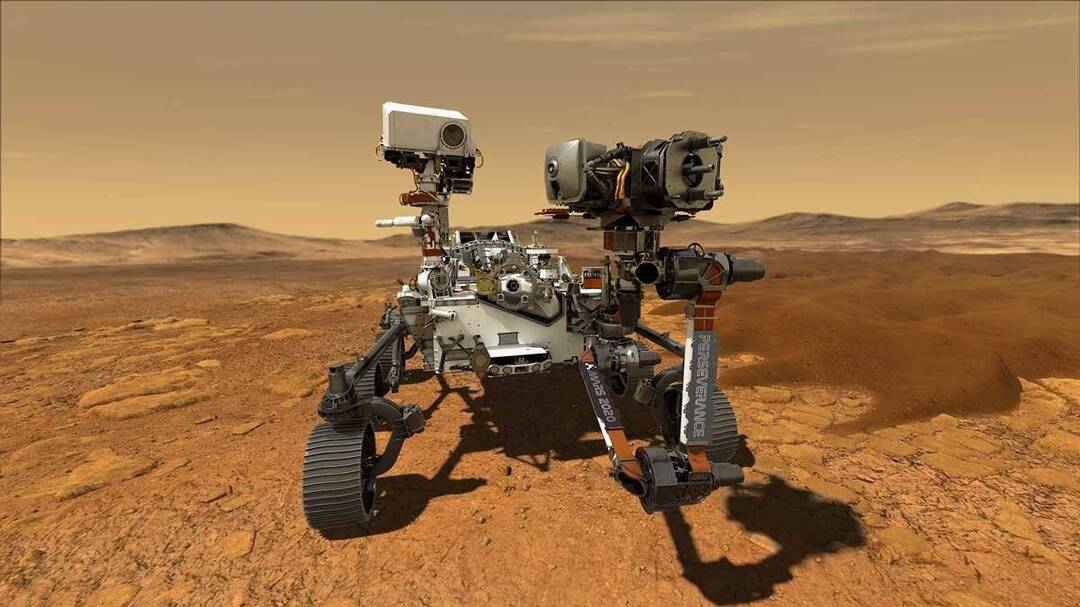
In a significant milestone for space exploration, NASA’s Perseverance rover has completed its first drive on Mars that was planned by artificial intelligence. The demonstration, which took place on December 8 and 10, was led by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. This achievement marks a major step forward in the use of AI in space exploration and paves the way for more autonomous and efficient exploration of other worlds.
According to NASA, the AI-planned drive was a significant success, with the Perseverance rover navigating a complex terrain on Mars with ease. The rover, which is equipped with a range of instruments and cameras, was able to identify and avoid obstacles, and adjust its route in real-time to ensure a safe and efficient journey. The demonstration was made possible by the use of advanced AI algorithms and machine learning techniques, which enabled the rover to analyze data from its sensors and cameras and make decisions in real-time.
“This demonstration shows how far our capabilities have advanced and broadens how we will explore other worlds,” NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman said. “The use of AI in space exploration is a key part of our strategy to explore the universe more efficiently and effectively. By leveraging AI and machine learning, we can enable our spacecraft and rovers to make decisions in real-time, without the need for human intervention. This will allow us to explore more of the Martian surface, and to do so more quickly and efficiently than ever before.”
The Perseverance rover, which launched in July 2020, is equipped with a range of instruments and cameras designed to study the Martian geology and search for signs of past or present life on the Red Planet. The rover is also equipped with a range of advanced technologies, including a sample collection system and a helicopter called Ingenuity, which has been used to conduct reconnaissance and scouting missions on Mars.
The use of AI in space exploration is a key part of NASA’s strategy to explore the universe more efficiently and effectively. By leveraging AI and machine learning, NASA can enable its spacecraft and rovers to make decisions in real-time, without the need for human intervention. This will allow NASA to explore more of the Martian surface, and to do so more quickly and efficiently than ever before.
The AI-planned drive on Mars is just the latest example of the many ways in which AI is being used in space exploration. From the use of machine learning algorithms to analyze data from spacecraft and telescopes, to the development of autonomous systems that can navigate and explore other worlds, AI is playing an increasingly important role in the exploration of the universe.
One of the key benefits of using AI in space exploration is the ability to process and analyze large amounts of data in real-time. Spacecraft and rovers often generate vast amounts of data, which can be difficult and time-consuming to analyze using traditional methods. By using AI and machine learning, NASA can quickly and efficiently analyze this data, and make decisions in real-time.
Another benefit of using AI in space exploration is the ability to enable autonomous systems that can navigate and explore other worlds. Autonomous systems, such as the Perseverance rover, can operate for extended periods of time without the need for human intervention, allowing NASA to explore more of the Martian surface and to do so more quickly and efficiently than ever before.
The use of AI in space exploration also has the potential to reduce the risk of human error. By enabling spacecraft and rovers to make decisions in real-time, without the need for human intervention, NASA can reduce the risk of accidents and errors that can occur when humans are involved in the decision-making process.
In addition to the Perseverance rover, NASA is also using AI in a range of other missions and applications. For example, the agency is using machine learning algorithms to analyze data from the Hubble Space Telescope, and to identify potential exoplanets that could be capable of supporting life. NASA is also using AI to develop autonomous systems that can navigate and explore other worlds, such as the Dragonfly mission, which will send a rotorcraft-lander to Saturn’s moon Titan in the mid-2020s.
In conclusion, the completion of the first AI-planned drive on Mars by the Perseverance rover is a significant milestone for space exploration. The use of AI and machine learning in space exploration has the potential to revolutionize the way we explore the universe, enabling us to explore more of the Martian surface, and to do so more quickly and efficiently than ever before. As NASA continues to push the boundaries of what is possible with AI and machine learning, we can expect to see even more exciting developments in the field of space exploration.