NASA’s Perseverance rover completes 1st AI-planned drive on Mars
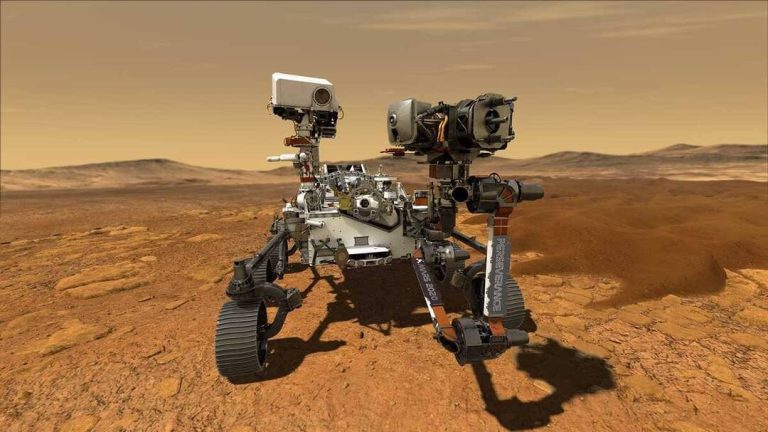
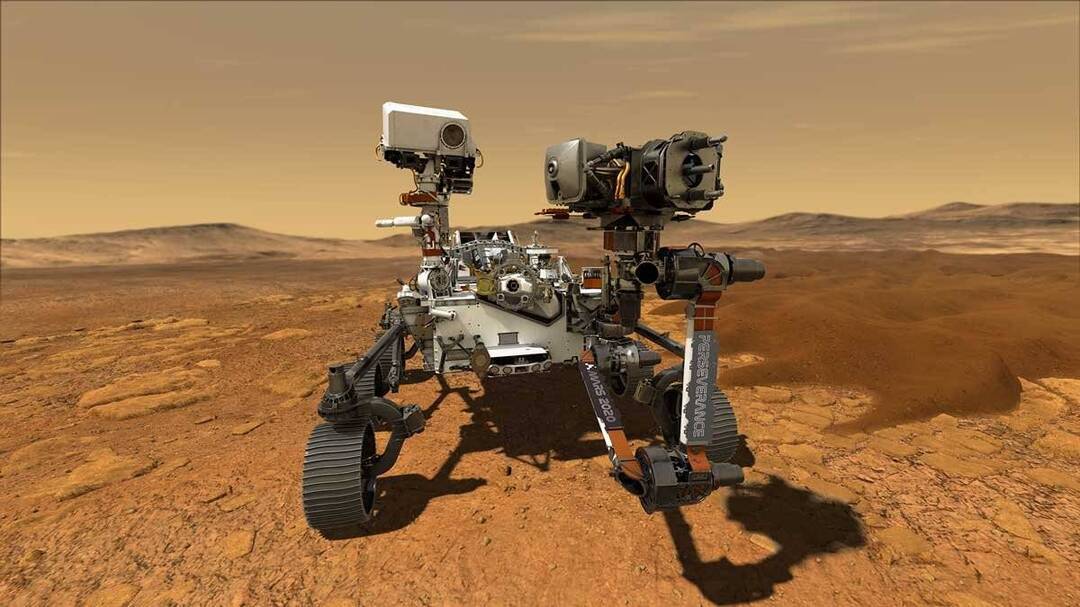
In a groundbreaking achievement, NASA’s Perseverance rover has successfully completed its first drive on Mars that was planned by artificial intelligence. This significant milestone marks a major advancement in the capabilities of space exploration and demonstrates the potential of AI in planning and executing complex missions on other planets.
The demonstration, which took place on December 8 and 10, was led by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. The Perseverance rover, which has been exploring Mars since February 2021, was able to navigate through the Martian terrain using a sophisticated AI system that planned the most efficient and safest route.
According to NASA, the AI system used a combination of data from the rover’s instruments, including its cameras, lidar, and radar, to create a detailed map of the terrain. The system then used this map to plan a route that avoided obstacles and ensured the rover’s safety. The demonstration showed that the AI system was able to plan a route that was not only efficient but also safe, taking into account the rover’s capabilities and the Martian terrain.
“This demonstration shows how far our capabilities have advanced and broadens how we will explore other worlds,” NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman said. “The use of AI in space exploration is a significant step forward, and we are excited to see the potential benefits it can bring to our future missions.”
The use of AI in space exploration is not new, but the Perseverance rover’s demonstration marks a significant milestone in the development of autonomous systems. Autonomous systems are capable of making decisions without human intervention, and they have the potential to revolutionize the way we explore space.
The Perseverance rover’s AI system is based on a technology called “autonomy,” which allows the rover to make decisions based on its surroundings. The system uses a combination of machine learning algorithms and computer vision to analyze data from the rover’s instruments and make decisions in real-time.
The demonstration is a significant step forward for NASA’s plans to return humans to the Moon and eventually send humans to Mars. Autonomous systems like the one used by the Perseverance rover will be critical for future missions, where communication delays between Earth and Mars can be up to 20 minutes each way.
“Autonomy is essential for future missions, where communication delays will be significant,” said Dr. Jennifer Trosper, the deputy project manager for the Perseverance rover. “The ability to make decisions in real-time will be critical for ensuring the safety and success of our missions.”
The Perseverance rover’s demonstration is also a significant step forward for the development of autonomous systems for space exploration. The technology used by the rover has the potential to be used on other missions, including future Mars missions and missions to other planets.
In addition to the AI system, the Perseverance rover is also equipped with a range of other advanced technologies, including a sample collection system and a suite of scientific instruments. The rover is designed to explore Mars’ Jezero crater, which is believed to have been home to a lake billions of years ago.
The Perseverance rover’s mission is to search for signs of past or present life on Mars and to study the planet’s geology and climate. The rover is equipped with a range of scientific instruments, including cameras, spectrometers, and a radar system.
The success of the Perseverance rover’s AI-planned drive is a significant achievement for NASA and the space exploration community. It demonstrates the potential of autonomous systems to revolutionize the way we explore space and marks a major milestone in the development of AI for space exploration.
As NASA continues to push the boundaries of space exploration, the use of AI and autonomous systems will play an increasingly important role. The Perseverance rover’s demonstration is a significant step forward for the development of these technologies, and it will pave the way for future missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.