What Errors Do Multi-Agent Systems Help Avoid?
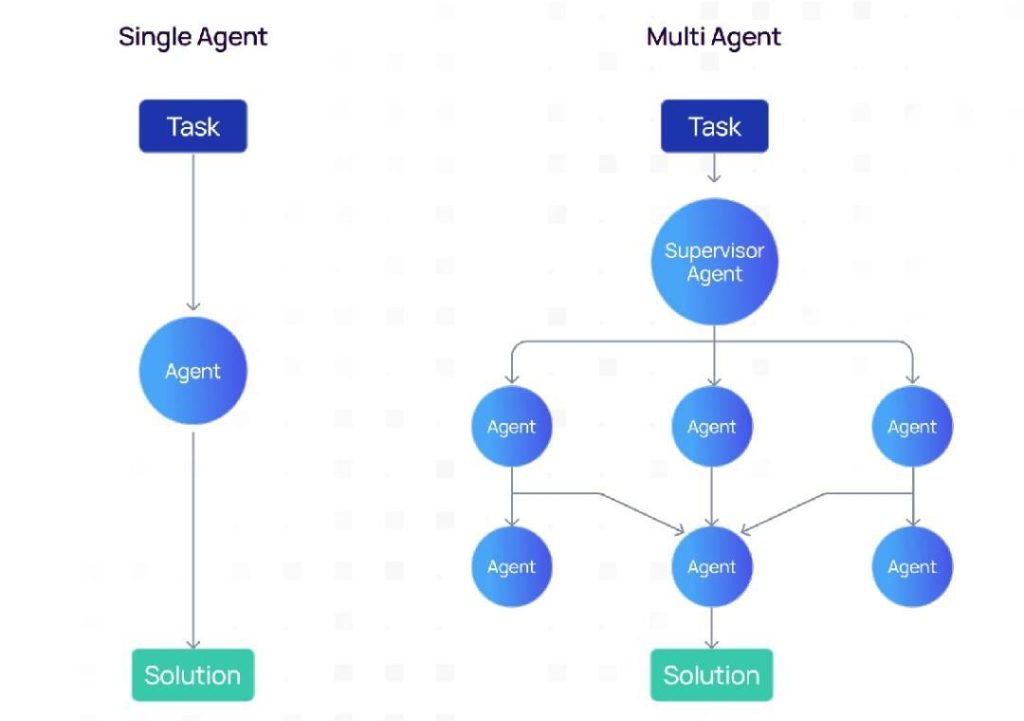
In the complex workflows of modern industries, single-agent systems often struggle to deliver results efficiently and effectively. The limitations of these systems can arise from several factors, including limited context, conflicting responsibilities, and a lack of scalability. In a single-agent system, all tasks are handled by a single entity, which can lead to bottlenecks and a higher risk of errors. However, multi-agent systems offer a more robust and resilient approach to automation, allowing organizations to avoid common pitfalls and optimize their workflows.
The Problem with Single-Agent Systems
Single-agent systems, where a single entity is responsible for all tasks, can lead to several problems, including:
- Limited Context: A single agent may not have the necessary context to make informed decisions, especially in complex and dynamic environments. This can result in suboptimal outcomes and a higher risk of errors.
- Conflicting Responsibilities: When a single agent is responsible for multiple tasks, it may lead to conflicting priorities and responsibilities. This can cause the agent to focus on the wrong tasks, leading to delays and inaccuracies.
- Scalability Issues: Single-agent systems can become bottlenecks as the volume of tasks increases. This can lead to delays, errors, and a decreased ability to handle changes in the environment.
- Single Point of Failure: A single-agent system is vulnerable to a single point of failure, where the failure of the agent can bring the entire system down.
The Benefits of Multi-Agent Systems
Multi-agent systems, on the other hand, are designed to address these limitations by breaking down complex tasks into smaller, more manageable components. Each agent is responsible for a specific task or set of tasks, which allows for greater scalability, flexibility, and resilience. The benefits of multi-agent systems include:
- Increased Scalability: Multi-agent systems can handle a larger volume of tasks by distributing them across multiple agents. This allows for greater scalability and the ability to handle changes in the environment.
- Improved Fault Tolerance: If one agent fails, the other agents can continue to function unaffected, ensuring that the system remains operational. This improves fault tolerance and reduces the risk of errors.
- Simplified Debugging: With a multi-agent system, debugging becomes easier because each agent is responsible for a specific task. This allows developers to isolate and debug individual agents without affecting the entire system.
- Better Decision-Making: Multi-agent systems can make better decisions by taking into account the expertise and knowledge of each agent. This allows for more informed decision-making and a higher level of accuracy.
How Multi-Agent Systems Avoid Errors
Multi-agent systems help avoid errors in several ways:
- Isolation of Functionality: Each agent is responsible for a specific task or set of tasks, which allows for greater isolation of functionality. This reduces the risk of errors and improves fault tolerance.
- Redundancy: By distributing tasks across multiple agents, multi-agent systems can reduce the risk of errors by providing redundancy. If one agent fails, another agent can take over the task.
- Conflict Resolution: Multi-agent systems can resolve conflicts between agents by using algorithms and protocols that ensure cooperation and coordination. This reduces the risk of errors caused by conflicting priorities and responsibilities.
- Continuous Monitoring: Multi-agent systems can continuously monitor the performance of each agent and adjust the system as needed. This allows for real-time error detection and correction.
Conclusion
In conclusion, multi-agent systems offer a more robust and resilient approach to automation than single-agent systems. By breaking down complex tasks into smaller, more manageable components, multi-agent systems can improve scalability, fault tolerance, and decision-making. Additionally, multi-agent systems can reduce the risk of errors by isolating functionality, providing redundancy, resolving conflicts, and continuously monitoring performance. As a result, organizations can optimize their workflows and achieve greater efficiency and effectiveness.
Source:
https://www.growthjockey.com/blogs/singleagent-vs-multiagent






