Is Edge Computing the Missing Link for IoT Scale?
The Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed the way we live and work, with more devices than ever connecting to the internet and generating vast amounts of data. However, as the number of connected devices continues to surge, the limitations of traditional cloud-based infrastructure are becoming increasingly apparent. Edge computing, a relatively new concept, is poised to revolutionize the IoT landscape by processing data closer to its source, reducing latency, and improving overall efficiency. In this post, we’ll explore the role of edge computing in scaling IoT, its benefits, and how it’s set to transform critical industries like autonomous vehicles and industrial systems.
The Challenges of IoT Scale
As IoT devices proliferate, the sheer volume of data generated creates a significant challenge for cloud-based infrastructure. Cloud computing, which relies on centralized data processing, can lead to:
- Latency: Data transmission delays can result in poor user experiences, particularly in applications like autonomous vehicles, where real-time processing is crucial.
- Bandwidth consumption: The constant influx of data can overwhelm cloud networks, leading to increased costs and reduced scalability.
- Security concerns: Centralized data processing makes it more vulnerable to cyber-attacks, as a single breach can compromise an entire system.
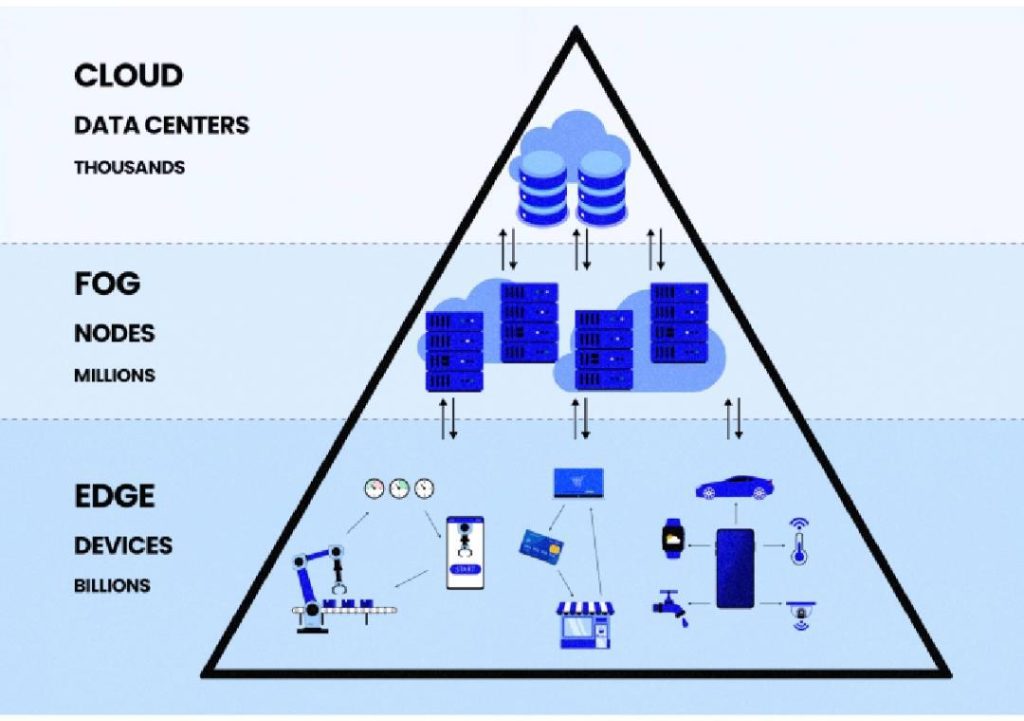
Edge Computing: The Solution to IoT Scale
Edge computing, also known as fog computing, processes data closer to its source, reducing the need for data to travel to the cloud or a central location. This approach offers several benefits:
- Faster processing: Edge computing enables real-time processing, reducing latency and enabling faster responses in critical applications.
- Reduced bandwidth: By processing data locally, edge computing reduces the amount of data transmitted to the cloud, conserving bandwidth and lowering costs.
- Improved security: Edge computing reduces the attack surface, as sensitive data is processed and stored closer to its source, making it more difficult for hackers to access.
Use Cases: Transforming Critical Industries
Edge computing is set to transform several critical industries, including:
- Autonomous vehicles: Edge computing enables real-time processing of sensor data, allowing autonomous vehicles to make quick decisions and respond to changing circumstances.
- Industrial systems: Edge computing improves process control, reduces downtime, and enhances predictive maintenance in industrial settings.
- Smart cities: Edge computing enables real-time monitoring and management of urban infrastructure, such as traffic, energy, and water management systems.
Real-World Examples
Several companies are already leveraging edge computing to drive innovation in their respective industries:
- NXP Semiconductors: NXP’s edge computing platform enables real-time processing of sensor data in industrial automation, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
- Microsoft: Microsoft’s Azure Edge Zones allow customers to deploy edge computing solutions on-premises or in the cloud, enabling faster processing and reduced latency.
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE): HPE’s Edgeline IoT gateway enables edge computing in industrial settings, improving process control and reducing downtime.
The Future of IoT: Edge Computing as the Missing Link
As the IoT continues to grow, edge computing will be the missing link that enables scale without straining cloud networks. By processing data closer to its source, edge computing addresses the limitations of traditional cloud-based infrastructure, enabling:
- Faster processing: Real-time processing in critical applications
- Improved security: Reduced attack surface and enhanced data protection
- Reduced bandwidth: Conservation of bandwidth and lower costs
In conclusion, edge computing is poised to revolutionize the IoT landscape by processing data closer to its source, reducing latency, and improving overall efficiency. As the number of connected devices continues to surge, edge computing will be the key to scaling IoT without compromising performance, security, or cost.
Source:
https://www.growthjockey.com/blogs/edge-computing-and-future-of-iot






