Skull reveals some ancient humans had more ‘primitive’ faces
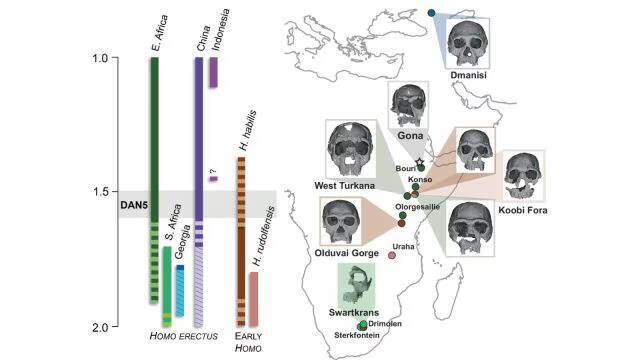
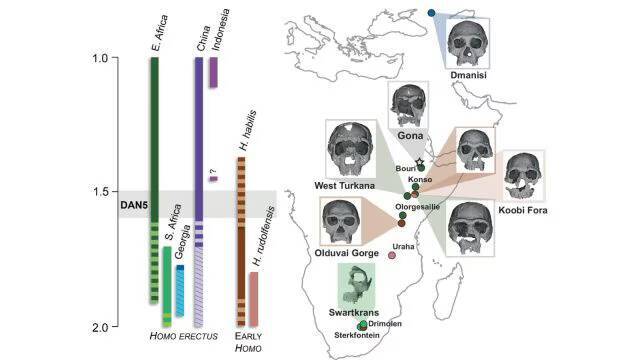
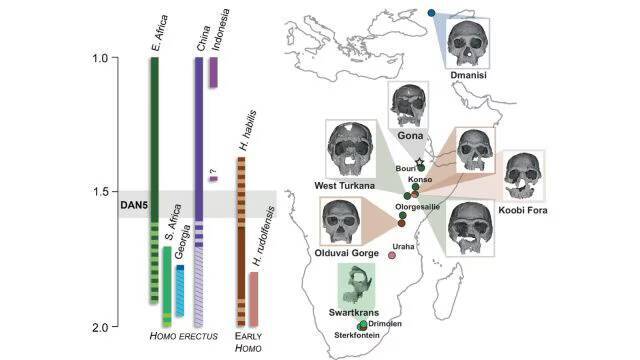
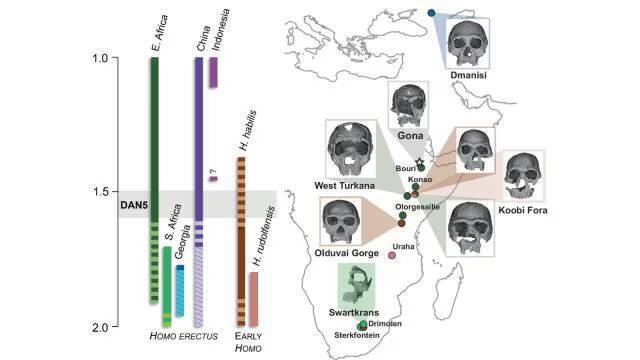
The discovery of a 1.5-1.6 million-year-old Homo erectus skull in Ethiopia has provided significant insights into the evolution of early humans. A recent study has revealed that this ancient skull, known as DAN5, exhibits more primitive facial traits than previously anticipated. The findings of this research have shed new light on the evolution of Homo erectus, a species that is considered to be a crucial link between earlier human ancestors and modern humans.
The reconstruction of the DAN5 skull was made possible through the use of micro-CT modeling, a technique that allows researchers to create detailed 3D images of fossilized remains. This technology has enabled scientists to study the skull in unprecedented detail, revealing a number of ancestral features that were not previously known. According to Dr. Baab, one of the researchers involved in the study, “The face is more archaic than we anticipated.” The discovery of these primitive facial traits has significant implications for our understanding of human evolution, suggesting that some ancient humans may have retained more primitive characteristics than previously thought.
One of the most striking features of the DAN5 skull is its small braincase, which is paired with a number of ancestral traits, including a flat nasal bridge and large molars. These characteristics are more commonly associated with earlier human ancestors, such as Homo habilis, and were thought to have been lost in the evolution of Homo erectus. However, the discovery of the DAN5 skull suggests that some populations of Homo erectus may have retained these primitive traits, even as others were evolving more modern characteristics.
The discovery of the DAN5 skull has also highlighted the complexity and diversity of human evolution. According to Yousuke Kaifu, another researcher involved in the study, “Seeing such a primitive face on a fossil this young was surprising.” This finding suggests that human evolution was not a linear process, but rather a complex and multifaceted one, with different populations evolving at different rates and in different ways.
The study of the DAN5 skull has also provided insights into the lifestyle and behavior of early Homo erectus. The presence of a small braincase and primitive facial traits suggests that this species may have been more adapted to a primitive, nomadic lifestyle, rather than the more complex societies that are associated with modern humans. This is supported by the fact that the DAN5 skull was found in association with a number of stone tools, which would have been used for hunting and gathering.
The discovery of the DAN5 skull is a significant one, and has the potential to reshape our understanding of human evolution. The fact that some ancient humans retained more primitive facial traits than previously thought suggests that human evolution was a more complex and nuanced process than previously imagined. This finding also highlights the importance of continued research and discovery in the field of paleoanthropology, as new discoveries continue to shed light on the intricacies of human evolution.
In conclusion, the discovery of the DAN5 skull has provided significant insights into the evolution of early humans. The presence of primitive facial traits, including a flat nasal bridge and large molars, suggests that some ancient humans may have retained more primitive characteristics than previously thought. This finding has significant implications for our understanding of human evolution, and highlights the complexity and diversity of the human evolutionary process. As researchers continue to study the DAN5 skull and other fossilized remains, we can expect to learn even more about the intricacies of human evolution, and the many different paths that our ancestors took on the journey to modern humanity.
The study of human evolution is a fascinating and complex field, and one that continues to capture the imagination of scientists and the general public alike. As new discoveries are made, and our understanding of human evolution continues to grow, we are reminded of the many mysteries that still remain to be uncovered. The discovery of the DAN5 skull is a significant one, and serves as a reminder of the importance of continued research and exploration in the field of paleoanthropology.
As we continue to learn more about the evolution of our ancient ancestors, we are also reminded of the many ways in which our understanding of human evolution can inform and shape our understanding of modern society. By studying the fossilized remains of our ancestors, we can gain insights into the many different factors that have shaped the course of human history, from the development of language and culture to the evolution of social and economic systems.
In the end, the discovery of the DAN5 skull is a powerful reminder of the many wonders and mysteries that still remain to be uncovered in the field of human evolution. As researchers continue to study this fascinating fossil, and to explore the many different paths that our ancestors took on the journey to modern humanity, we can expect to learn even more about the intricacies of human evolution, and the many different ways in which our understanding of the past can inform and shape our understanding of the present.