Skull reveals some ancient humans had more ‘primitive’ faces
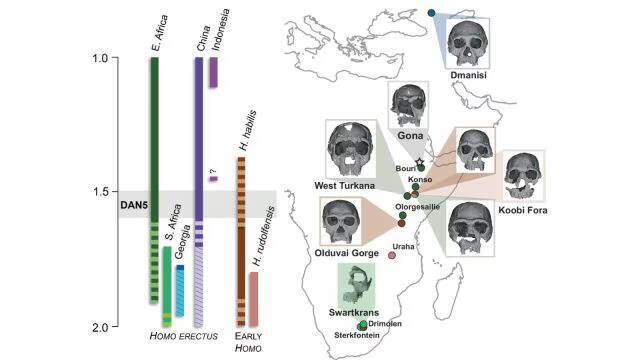
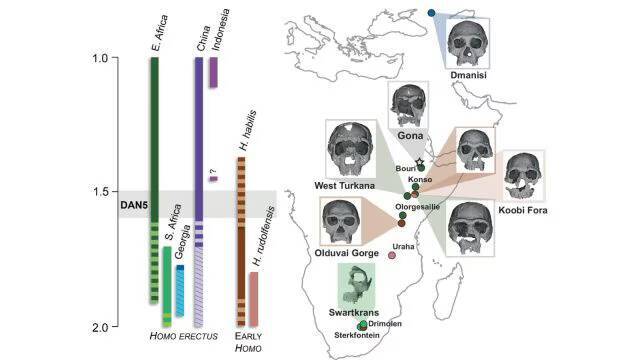
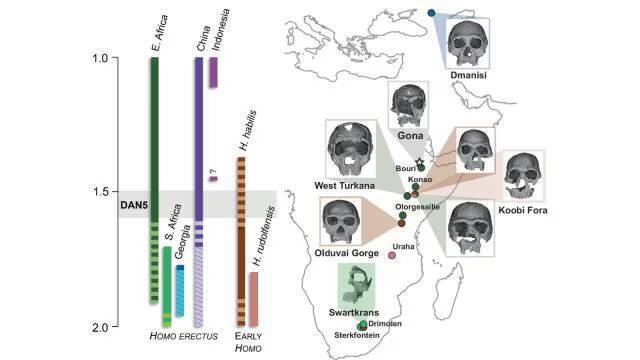
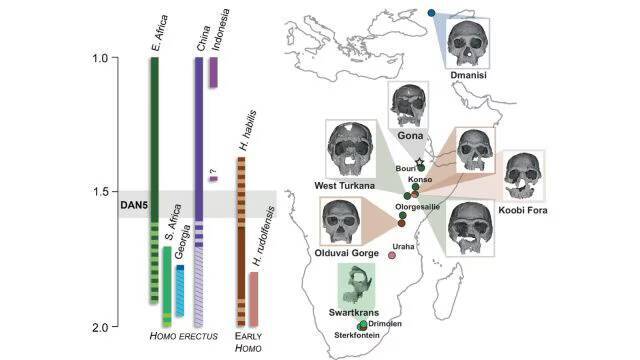
The study of human evolution has always been a fascinating field, with scientists continually uncovering new evidence that sheds light on the history of our species. Recently, a groundbreaking discovery was made in the form of a 1.5-1.6-million-year-old Homo erectus skull, which has revealed that some ancient humans had more ‘primitive’ faces than previously thought. The skull, known as DAN5, was found in Ethiopia and has been the subject of a comprehensive study that has provided valuable insights into the evolution of the human face.
According to Dr. Baab, one of the researchers involved in the study, “The face is more archaic than we anticipated.” The team used micro-CT modelling to analyze the skull and found that it had a small braincase paired with ancestral features, including a flat nasal bridge and large molars. These characteristics are more commonly associated with earlier human ancestors, such as Homo habilis, rather than the more advanced Homo erectus.
The discovery of the DAN5 skull has significant implications for our understanding of human evolution. It suggests that the process of evolution was more complex and nuanced than previously thought, with different species and populations exhibiting a range of characteristics. The fact that the DAN5 skull has a more primitive face than expected is a surprise, as it was previously believed that Homo erectus had a more modern face.
Yousuke Kaifu, another researcher involved in the study, commented, “Seeing such a primitive face on a fossil this young was surprising.” This sentiment is echoed by Dr. Baab, who notes that the discovery of the DAN5 skull has forced scientists to re-evaluate their understanding of human evolution. The study’s findings suggest that the evolution of the human face was a gradual process that occurred over millions of years, with different populations and species exhibiting different characteristics.
The DAN5 skull is significant not only because of its age but also because of its condition. The skull is remarkably well-preserved, with many of its original features still intact. This has allowed scientists to study the skull in detail, using advanced techniques such as micro-CT modelling to analyze its structure and composition.
The use of micro-CT modelling has been instrumental in the study of the DAN5 skull. This technique allows scientists to create highly detailed images of the skull’s internal structure, which can be used to analyze its anatomy and morphology. The images produced by micro-CT modelling are so detailed that they can reveal even the smallest features of the skull, such as the structure of the inner ear and the morphology of the teeth.
The discovery of the DAN5 skull has also highlighted the importance of Ethiopia as a location for paleontological research. The country has a rich fossil record, with many significant discoveries having been made there in recent years. The DAN5 skull is just the latest in a long line of important finds, and it is likely that future discoveries will continue to shed light on the history of human evolution.
In conclusion, the discovery of the DAN5 skull has provided significant insights into the evolution of the human face. The fact that the skull has a more primitive face than expected is a surprise, and it highlights the complexity and nuance of the evolutionary process. The study of the DAN5 skull is a testament to the power of scientific inquiry and the importance of continued research into the history of our species.
As scientists continue to study the DAN5 skull and other fossils, we can expect to learn even more about the evolution of the human face and the history of our species. The discovery of the DAN5 skull is a significant milestone in the field of paleontology, and it is likely to have a lasting impact on our understanding of human evolution.
The study of human evolution is an ongoing process, and new discoveries are continually being made. As our understanding of the past continues to grow, we can expect to learn even more about the history of our species and the processes that have shaped us into what we are today.
In the end, the discovery of the DAN5 skull is a reminder of the importance of scientific inquiry and the need for continued research into the history of our species. As we continue to explore the fossil record and uncover new evidence, we can expect to gain a deeper understanding of the complex and fascinating process of human evolution.