Skull reveals some ancient humans had more ‘primitive’ faces
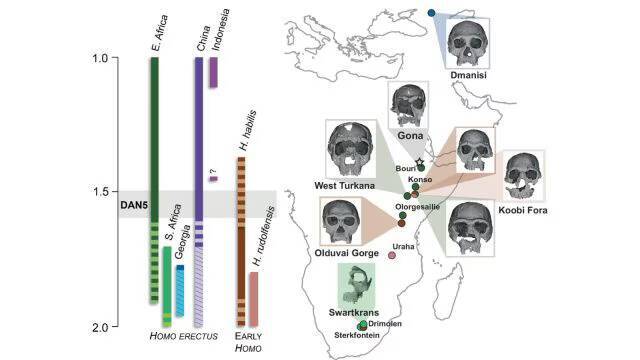
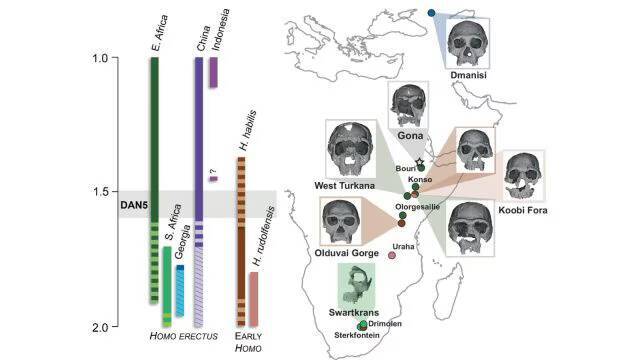
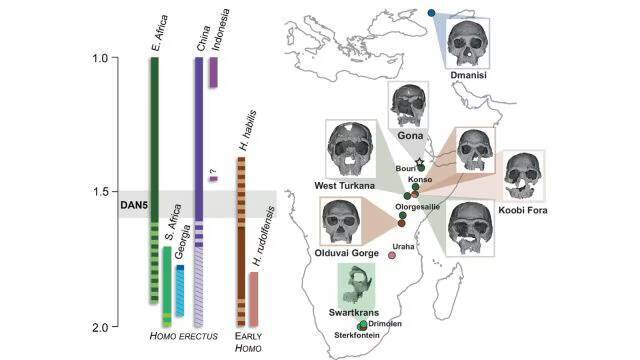
The study of human evolution has always been a fascinating and complex field, with new discoveries constantly reshaping our understanding of how our species came to be. A recent study published on a 1.5-1.6-million-year-old Homo erectus skull, known as DAN5, has shed new light on the evolution of early humans, revealing that some ancient humans had more ‘primitive’ faces than previously thought. The findings of this study have significant implications for our understanding of human evolution and the diversity of ancient human populations.
The DAN5 skull, discovered in Ethiopia, is a remarkable specimen that has provided scientists with a unique opportunity to study the facial structure of early Homo erectus. Using micro-CT modelling, researchers were able to reconstruct the skull and gain insights into its anatomy. The results were surprising, with the skull showing a small braincase paired with ancestral features, including a flat nasal bridge and large molars. According to Dr Baab, one of the researchers involved in the study, “The face is more archaic than we anticipated.” This suggests that early Homo erectus had more primitive facial traits than previously thought, which challenges our existing understanding of human evolution.
One of the most significant findings of this study is the combination of primitive and modern traits in the DAN5 skull. While the skull shows a small braincase, which is characteristic of earlier human ancestors, it also exhibits features that are more typical of modern humans, such as a relatively modern skull shape. This combination of traits is unusual and suggests that human evolution was more complex and nuanced than previously thought. As Yousuke Kaifu, another researcher involved in the study, noted, “Seeing such a primitive face on a fossil this young was surprising.” This highlights the importance of continued research and discovery in the field of human evolution, as new findings can significantly impact our understanding of human history.
The discovery of the DAN5 skull and its primitive facial traits also raises questions about the diversity of ancient human populations. It is possible that early Homo erectus populations exhibited a range of facial traits, with some individuals having more primitive features than others. This diversity could have been influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, environment, and lifestyle. Further research is needed to fully understand the implications of this discovery and to shed more light on the evolution of human facial structure.
The study of human evolution is a complex and multidisciplinary field, drawing on insights from anthropology, archaeology, genetics, and other sciences. The discovery of the DAN5 skull and its primitive facial traits is a significant contribution to this field, highlighting the importance of continued research and discovery. As scientists continue to study human evolution, they are constantly refining our understanding of human history and the processes that have shaped our species.
In conclusion, the discovery of the DAN5 skull and its primitive facial traits is a significant finding that sheds new light on human evolution. The combination of primitive and modern traits in the skull suggests that human evolution was more complex and nuanced than previously thought, and highlights the importance of continued research and discovery in this field. As scientists continue to study human evolution, they are refining our understanding of human history and the processes that have shaped our species. The study of human evolution is a fascinating and dynamic field, and new discoveries like the DAN5 skull are constantly reshaping our understanding of who we are and where we come from.
The implications of this discovery are significant, and they highlight the importance of continued research and discovery in the field of human evolution. As scientists continue to study human evolution, they are constantly refining our understanding of human history and the processes that have shaped our species. The discovery of the DAN5 skull and its primitive facial traits is a significant contribution to this field, and it will likely have a lasting impact on our understanding of human evolution.
The study of human evolution is a complex and multidisciplinary field, drawing on insights from anthropology, archaeology, genetics, and other sciences. The discovery of the DAN5 skull and its primitive facial traits is a significant finding that highlights the importance of continued research and discovery in this field. As scientists continue to study human evolution, they are constantly refining our understanding of human history and the processes that have shaped our species.
In the end, the discovery of the DAN5 skull and its primitive facial traits is a significant finding that sheds new light on human evolution. The combination of primitive and modern traits in the skull suggests that human evolution was more complex and nuanced than previously thought, and highlights the importance of continued research and discovery in this field. As scientists continue to study human evolution, they are refining our understanding of human history and the processes that have shaped our species.