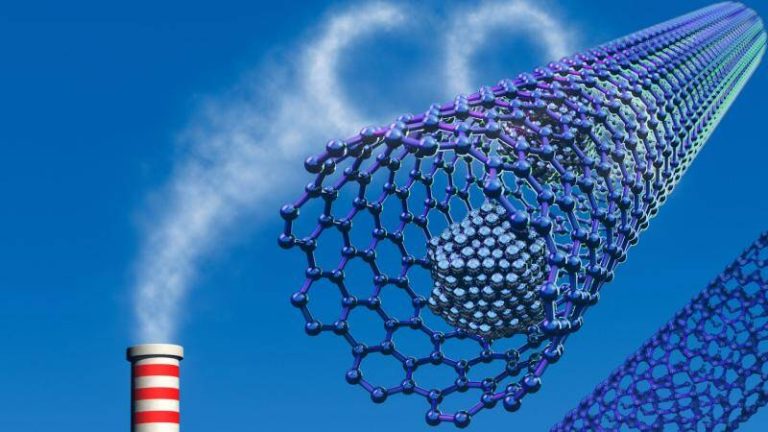
Safer method boosts gas capture for clean energy
The world is shifting towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources to combat the growing concerns of climate change. One of the key strategies in this fight is the capture and storage of greenhouse gases, particularly carbon dioxide. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have emerged as a promising material for this application due to their high surface area and tunable properties. However, the traditional synthesis methods for MOFs often involve the use of toxic hydrofluoric acid, which poses significant safety risks. Recently, researchers have developed a fluoride-free synthesis method that replaces hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators, paving the way for more efficient and environmentally friendly carbon capture and storage.
The new method, which has been gaining attention in the scientific community, uses a combination of safer chemicals to synthesize MOFs. These materials have been shown to exhibit superior properties, including higher surface areas and improved stability, making them ideal for capturing and storing greenhouse gases. The simplified synthesis process also allows for the production of high-quality MOF crystals at room temperature, which is a significant advantage over traditional methods that require high temperatures and pressures.
One of the most significant benefits of this new method is the potential for more efficient carbon capture and storage. MOFs synthesized using this technique have been shown to exhibit enhanced CO2 adsorption capacities, making them suitable for use in carbon scrubbers and other applications. Additionally, the improved stability of these materials means that they can withstand the harsh conditions often encountered in industrial settings, reducing the need for costly maintenance and replacement.
The implications of this breakthrough are far-reaching and have the potential to make a significant impact on the global effort to combat climate change. With the ability to capture and store CO2 more efficiently, industries such as power generation and cement production can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a cleaner and healthier environment. Furthermore, the use of MOFs in advanced atmospheric water harvesting systems could provide a sustainable source of clean water for communities around the world, helping to alleviate the growing concerns of water scarcity.
The development of this safer synthesis method is also expected to have a positive impact on the cost-effectiveness of carbon capture and storage technologies. By reducing the need for expensive and hazardous chemicals, the production of MOFs can become more economically viable, making these materials more accessible to industries and researchers. This, in turn, could lead to the widespread adoption of carbon capture and storage technologies, helping to accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy.
In addition to their potential for carbon capture and storage, MOFs synthesized using this new method also show promise for hydrogen storage applications. Hydrogen is a clean-burning fuel that can be used to power vehicles and generate electricity, making it an attractive alternative to fossil fuels. However, the storage of hydrogen is a significant challenge due to its low density and high reactivity. MOFs, with their high surface areas and tunable properties, have been identified as potential materials for hydrogen storage, and the new synthesis method could help to overcome the technical hurdles that have limited their adoption.
The use of safer modulators in the synthesis of MOFs is not only beneficial for the environment, but it also improves the working conditions for researchers and industry professionals. Hydrofluoric acid is a highly toxic and corrosive substance that requires specialized handling and safety equipment, making it a hazardous material to work with. By replacing this chemical with safer alternatives, the risk of accidents and exposure can be significantly reduced, creating a healthier and more sustainable work environment.
In conclusion, the development of a fluoride-free synthesis method for metal-organic frameworks is a significant breakthrough in the field of clean energy. By replacing toxic hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators, researchers have created a more efficient and environmentally friendly method for producing high-quality MOF crystals. These materials have the potential to play a key role in the capture and storage of greenhouse gases, as well as the storage of hydrogen, making them a crucial component in the transition to a low-carbon economy. As the world continues to shift towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, innovations like this will be essential in helping to combat climate change and create a healthier and more sustainable future for all.
News Source: https://researchmatters.in/news/greener-path-synthesising-metal-organic-frameworks-carbon-capture-and-storage