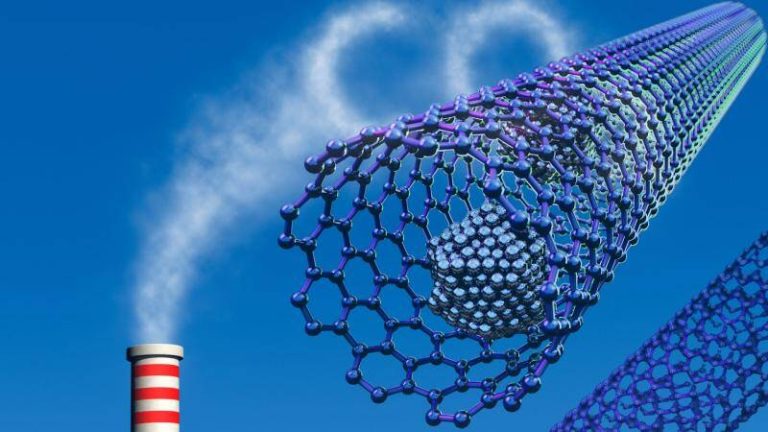
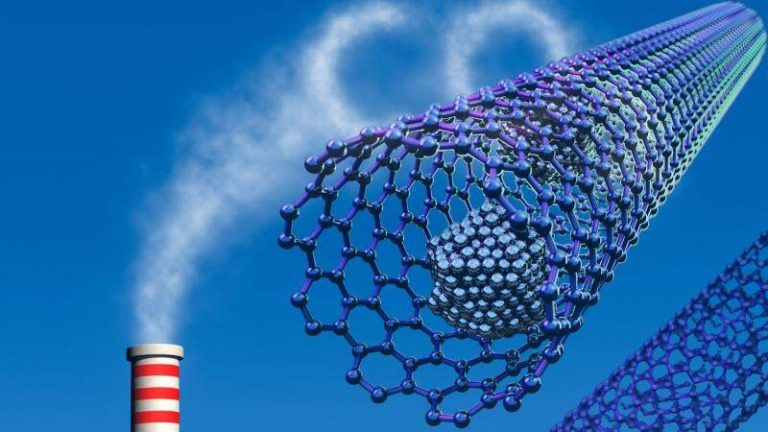
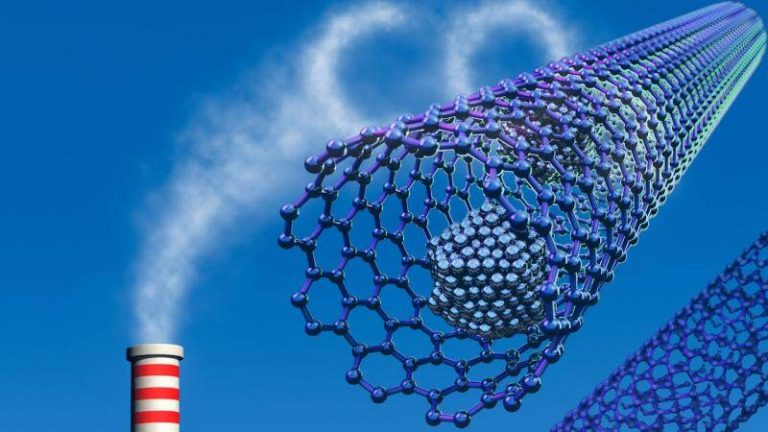
Safer method boosts gas capture for clean energy
The world is shifting towards cleaner energy sources to combat climate change, and one crucial step in this transition is the development of efficient methods for capturing and storing greenhouse gases. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have emerged as a promising solution for this challenge, with their ability to trap carbon dioxide and other gases. However, the traditional synthesis methods for MOFs have been limited by the use of toxic hydrofluoric acid, which poses significant safety risks. Recently, researchers have made a breakthrough by developing a fluoride-free synthesis method for MOFs, replacing hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators. This innovative approach not only simplifies the production process but also yields superior crystals that can capture greenhouse gases and store hydrogen more efficiently at room temperature.
The new synthesis method has significant implications for the development of affordable carbon scrubbers and advanced atmospheric water harvesting systems, which are essential tools in the fight against climate change. By providing a safer and more efficient way to produce MOFs, this breakthrough paves the way for the widespread adoption of these materials in various applications, from industrial gas capture to environmental remediation.
The challenge of traditional MOF synthesis
Traditional methods for synthesizing MOFs rely on the use of hydrofluoric acid, a highly toxic and corrosive substance that requires specialized handling and equipment. The use of hydrofluoric acid poses significant safety risks, not only for the researchers involved in the synthesis process but also for the environment. Moreover, the traditional synthesis methods often result in MOFs with limited surface areas and poor crystallinity, which can compromise their gas capture and storage capabilities.
The breakthrough: fluoride-free synthesis
The new synthesis method developed by researchers replaces hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators, such as benign organic acids or salts. These modulators can effectively control the growth of MOF crystals, allowing for the production of high-quality materials with superior surface areas and crystallinity. The fluoride-free synthesis method is not only safer but also more efficient, as it eliminates the need for specialized equipment and handling procedures.
The resulting MOFs have shown impressive gas capture and storage capabilities, with enhanced selectivity and capacity for carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases. Moreover, these materials have demonstrated improved stability and durability, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, from industrial gas capture to environmental remediation.
Implications for clean energy and climate change mitigation
The development of a safer and more efficient synthesis method for MOFs has significant implications for the transition to clean energy and the mitigation of climate change. By providing a cost-effective and scalable way to produce high-quality MOFs, this breakthrough paves the way for the widespread adoption of these materials in various applications, including:
- Carbon capture and storage: MOFs can be used to capture carbon dioxide from power plant emissions, industrial processes, and even directly from the atmosphere. The captured carbon can then be stored or utilized in various applications, such as enhanced oil recovery or chemical synthesis.
- Hydrogen storage: MOFs can also be used to store hydrogen, which is a promising clean energy carrier. The development of efficient and safe hydrogen storage systems is critical for the widespread adoption of fuel cell technologies and the transition to a hydrogen-based economy.
- Atmospheric water harvesting: MOFs can be used to capture water vapor from the air, providing a sustainable source of clean water for communities in water-scarce regions. This application has significant implications for global food security, human health, and environmental sustainability.
Conclusion
The development of a fluoride-free synthesis method for metal-organic frameworks marks a significant breakthrough in the field of clean energy and climate change mitigation. By providing a safer and more efficient way to produce high-quality MOFs, this innovation paves the way for the widespread adoption of these materials in various applications, from industrial gas capture to environmental remediation. As the world continues to transition towards cleaner energy sources and more sustainable technologies, the importance of MOFs and other advanced materials will only continue to grow. By supporting research and development in this field, we can accelerate the transition to a more sustainable and equitable future for all.
News source: https://researchmatters.in/news/greener-path-synthesising-metal-organic-frameworks-carbon-capture-and-storage