Safer method boosts gas capture for clean energy
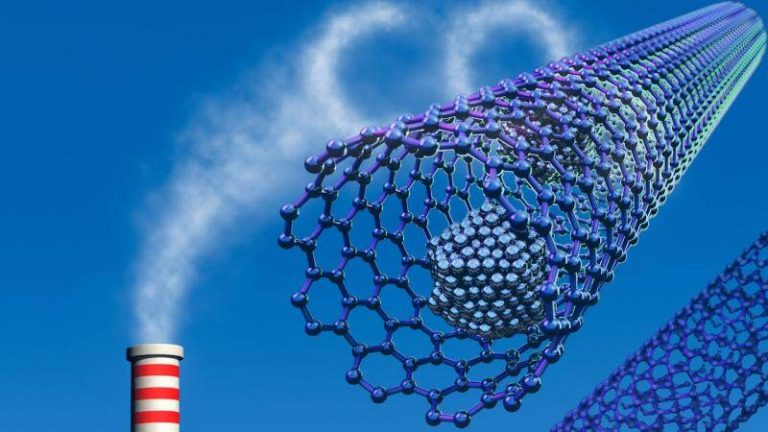
The world is shifting towards cleaner energy sources to combat climate change, and researchers are playing a crucial role in developing innovative technologies to support this transition. One such breakthrough has been achieved by a team of scientists who have developed a safer method for synthesizing metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), which are porous materials that can efficiently capture greenhouse gases and store hydrogen. This new method replaces toxic hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators, paving the way for the production of superior crystals that can trap gases more effectively at room temperature.
Metal-organic frameworks are a class of materials that have gained significant attention in recent years due to their unique properties. They are composed of metal ions or clusters connected by organic linkers, resulting in a three-dimensional structure with a high surface area. This structure allows MOFs to adsorb and store large amounts of gases, making them ideal for applications such as carbon capture and storage, hydrogen storage, and atmospheric water harvesting.
However, the traditional method of synthesizing MOFs involves the use of hydrofluoric acid, a highly toxic and corrosive substance that requires special handling and equipment. This not only poses a risk to the researchers involved in the synthesis process but also limits the scalability of MOF production. Furthermore, the use of hydrofluoric acid can result in the formation of defects in the MOF structure, which can compromise its performance.
To overcome these challenges, the research team developed a fluoride-free synthesis method that uses safer modulators to control the growth of MOF crystals. This approach allows for the production of high-quality MOFs with superior properties, including increased surface area, pore volume, and thermal stability. The resulting MOFs are also more efficient at capturing greenhouse gases and storing hydrogen, making them ideal for applications in clean energy.
One of the most significant advantages of this new method is that it enables the synthesis of MOFs at room temperature, which simplifies the production process and reduces the energy required. This is in contrast to traditional methods, which often require high temperatures and pressures to synthesize MOFs. The room-temperature synthesis also allows for the production of MOFs with more uniform properties, which is critical for large-scale applications.
The potential impact of this breakthrough is significant, as it could enable the widespread adoption of MOFs for carbon capture and storage, as well as hydrogen storage. Carbon capture and storage is a critical technology for reducing greenhouse gas emissions from power plants and industrial processes, while hydrogen storage is essential for the development of fuel cell vehicles and other hydrogen-based energy systems.
The new method could also pave the way for the development of advanced atmospheric water harvesting systems, which could provide clean drinking water for millions of people around the world. By using MOFs to capture water vapor from the air, these systems could provide a sustainable source of clean water, even in areas where traditional water sources are scarce.
In addition to its technical advantages, the new method is also more environmentally friendly than traditional synthesis methods. The use of safer modulators and the elimination of hydrofluoric acid reduce the risk of accidents and minimize the environmental impact of MOF production. This is critical, as the production of clean energy technologies should not come at the expense of the environment.
In conclusion, the development of a safer method for synthesizing metal-organic frameworks is a significant breakthrough that could have far-reaching implications for the clean energy sector. By enabling the production of high-quality MOFs with superior properties, this method could pave the way for the widespread adoption of carbon capture and storage, hydrogen storage, and atmospheric water harvesting systems. As the world continues to transition towards cleaner energy sources, innovations like this will play a critical role in supporting a more sustainable future.
News Source: https://researchmatters.in/news/greener-path-synthesising-metal-organic-frameworks-carbon-capture-and-storage