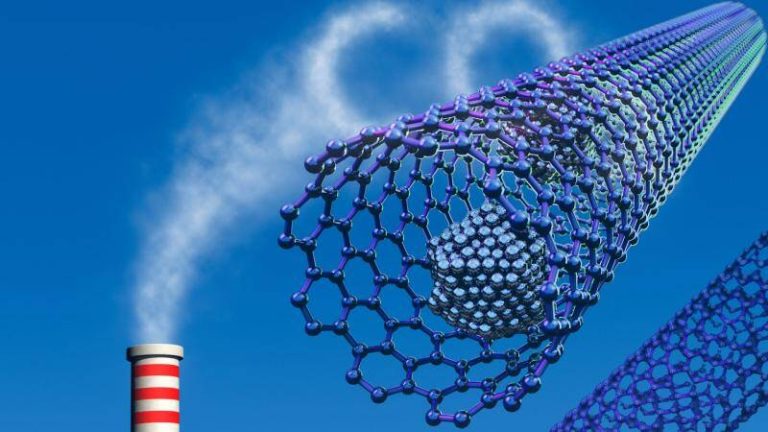
Safer method boosts gas capture for clean energy
The world is shifting towards clean energy to combat climate change, and one of the key strategies is to capture and utilize greenhouse gases. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have emerged as a promising material for carbon capture and storage, as well as hydrogen storage. However, the traditional synthesis method for MOFs involves the use of toxic hydrofluoric acid, which poses significant environmental and health risks. Recently, researchers have developed a fluoride-free synthesis method that replaces hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators, paving the way for more efficient and affordable carbon capture and storage systems.
The new synthesis method produces superior MOF crystals that can trap greenhouse gases and store hydrogen more efficiently at room temperature. This breakthrough has significant implications for the development of carbon scrubbers and advanced atmospheric water harvesting systems, which can help mitigate climate change globally. In this blog post, we will delve into the details of the new synthesis method, its advantages, and the potential applications of MOFs in clean energy.
The traditional synthesis method: limitations and risks
The traditional synthesis method for MOFs involves the use of hydrofluoric acid, a highly toxic and corrosive substance. Hydrofluoric acid is used as a modulator to control the crystal growth of MOFs, but it poses significant environmental and health risks. The use of hydrofluoric acid requires specialized equipment and handling procedures, which increases the cost and complexity of the synthesis process. Moreover, the disposal of hydrofluoric acid waste is a significant challenge, as it can contaminate soil and water sources.
The new synthesis method: a safer and more efficient approach
The new synthesis method developed by researchers replaces hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators, such as benzoic acid or acetic acid. These modulators are less toxic and more environmentally friendly, making the synthesis process safer and more sustainable. The new method also simplifies the synthesis process, reducing the number of steps and the amount of waste generated.
The new synthesis method produces MOF crystals with improved properties, such as higher surface area and pore volume. These properties enable the MOFs to trap greenhouse gases and store hydrogen more efficiently at room temperature. The MOFs synthesized using the new method also exhibit improved thermal stability, which is essential for industrial applications.
Applications of MOFs in clean energy
MOFs have a wide range of applications in clean energy, including carbon capture and storage, hydrogen storage, and atmospheric water harvesting. Carbon capture and storage is a critical technology for reducing greenhouse gas emissions from power plants and industrial processes. MOFs can be used to capture CO2 from flue gas streams, which can then be stored in geological formations or utilized in industrial processes.
Hydrogen storage is another promising application of MOFs. Hydrogen is a clean-burning fuel that can be used in fuel cells, internal combustion engines, and power generation. MOFs can be used to store hydrogen at room temperature, which is essential for industrial applications. The new synthesis method can produce MOFs with improved hydrogen storage capacity, making them more suitable for industrial applications.
Atmospheric water harvesting is a novel application of MOFs, which involves capturing water vapor from the air and condensing it into liquid water. MOFs can be used to capture water vapor from the air, even in arid regions, providing a sustainable source of clean water. The new synthesis method can produce MOFs with improved water vapor capture capacity, making them more suitable for atmospheric water harvesting applications.
Conclusion
The new synthesis method for MOFs is a significant breakthrough in the field of clean energy. The replacement of hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators makes the synthesis process more sustainable and environmentally friendly. The improved properties of the MOFs synthesized using the new method, such as higher surface area and pore volume, enable them to trap greenhouse gases and store hydrogen more efficiently at room temperature.
The applications of MOFs in clean energy are vast and promising, ranging from carbon capture and storage to hydrogen storage and atmospheric water harvesting. The new synthesis method can produce MOFs with improved properties, making them more suitable for industrial applications. As the world shifts towards clean energy, the development of more efficient and affordable carbon capture and storage systems is critical. The new synthesis method for MOFs is a significant step towards achieving this goal, and it has the potential to make a significant impact in the fight against climate change globally.
News source: https://researchmatters.in/news/greener-path-synthesising-metal-organic-frameworks-carbon-capture-and-storage