Safer method boosts gas capture for clean energy
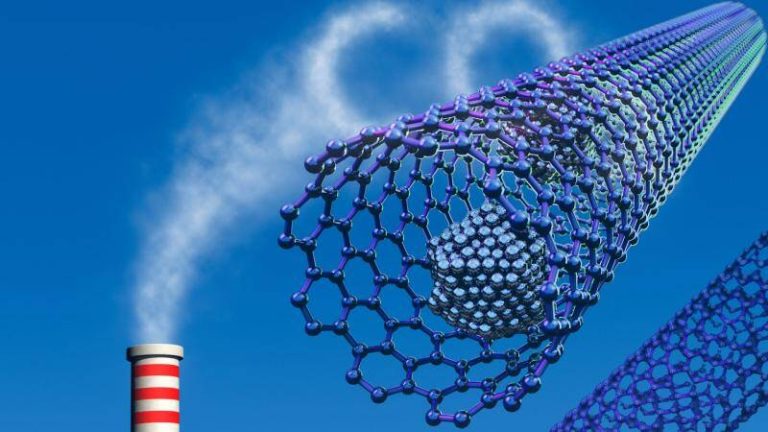
The world is grappling with the challenges of climate change, and one of the most pressing issues is the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. The burning of fossil fuels releases massive amounts of carbon dioxide and other gases into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and its associated problems. To combat this, researchers have been exploring various methods for capturing and storing these gases, with metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) emerging as a promising solution. Recently, a team of scientists has developed a safer and more efficient method for synthesizing MOFs, which could pave the way for the widespread adoption of carbon capture and storage technologies.
Traditionally, the synthesis of MOFs involves the use of hydrofluoric acid, a highly toxic and corrosive substance that poses significant risks to human health and the environment. The use of this acid also requires specialized equipment and handling procedures, which can drive up costs and limit the scalability of MOF production. In contrast, the new method developed by researchers uses safer modulators to facilitate the synthesis of MOFs, eliminating the need for hydrofluoric acid.
This fluoride-free synthesis method has several advantages over traditional approaches. For one, it simplifies the production process, making it easier and less expensive to manufacture MOFs on a large scale. Additionally, the resulting MOF crystals are of superior quality, with a more uniform structure and higher surface area. These characteristics enable the MOFs to trap greenhouse gases and store hydrogen more efficiently, even at room temperature.
The implications of this breakthrough are significant, as it could enable the widespread adoption of carbon capture and storage technologies. By using MOFs to capture and store carbon dioxide, industries such as power generation and cement production could significantly reduce their greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, the ability to store hydrogen efficiently at room temperature could pave the way for the development of advanced fuel cell technologies, which could power everything from vehicles to homes and businesses.
Another potential application of this technology is in the field of atmospheric water harvesting. By using MOFs to capture and condense water vapor from the air, it may be possible to develop systems that can provide clean drinking water for communities in need. This could be especially beneficial in areas where access to clean water is limited, such as in developing countries or regions affected by drought.
The development of this safer and more efficient method for synthesizing MOFs is a significant step forward in the quest for clean energy and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. As researchers continue to explore and refine this technology, it is likely that we will see the emergence of new and innovative applications for MOFs. From carbon capture and storage to hydrogen fuel cells and atmospheric water harvesting, the potential benefits of this technology are vast and far-reaching.
In conclusion, the discovery of a safer and more efficient method for synthesizing metal-organic frameworks is a major breakthrough in the field of clean energy. By eliminating the need for hydrofluoric acid and simplifying the production process, this new method could enable the widespread adoption of carbon capture and storage technologies, as well as other innovative applications such as hydrogen fuel cells and atmospheric water harvesting. As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change, the development of this technology is a significant step forward in the quest for a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future.
The research in this area is ongoing, and it will be exciting to see the developments that emerge in the coming years. With the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, provide clean drinking water, and enable the efficient storage of hydrogen, the possibilities are vast and promising. As we move forward, it is essential to continue investing in research and development, as well as to support the scaling up of these technologies to meet the demands of a rapidly changing world.
In the fight against climate change, every innovation and breakthrough counts, and the development of this safer and more efficient method for synthesizing MOFs is a significant contribution to this effort. As we strive to create a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future, it is essential to continue pushing the boundaries of what is possible and to explore new and innovative solutions to the challenges we face.