New research explains same-sex behaviour across animal species
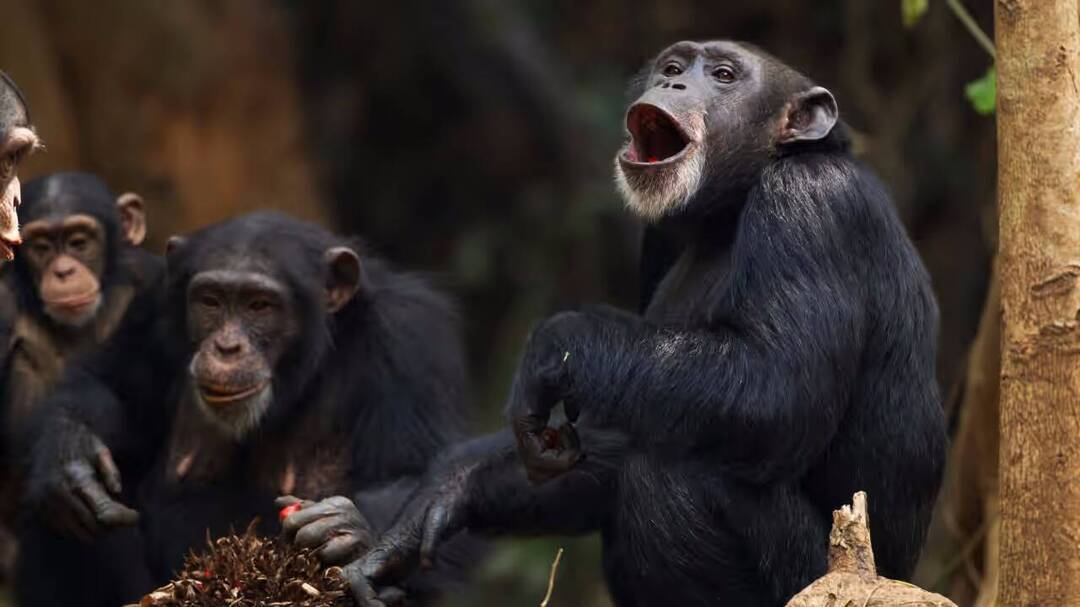
For a long time, scientists have been fascinated by the prevalence of same-sex behaviour in the animal kingdom. From birds to mammals, and even fish, same-sex interactions have been observed in hundreds of species, leaving researchers wondering about the underlying reasons. Now, a new study by researchers at Imperial College London has shed light on this phenomenon, suggesting that same-sex behaviour plays a crucial role in strengthening social bonds, particularly in complex or harsh environments.
The study, which covered hundreds of species, reveals that environmental and social pressures, rather than genetics alone, drive same-sex behaviour across the animal kingdom. This groundbreaking research provides a new perspective on the evolution of same-sex behaviour, highlighting its importance in promoting cooperation and survival in various species.
The significance of same-sex behaviour in animals
Same-sex behaviour in animals has long been a topic of interest, with many scientists assuming it was an anomaly or a byproduct of other factors. However, the new study demonstrates that same-sex interactions are, in fact, an adaptive strategy that helps animals cope with challenging environments. By forming close bonds with members of the same sex, animals can improve their chances of survival, gain access to resources, and even enhance their social status.
One of the key findings of the study is that same-sex behaviour is more common in species that live in complex or unstable environments. For example, in species that experience high levels of predation or competition for resources, same-sex interactions can provide a sense of security and cooperation, allowing individuals to work together to overcome these challenges.
The role of environmental pressures
The researchers found that environmental pressures, such as climate change, predation, and competition for resources, play a significant role in driving same-sex behaviour in animals. In species that live in harsh or unpredictable environments, same-sex interactions can provide a sense of stability and support, helping individuals to cope with the challenges they face.
For instance, in some species of birds, same-sex pairs have been observed forming long-term bonds, which can provide mutual benefits, such as shared parental care and increased access to resources. Similarly, in some species of mammals, same-sex interactions have been observed in the form of grooming and play, which can help to strengthen social bonds and reduce stress.
The importance of social bonds
The study also highlights the importance of social bonds in driving same-sex behaviour in animals. In species that live in complex societies, same-sex interactions can provide a sense of belonging and identity, helping individuals to navigate their social hierarchies and establish relationships with others.
In some species, same-sex behaviour has even been observed in the form of romantic courtship, with individuals performing elaborate displays of affection and loyalty. For example, in some species of fish, same-sex pairs have been observed forming long-term bonds, which can involve complex courtship rituals and displays of affection.
The implications of the study
The new study has significant implications for our understanding of same-sex behaviour in animals. By demonstrating that same-sex interactions are an adaptive strategy that helps animals cope with challenging environments, the researchers have challenged the traditional view that same-sex behaviour is an anomaly or a byproduct of other factors.
The study also highlights the importance of considering the social and environmental context in which same-sex behaviour occurs. By recognizing that same-sex interactions are a natural and common aspect of animal behaviour, we can gain a deeper understanding of the complex social dynamics that shape the lives of animals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the new study by researchers at Imperial College London provides a groundbreaking perspective on same-sex behaviour in animals. By demonstrating that same-sex interactions are an adaptive strategy that helps animals cope with challenging environments, the researchers have challenged our traditional understanding of same-sex behaviour and highlighted its importance in promoting cooperation and survival.
The study’s findings have significant implications for our understanding of animal behaviour and social dynamics, and highlight the need for further research into the complex and fascinating world of same-sex interactions in the animal kingdom.
To learn more about this study, you can visit the news source: https://newsable.asianetnews.com/international/science/scientists-discover-why-same-sex-behaviour-evolves-in-animal-species-articleshow-zd8b90h