New Research Explains Same-Sex Behaviour Across Animal Species
For a long time, same-sex behaviour in animals has been a topic of fascination and debate among scientists and the general public alike. While it was once thought to be an anomaly or a result of genetic defects, new research has shed light on the reasons behind this phenomenon. A recent study by researchers at Imperial College London has found that same-sex behaviour is common in animals and serves a crucial purpose in strengthening social bonds, improving cooperation, and enhancing survival rates.
The study, which covered hundreds of species, reveals that environmental and social pressures, rather than genetics alone, drive same-sex behaviour across the animal kingdom. This groundbreaking research has significant implications for our understanding of animal behaviour, social structures, and the evolution of same-sex behaviour.
The Prevalence of Same-Sex Behaviour in Animals
Same-sex behaviour is more common in the animal kingdom than previously thought. From birds and mammals to fish and reptiles, same-sex behaviour has been observed in a wide range of species. In some cases, same-sex behaviour is a regular occurrence, while in others, it is a rare but significant event.
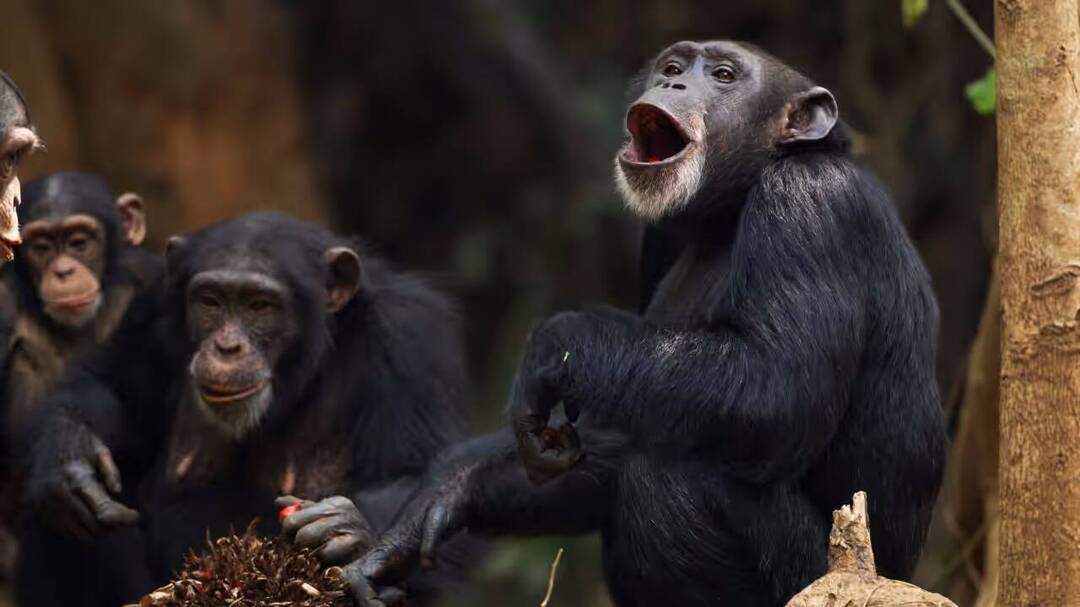
For example, some species of birds, such as swans and geese, are known to form long-term same-sex pairs, with some pairs staying together for over 20 years. Similarly, some species of primates, such as bonobos and chimpanzees, engage in same-sex behaviour as a way of strengthening social bonds and reducing conflict.
The Role of Environmental and Social Pressures
The new research suggests that environmental and social pressures play a significant role in the evolution of same-sex behaviour in animals. In complex or harsh environments, same-sex behaviour can serve as a mechanism for strengthening social bonds, improving cooperation, and enhancing survival rates.
For instance, in species that live in large groups, same-sex behaviour can help to reduce conflict and promote social cohesion. In species that live in harsh or unpredictable environments, same-sex behaviour can provide a means of support and protection, increasing the chances of survival.
The Benefits of Same-Sex Behaviour
The research highlights several benefits of same-sex behaviour in animals, including:
- Strengthening social bonds: Same-sex behaviour can help to strengthen social bonds between individuals, promoting cooperation and reducing conflict.
- Improving cooperation: Same-sex behaviour can improve cooperation between individuals, leading to better outcomes in terms of survival, reproduction, and overall fitness.
- Enhancing survival rates: Same-sex behaviour can enhance survival rates by providing a means of support and protection, particularly in harsh or unpredictable environments.
- Reducing stress: Same-sex behaviour can help to reduce stress and promote social cohesion, leading to better overall health and well-being.
The Implications of the Research
The new research has significant implications for our understanding of animal behaviour, social structures, and the evolution of same-sex behaviour. It suggests that same-sex behaviour is not an anomaly or a result of genetic defects, but rather an adaptation that has evolved in response to environmental and social pressures.
The research also highlights the importance of considering the social and environmental context in which same-sex behaviour occurs. By understanding the role of same-sex behaviour in different species and contexts, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity and complexity of animal social behaviour.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the new research by Imperial College London provides a groundbreaking insight into the reasons behind same-sex behaviour in animals. By highlighting the role of environmental and social pressures, the research shows that same-sex behaviour is not an anomaly, but rather an adaptation that has evolved to strengthen social bonds, improve cooperation, and enhance survival rates.
As we continue to explore and understand the complexities of animal social behaviour, it is essential to consider the social and environmental context in which same-sex behaviour occurs. By doing so, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity and complexity of the animal kingdom and the many ways in which animals interact and adapt to their environments.
Read more about this research at: https://newsable.asianetnews.com/international/science/scientists-discover-why-same-sex-behaviour-evolves-in-animal-species-articleshow-zd8b90h