Largest Solar Storm in Over 20 Years Hits Earth
A powerful solar storm hit the Earth on Monday evening and early Tuesday morning, creating dazzling auroral displays at several locations across the globe. The storm, which is the largest to affect our planet in over 20 years, has the potential to disrupt satellite-based communications and GPS accuracy, posing a significant threat to our technological infrastructure. Additionally, solar radiation storms can cause increased radiation exposure risks for passengers on flights that are traveling polar routes.
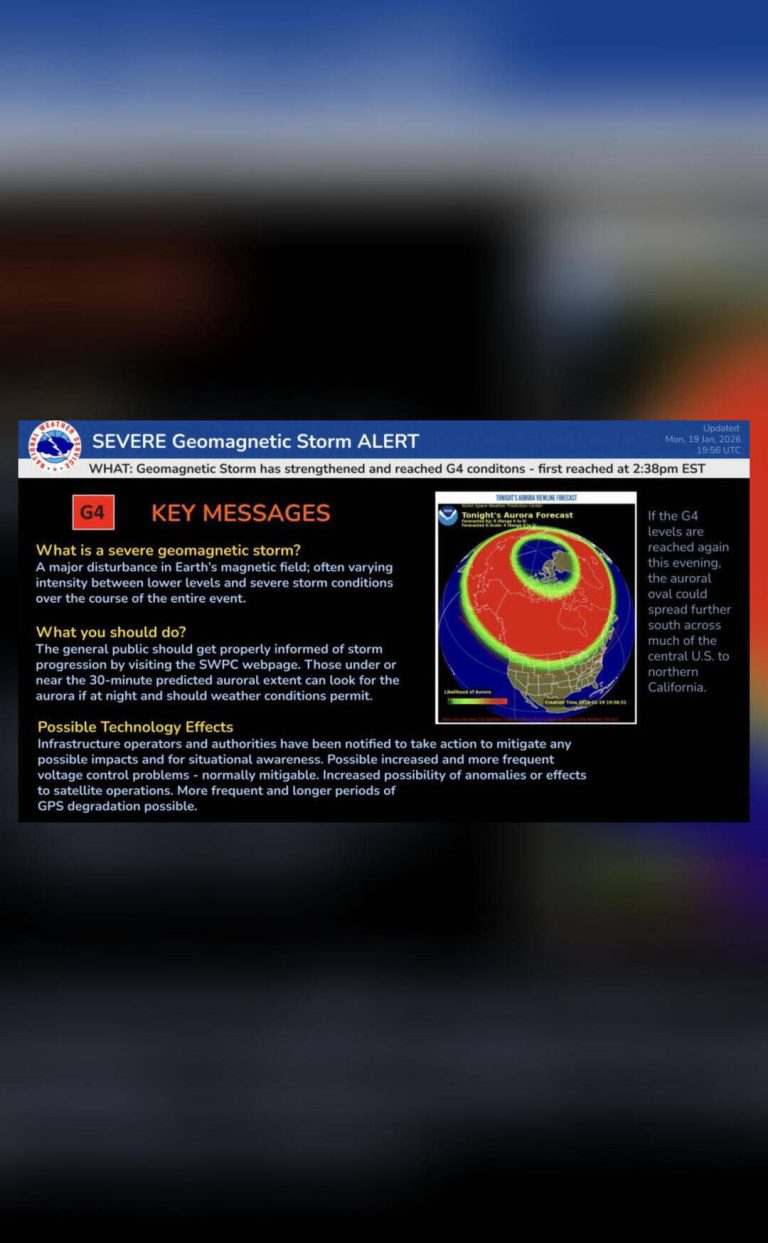
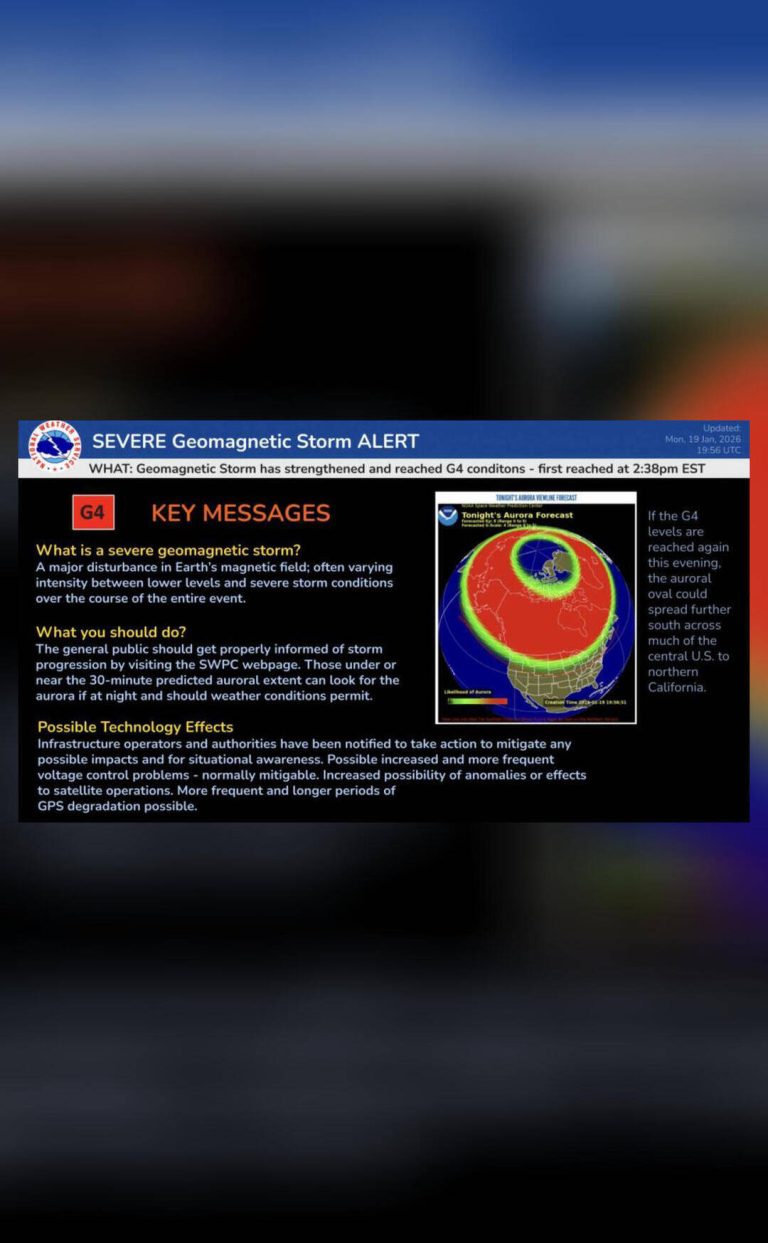
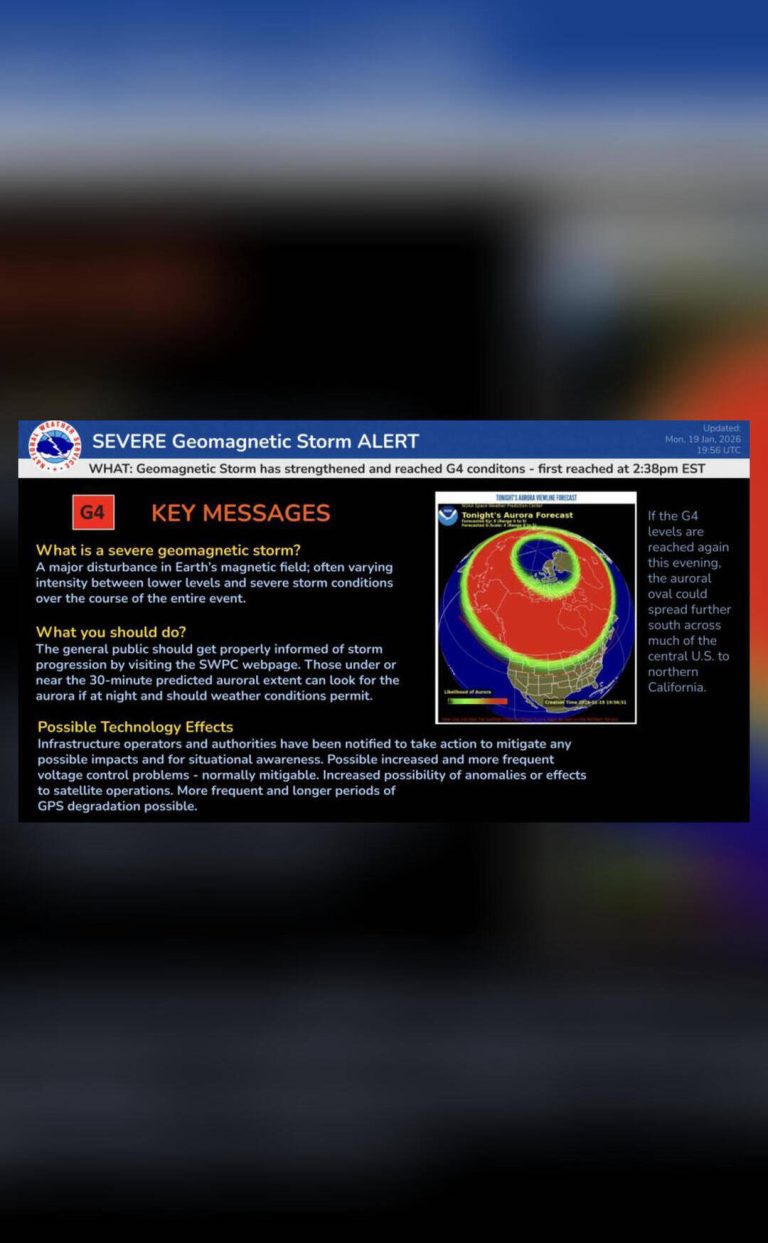
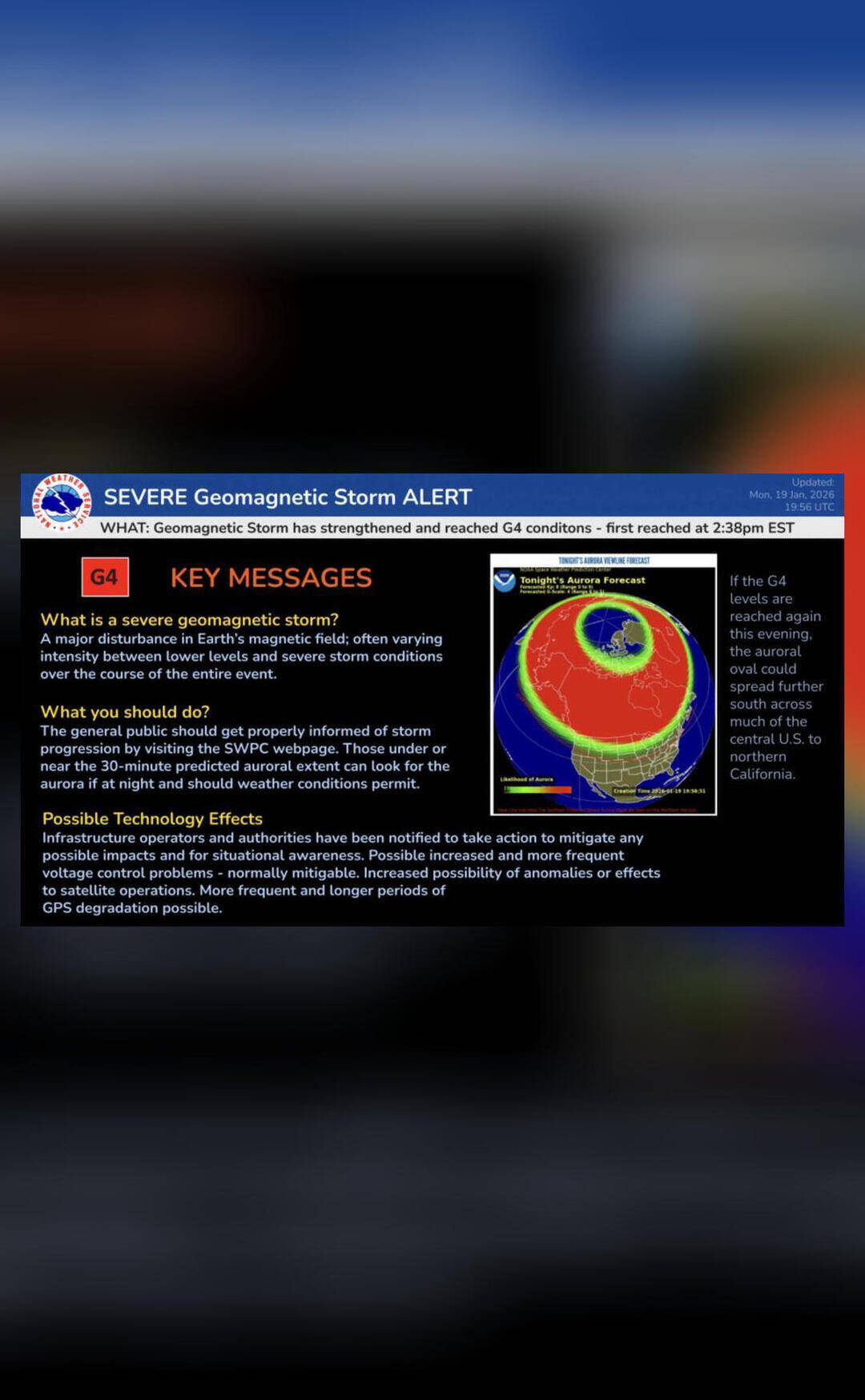
The solar storm, which was classified as a G5-level geomagnetic storm, is the strongest to hit the Earth since 2001. G5-level storms are the highest level of classification, indicating a significant impact on the Earth’s magnetic field. The storm was caused by a massive coronal mass ejection (CME) from the sun, which sent a huge cloud of charged particles hurtling towards our planet.
As the storm hit the Earth, it created spectacular auroral displays in the northern and southern hemispheres. The aurora borealis, also known as the northern lights, was visible in countries such as Canada, Norway, and Sweden, while the aurora australis, or southern lights, was visible in countries such as Australia and New Zealand. The displays were characterized by vibrant colors and patterns, with some observers reporting seeing the aurora as far south as the northern United States.
While the auroral displays were a beautiful sight to behold, the solar storm also has the potential to cause significant disruptions to our technological systems. Satellite-based communications, such as those used for television and radio broadcasts, may be affected by the storm, leading to blackouts and disruptions. GPS accuracy may also be impacted, which could have significant consequences for navigation and transportation systems.
Furthermore, the solar radiation storm poses a risk to passengers on flights that are traveling polar routes. Solar radiation storms can cause increased radiation exposure risks, particularly for flights that are traveling at high altitudes and over the polar regions. This is because the Earth’s magnetic field is weaker over the poles, providing less protection against solar radiation. As a result, airlines may need to take precautions to minimize the risks to passengers, such as flying at lower altitudes or taking alternative routes.
The impact of the solar storm on our technological systems is a significant concern, as we rely increasingly on satellite-based communications and GPS for a wide range of applications. From navigation and transportation to communication and weather forecasting, our reliance on these systems is critical to our daily lives. As a result, it is essential that we take steps to mitigate the effects of solar storms, such as developing backup systems and implementing protective measures to prevent disruptions.
In addition to the technological impacts, the solar storm also has the potential to affect the Earth’s climate and weather patterns. Solar radiation storms can cause changes in the Earth’s atmospheric circulation, leading to changes in temperature and precipitation patterns. This can have significant consequences for agriculture, water resources, and other sectors that are sensitive to climate and weather conditions.
The study of solar storms and their impact on the Earth is an active area of research, with scientists working to better understand the causes and effects of these events. By studying the solar storm and its impact on our planet, scientists can gain valuable insights into the complex interactions between the sun, the Earth’s magnetic field, and our technological systems. This knowledge can be used to develop more effective mitigation strategies and to improve our preparedness for future solar storms.
In conclusion, the largest solar storm in over 20 years has hit the Earth, creating dazzling auroral displays and posing a significant threat to our technological infrastructure. As we continue to rely on satellite-based communications and GPS, it is essential that we take steps to mitigate the effects of solar storms and to develop backup systems to prevent disruptions. By working together to better understand the causes and effects of solar storms, we can reduce the risks and impacts of these events and ensure that our technological systems continue to function smoothly.