IIT Indore creates AI human replica to help detect diseases
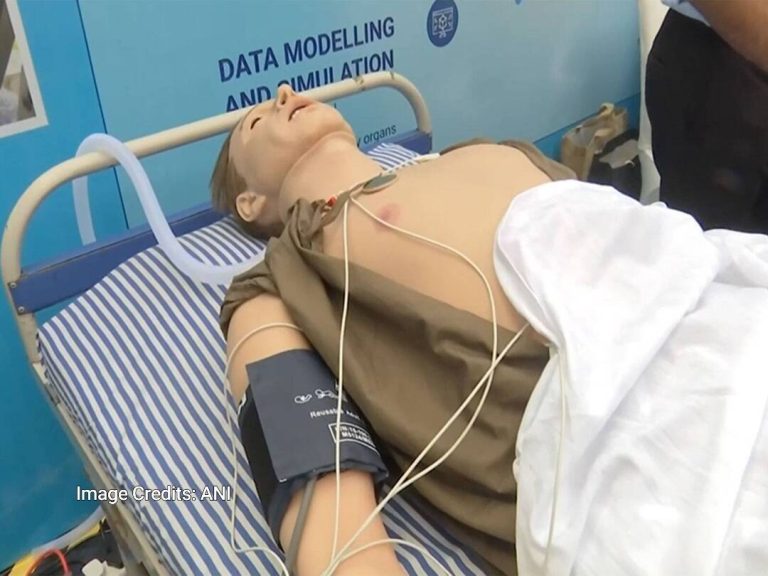
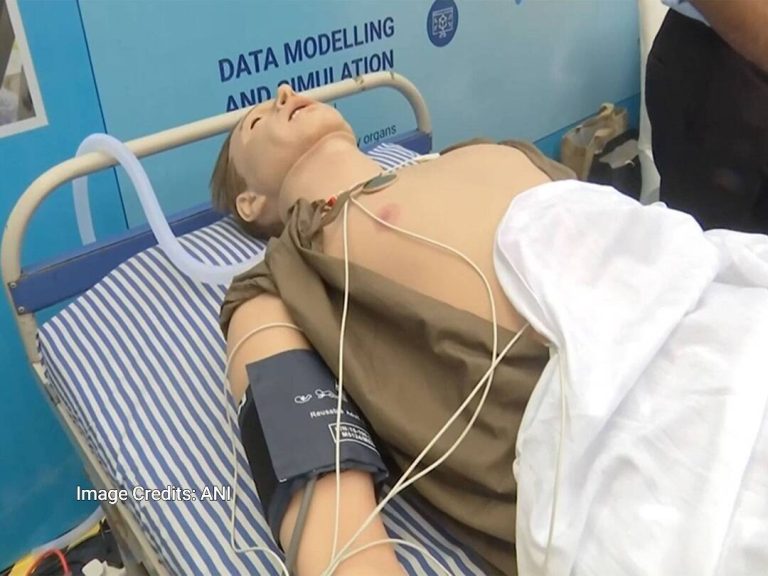
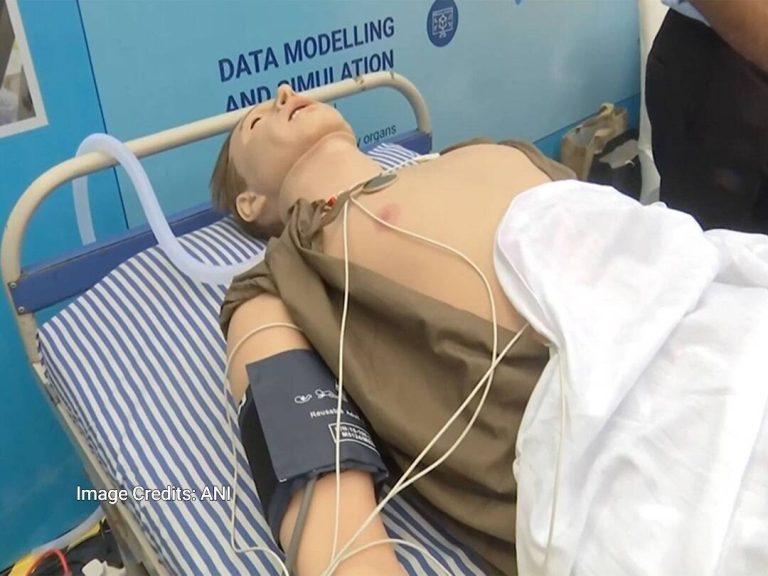
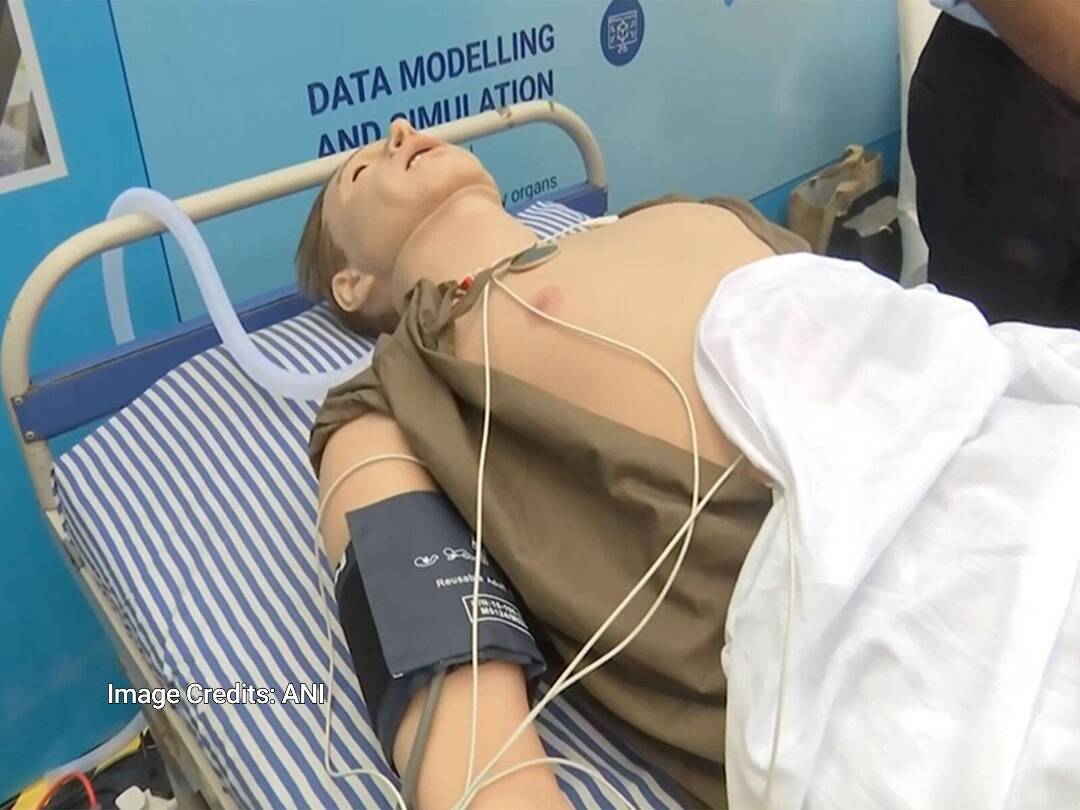
In a groundbreaking development, the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Indore has successfully created an AI-powered human-like replica that can aid in the detection of diseases in the human body. According to a report by ANI, this innovative technology has the potential to revolutionize the field of medicine by enabling early and preventive diagnosis of various diseases. The AI-powered replica is designed to mimic basic human functions such as blinking and breathing, making it an incredibly realistic and useful tool for medical professionals.
The human-like replica, powered by artificial intelligence, can simulate various human functions, allowing doctors to study and analyze the patterns of different diseases in various organs. This technology can be particularly useful in understanding the progression of diseases and identifying potential risk factors. By analyzing the data generated by the replica, medical professionals can develop more effective treatment plans and improve patient outcomes.
One of the most significant advantages of this technology is its ability to aid in early diagnosis. Many diseases, if detected early, can be treated and managed more effectively, reducing the risk of complications and improving patient outcomes. The AI-powered replica can help doctors identify potential health risks and develop preventive strategies, enabling patients to take proactive measures to protect their health.
The replica’s ability to mimic human functions such as blinking and breathing makes it an incredibly valuable tool for medical research and training. Medical students and professionals can use the replica to practice and refine their diagnostic skills, reducing the risk of errors and improving patient care. Additionally, the replica can be used to test and validate new medical devices and treatments, ensuring that they are safe and effective before they are used on human patients.
The development of this AI-powered human-like replica is a testament to the innovative spirit and capabilities of IIT Indore. The institute has consistently been at the forefront of technological advancements, and this latest development is a significant milestone in the field of medical research. The potential applications of this technology are vast, and it is likely to have a profound impact on the field of medicine in the years to come.
The use of AI in medicine is not new, but the development of a human-like replica takes it to a whole new level. AI has been used in various medical applications, including disease diagnosis, patient data analysis, and personalized medicine. However, the creation of a human-like replica that can mimic basic human functions is a significant breakthrough. It has the potential to revolutionize the way medical professionals diagnose and treat diseases, and it could lead to the development of more effective and targeted treatments.
The AI-powered replica can also be used to educate patients about various diseases and their treatment options. By simulating the progression of a disease, patients can gain a better understanding of their condition and the importance of adhering to their treatment plan. This can lead to improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
In addition to its potential applications in medicine, the AI-powered human-like replica can also be used in various other fields, including education and research. It can be used to teach students about human anatomy and physiology, allowing them to gain a deeper understanding of the human body and its functions. It can also be used to test and validate new medical devices and treatments, ensuring that they are safe and effective before they are used on human patients.
In conclusion, the development of an AI-powered human-like replica by IIT Indore is a significant breakthrough in the field of medicine. The replica’s ability to mimic basic human functions such as blinking and breathing makes it an incredibly valuable tool for medical professionals, allowing them to diagnose and treat diseases more effectively. The potential applications of this technology are vast, and it is likely to have a profound impact on the field of medicine in the years to come.