IIT Bombay’s AI Speeds Up Hurricane Damage Assessment
Hurricanes are one of the most destructive natural disasters, causing widespread damage to infrastructure, properties, and loss of life. In the aftermath of a hurricane, assessing the damage is crucial for relief efforts, rescue operations, and rebuilding. However, traditional methods of damage assessment can be time-consuming, labor-intensive, and often inaccurate. To address this challenge, researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Bombay have developed an innovative AI model called SpADANet, which can quickly and accurately identify building damage from aerial images.
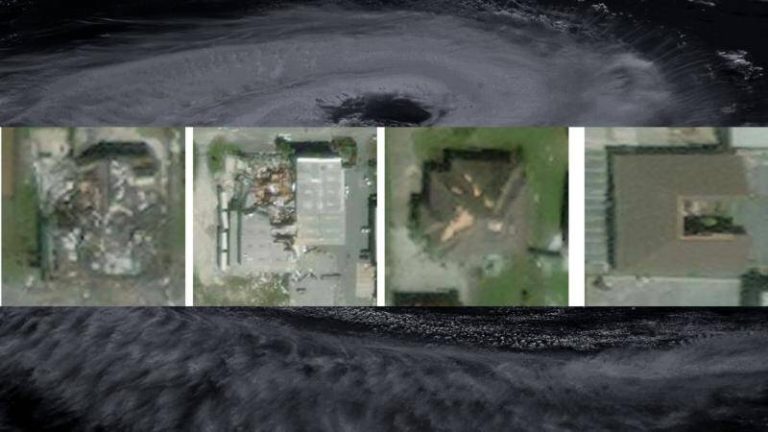
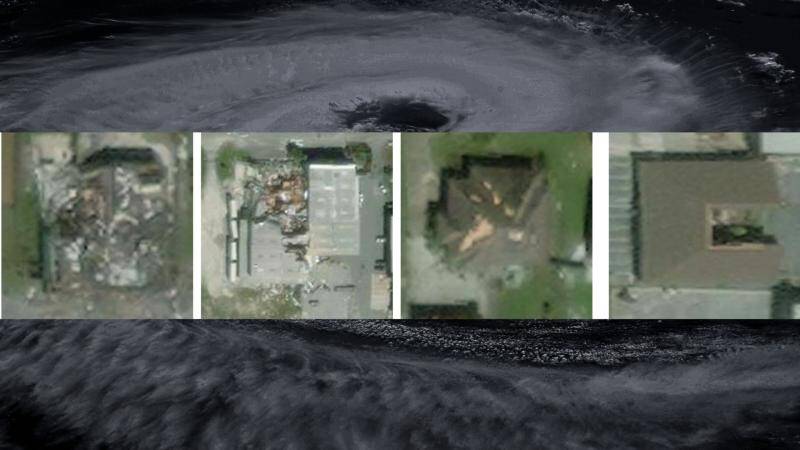
SpADANet is a spatially aware deep learning model that uses aerial images to detect and assess building damage caused by hurricanes. What makes SpADANet unique is its ability to overcome the “domain gap,” which refers to the difference in data distribution between the training data and the actual data collected during a hurricane. This means that SpADANet can adapt to different storms with minimal data, making it a highly versatile and effective tool for damage assessment.
One of the significant advantages of SpADANet is its ability to use spatial context to identify damage. Unlike existing methods that rely on individual image features, SpADANet takes into account the relationships between different objects in an image, such as buildings, roads, and vegetation. This spatial awareness allows SpADANet to better understand the context of the damage and provide more accurate assessments.
Another key feature of SpADANet is its optimization for mobile devices. This means that the model can be deployed on smartphones, tablets, or other mobile devices, making it easily accessible to emergency responders, relief workers, and other stakeholders in the field. The ability to assess damage in real-time, using mobile devices, can significantly improve the speed and effectiveness of disaster response and relief efforts.
The development of SpADANet is a significant breakthrough in the field of disaster management and damage assessment. Traditional methods of damage assessment often rely on manual surveys, which can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. Moreover, these methods can be inaccurate, as they rely on human judgment and may not take into account the full extent of the damage. SpADANet, on the other hand, provides a rapid and accurate assessment of damage, which can be used to inform relief efforts, prioritize resource allocation, and optimize rebuilding efforts.
The potential applications of SpADANet are vast and varied. In the context of hurricane damage assessment, SpADANet can be used to identify areas of greatest need, prioritize rescue operations, and allocate resources more effectively. Additionally, SpADANet can be used to assess damage to critical infrastructure, such as power plants, hospitals, and communication networks, which is essential for maintaining public safety and order.
Furthermore, SpADANet can be used in other disaster scenarios, such as earthquakes, floods, and wildfires, where rapid and accurate damage assessment is crucial. The model can be easily adapted to different types of disasters and can be used in conjunction with other technologies, such as drones and satellite imaging, to provide a more comprehensive picture of the damage.
In conclusion, the development of SpADANet by IIT Bombay researchers is a significant breakthrough in the field of disaster management and damage assessment. The model’s ability to overcome the “domain gap,” use spatial context, and optimize for mobile devices makes it a highly effective tool for rapid and accurate damage assessment. As the world becomes increasingly vulnerable to natural disasters, the development of innovative technologies like SpADANet is crucial for improving disaster response and relief efforts. With its potential applications in various disaster scenarios, SpADANet can play a vital role in saving lives, reducing economic losses, and rebuilding communities.