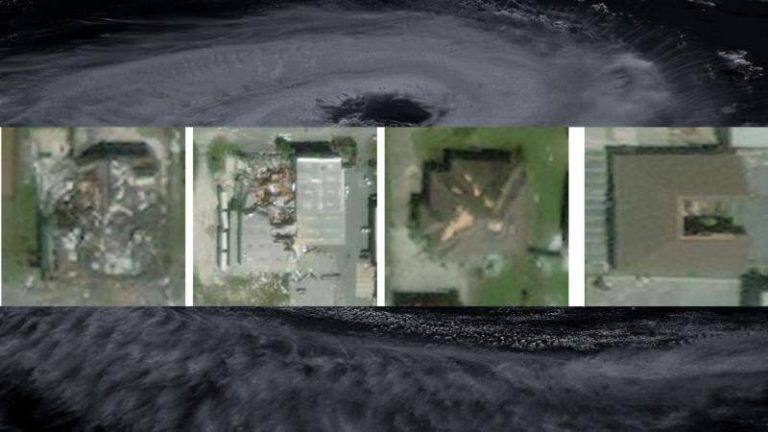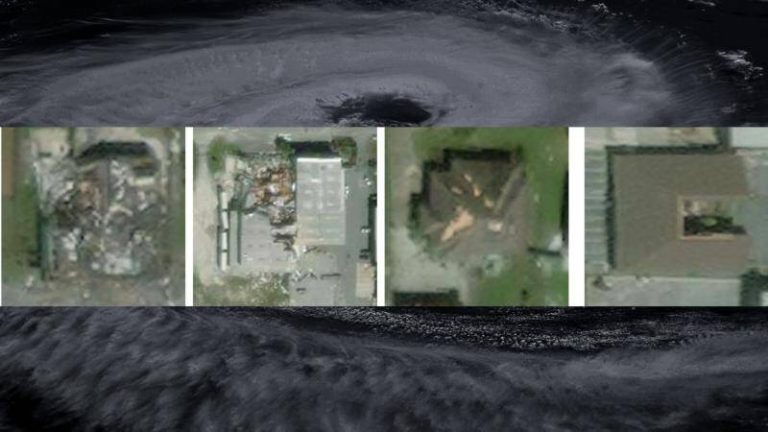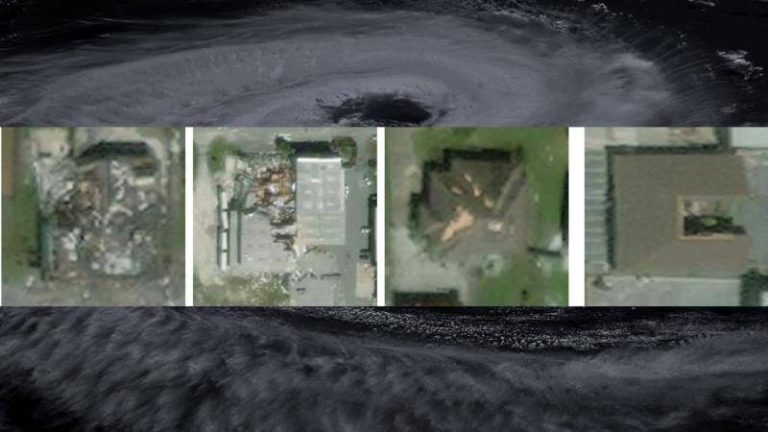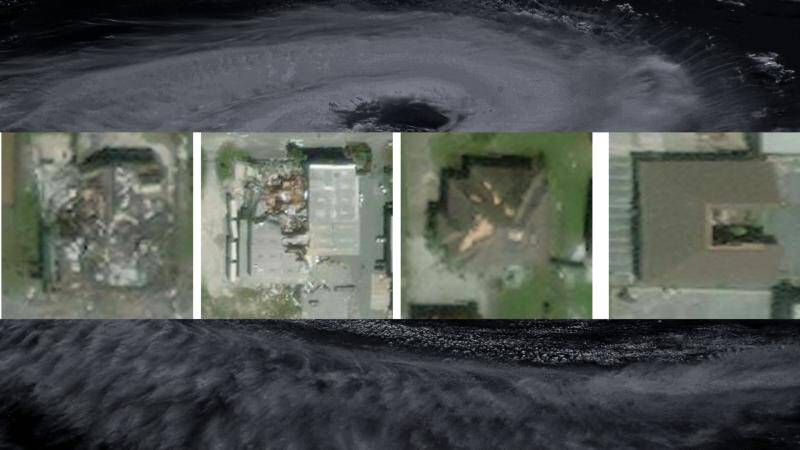
IIT Bombay’s AI speeds up hurricane damage assessment
Hurricanes are one of the most destructive natural disasters, causing widespread damage to infrastructure, properties, and human life. The aftermath of a hurricane is a critical period, where quick and accurate damage assessment is essential for effective disaster response and relief efforts. However, traditional methods of damage assessment can be time-consuming, labor-intensive, and often hampered by limited access to affected areas. To address this challenge, researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Bombay have developed an innovative AI model, called SpADANet, which can rapidly identify building damage from aerial images.
SpADANet is a spatially-aware deep learning model that leverages the power of artificial intelligence to analyze aerial images and detect damaged buildings. The model is designed to overcome the “domain gap” problem, which refers to the challenge of adapting AI models to new environments or datasets with minimal training data. This is particularly significant in the context of hurricane damage assessment, where the type and extent of damage can vary greatly from one storm to another. By adapting to different storms with minimal data, SpADANet can be applied to a wide range of disaster scenarios, making it a valuable tool for disaster response and relief efforts globally.
One of the key features of SpADANet is its ability to utilize spatial context to improve damage detection accuracy. The model takes into account the relationships between different objects in an image, such as buildings, roads, and vegetation, to better understand the context of the damage. This spatial awareness enables SpADANet to outperform existing methods, which often rely on simple image classification or object detection approaches. By considering the broader spatial context, SpADANet can identify subtle patterns and anomalies that may indicate damage, even if the damage is not immediately apparent.
Another significant advantage of SpADANet is its optimization for mobile devices. This means that the model can be deployed on a range of devices, from smartphones to drones, allowing for rapid and flexible damage assessment in the field. This is particularly important in disaster scenarios, where access to affected areas may be limited, and rapid assessment is critical to inform response and relief efforts.
The development of SpADANet has significant implications for disaster response and relief efforts. By providing rapid and accurate damage assessment, SpADANet can help emergency responders to prioritize their efforts, allocate resources more effectively, and ultimately save lives. The model can also be used to identify areas of greatest need, allowing for more targeted and efficient delivery of aid and support.
The potential applications of SpADANet extend beyond hurricane damage assessment to a range of other disaster scenarios, including earthquakes, floods, and wildfires. By adapting the model to different types of disasters and environments, researchers can create a powerful tool for disaster response and relief efforts globally.
In conclusion, the development of SpADANet by IIT Bombay researchers represents a significant breakthrough in the field of disaster damage assessment. By leveraging the power of AI and spatial context, SpADANet can rapidly and accurately identify building damage from aerial images, overcoming the challenges of traditional methods. With its optimization for mobile devices and ability to adapt to different storms with minimal data, SpADANet has the potential to revolutionize disaster response and relief efforts, saving lives and reducing the impact of disasters worldwide.
The development of SpADANet is a testament to the power of innovation and collaboration in addressing some of the world’s most pressing challenges. As researchers continue to refine and adapt the model to different disaster scenarios, it is likely that SpADANet will become an essential tool for emergency responders and disaster relief efforts globally.
For more information on this innovative AI model, please visit the research article published on the Research Matters website.
News Source: https://researchmatters.in/news/novel-spatially-aware-ai-model-makes-hurricane-damage-assessment-more-accurate