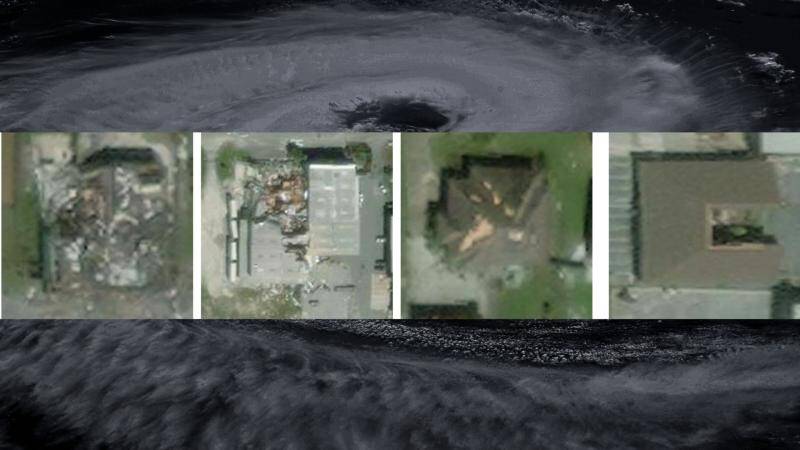
IIT Bombay’s AI speeds up hurricane damage assessment
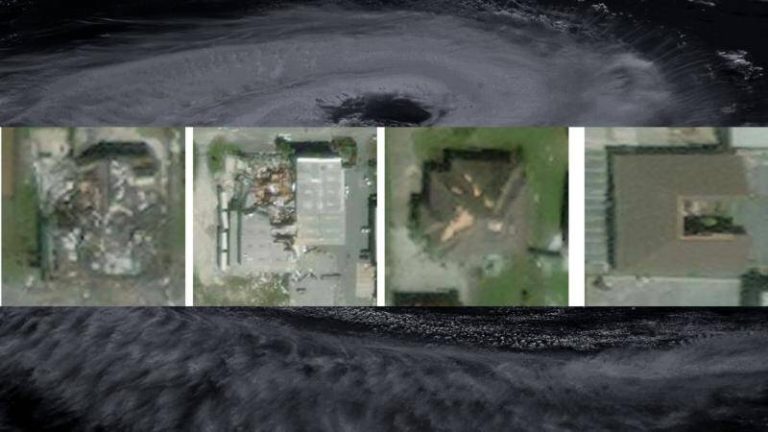
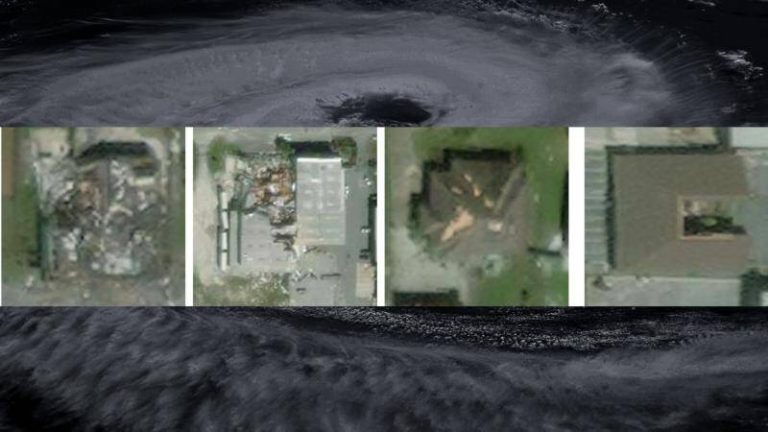
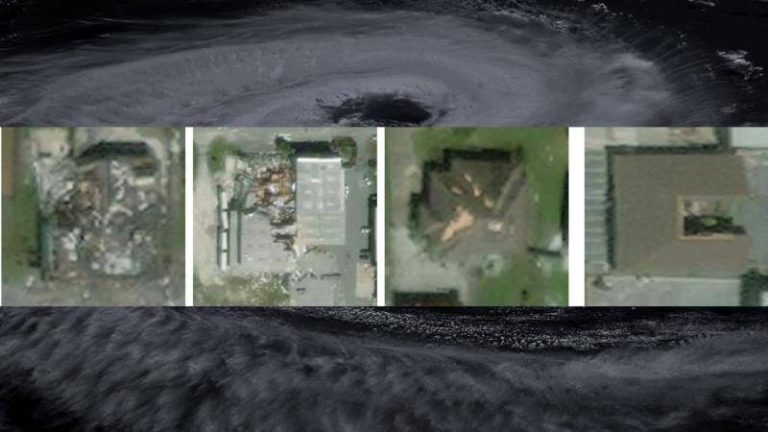
Natural disasters like hurricanes can be devastating, causing widespread destruction and loss of life. In the aftermath of such disasters, assessing the damage and providing relief to affected areas is crucial. However, this process can be time-consuming and labor-intensive, especially when it comes to evaluating the extent of damage to buildings and infrastructure. To address this challenge, researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Bombay have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) model that can quickly and accurately assess building damage from aerial images.
The AI model, called SpADANet, uses spatial context to identify damaged buildings and has been optimized for use on mobile devices. This makes it an ideal tool for disaster response and relief efforts, where quick and accurate assessments are critical. According to the researchers, SpADANet overcomes the “domain gap” that exists in traditional AI models, which can struggle to adapt to different types of storms and environments. This means that SpADANet can be used to assess damage from a variety of hurricanes, with minimal additional data required.
The development of SpADANet is a significant breakthrough in the field of disaster response and relief. Traditional methods of damage assessment often rely on manual surveys, which can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. These methods can also be prone to errors, particularly in the aftermath of a disaster when access to affected areas may be limited. SpADANet, on the other hand, can quickly analyze aerial images and provide an accurate assessment of building damage.
The AI model uses a combination of machine learning algorithms and spatial analysis to identify damaged buildings. It takes into account the spatial context of the images, including the location and orientation of buildings, as well as any visible signs of damage such as debris or structural damage. This allows SpADANet to provide a more accurate assessment of damage than traditional AI models, which may rely solely on visual features such as color and texture.
One of the key advantages of SpADANet is its ability to adapt to different types of storms and environments. Traditional AI models can struggle to generalize to new environments, particularly when there is limited data available. SpADANet, on the other hand, can learn from a small amount of data and apply its knowledge to new situations. This makes it an ideal tool for disaster response and relief efforts, where the ability to quickly adapt to new situations is critical.
The optimization of SpADANet for mobile devices is also significant. In the aftermath of a disaster, access to affected areas may be limited, and mobile devices may be the only means of communication available. By optimizing SpADANet for mobile devices, the researchers have made it possible for disaster response teams to quickly and accurately assess damage using a device that is likely to be readily available.
The potential applications of SpADANet are significant. In the aftermath of a hurricane, SpADANet could be used to quickly assess damage and prioritize relief efforts. This could help to save lives and reduce the economic impact of the disaster. SpADANet could also be used to identify areas that are at high risk of damage from future storms, allowing for proactive measures to be taken to mitigate the impact of the disaster.
In addition to its potential applications in disaster response and relief, SpADANet could also be used in a variety of other fields. For example, it could be used to assess damage to buildings and infrastructure after earthquakes or floods, or to identify areas that are at risk of landslides or other natural hazards. The ability of SpADANet to adapt to different types of storms and environments makes it a versatile tool that could be applied in a wide range of situations.
In conclusion, the development of SpADANet is a significant breakthrough in the field of disaster response and relief. The AI model’s ability to quickly and accurately assess building damage from aerial images makes it an ideal tool for disaster response teams. Its optimization for mobile devices and ability to adapt to different types of storms and environments make it a versatile tool that could be applied in a wide range of situations. As the world becomes increasingly vulnerable to natural disasters, the development of tools like SpADANet is critical to saving lives and reducing the economic impact of these events.
The researchers at IIT Bombay are to be commended for their work on SpADANet, and their commitment to developing innovative solutions to real-world problems. As the use of AI and machine learning continues to grow, it is likely that we will see more tools like SpADANet being developed to address the challenges posed by natural disasters.
For more information on SpADANet and its potential applications, readers can visit the IIT Bombay website or contact the researchers directly. The development of SpADANet is a significant achievement, and it has the potential to make a real difference in the field of disaster response and relief.
News Source: https://researchmatters.in/news/novel-spatially-aware-ai-model-makes-hurricane-damage-assessment-more-accurate