IIT Bombay Study Finds Important Insights in Blood Drying Pattern
Bloodstains are a crucial piece of evidence in crime scene investigations, providing valuable information about the circumstances surrounding a crime. However, analyzing these stains can be a complex process, requiring a deep understanding of the physical and chemical properties of blood. Recently, a team of researchers from IIT Bombay has made a significant breakthrough in this area, shedding light on the patterns of blood drying on tilted surfaces.
The study, published in the Journal of Physics: Conference Series, explored the effects of blood droplet volume and surface angle on the drying behavior and crack formation of bloodstains. The researchers found that these factors play a significant role in determining the final appearance of the stain, which can be crucial in forensic analysis.
Background
Bloodstains are a common occurrence at crime scenes, and their analysis is a critical component of forensic science. However, bloodstains are prone to degradation over time, making it challenging for investigators to collect and analyze them effectively. As a result, researchers have been working to develop new methods and techniques for analyzing bloodstains, with a focus on enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of crime scene reconstruction.
The Study
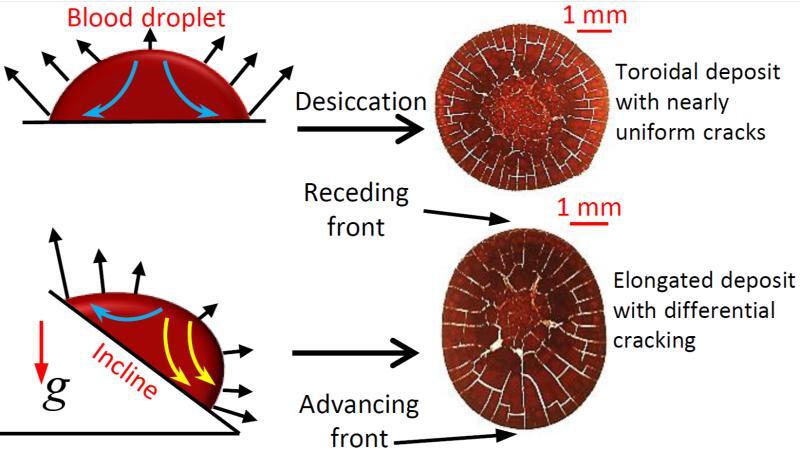
The IIT Bombay researchers conducted their study by creating a controlled environment in which they deposited blood droplets of varying volumes onto a tilted surface. They then monitored the drying process, observing the formation of cracks and other patterns on the surface of the bloodstain.
The team found that the volume of the blood droplet had a significant impact on the drying behavior of the stain. Larger droplets tended to dry more rapidly, with fewer cracks forming on the surface. Smaller droplets, on the other hand, took longer to dry and exhibited more extensive cracking.
The surface angle of the tilted surface also played a crucial role in the drying process. The researchers found that as the surface angle increased, the rate of drying decreased, and the number of cracks formed on the surface increased. This is because the blood droplet was able to spread more evenly on the surface at higher angles, reducing the likelihood of crack formation.
Implications for Forensic Analysis
The findings of the IIT Bombay study have significant implications for forensic analysis and crime scene reconstruction. By understanding how bloodstains dry on tilted surfaces, investigators can gain valuable insights into the initial conditions of a crime scene.
For example, if a bloodstain is found on a surface at a particular angle, the investigators can use the findings of the study to determine the volume of the original blood droplet and the rate at which it dried. This information can be used to reconstruct the events surrounding the crime, helping investigators to piece together the timeline of events and identify potential suspects.
The study’s findings can also aid in the interpretation of bloodstain patterns, allowing investigators to differentiate between bloodstains that were created at the same time and those that were created at different times. This can be particularly useful in cases where multiple bloodstains are found at the same location, as it can help investigators to determine the sequence of events.
Conclusion
The IIT Bombay study provides important insights into the drying patterns of bloodstains on tilted surfaces, highlighting the significant impact of blood droplet volume and surface angle on the drying behavior and crack formation of these stains. These findings can enhance forensic analysis and aid in crime scene reconstruction, allowing investigators to gain a deeper understanding of the events surrounding a crime.
As researchers continue to develop new methods and techniques for analyzing bloodstains, the study’s findings will play a critical role in informing their work. By combining cutting-edge research with practical applications, the IIT Bombay team is helping to advance the field of forensic science and improve the accuracy and efficiency of crime scene investigations.
Source:






