How Moon altered the orbit of Chandrayaan-3’s propulsion module?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has been making headlines with its Chandrayaan-3 mission, which aims to land a rover on the lunar surface. However, a recent development has shed light on the fascinating dynamics of space travel and the influence of celestial bodies on spacecraft trajectories. In November 2025, the Chandrayaan-3’s propulsion module had its Earth orbit significantly altered after passing close to the Moon. This change in orbit was not achieved through the use of fuel, but rather by harnessing the power of lunar gravity.
The propulsion module, which is a crucial component of the Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft, had been orbiting the Earth in a specific trajectory. However, as it approached the Moon, the lunar gravity began to exert its influence on the module. During two flybys, one on November 6 at a distance of 3,740 km and another on November 11 at a distance of 4,537 km, the Moon’s gravity pulled the spacecraft, naturally altering its path. This phenomenon is a testament to the complex and intricate dance of celestial mechanics, where the gravitational forces of nearby bodies can significantly impact the trajectory of a spacecraft.
The ISRO has confirmed that the lunar gravity has changed the module’s orbit size and direction. This alteration in orbit is a result of the gravitational force exerted by the Moon on the spacecraft. As the propulsion module passed close to the Moon, the lunar gravity began to pull it, slowing it down and changing its trajectory. This process, known as a gravity assist, is a common technique used by space agencies to alter the trajectory of a spacecraft without using fuel.
The gravity assist maneuver is a fascinating phenomenon that has been used by space agencies to explore the solar system. By flying a spacecraft close to a celestial body, such as a planet or moon, the spacecraft can harness the gravitational force of the body to change its trajectory. This technique has been used by NASA’s Voyager spacecraft to explore the outer reaches of the solar system, as well as by the European Space Agency’s Rosetta mission to land a probe on a comet.
In the case of the Chandrayaan-3 propulsion module, the gravity assist maneuver was not a deliberate attempt to alter the spacecraft’s trajectory. Rather, it was a natural consequence of the module’s close approach to the Moon. The ISRO had planned the spacecraft’s trajectory to take into account the gravitational influence of the Moon, but the actual change in orbit was still a significant event that highlights the complexities of space travel.
The alteration in the propulsion module’s orbit has significant implications for the Chandrayaan-3 mission. The changed orbit size and direction will require adjustments to be made to the spacecraft’s trajectory in order to ensure a successful landing on the lunar surface. The ISRO will need to carefully plan and execute a series of maneuvers to ensure that the spacecraft is on the correct trajectory to land safely on the Moon.
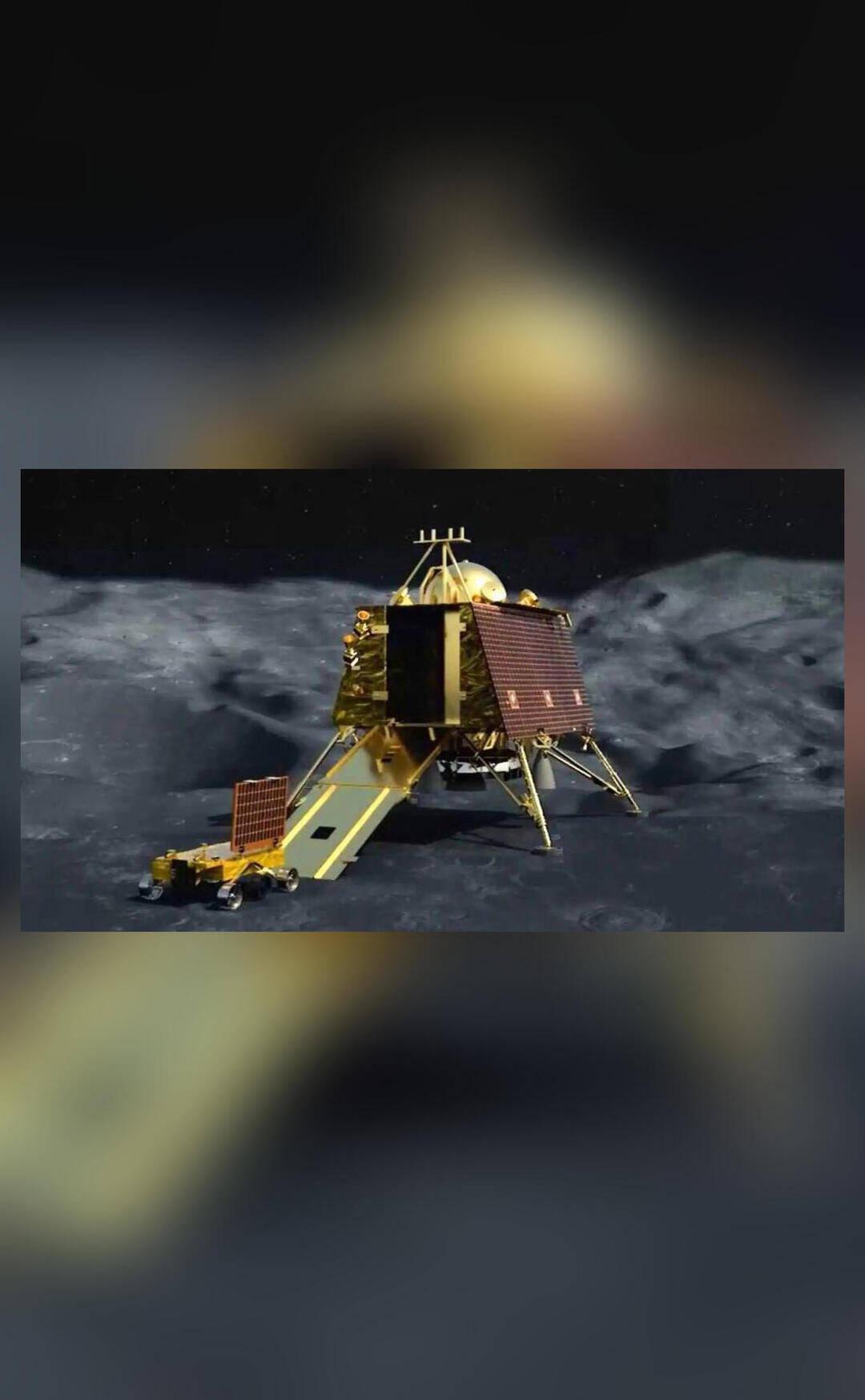
The Chandrayaan-3 mission is a significant milestone in India’s space program, marking the country’s second attempt to land a rover on the lunar surface. The mission is designed to demonstrate the capability to soft-land on the lunar surface and to conduct scientific experiments. The spacecraft is equipped with a range of instruments, including a lunar lander, a rover, and a propulsion module.
The lunar lander is designed to separate from the propulsion module and descend to the lunar surface, where it will deploy the rover. The rover is equipped with a range of scientific instruments, including cameras, spectrometers, and a seismometer, which will be used to conduct experiments on the lunar surface. The propulsion module, which has had its orbit altered by the Moon’s gravity, will remain in orbit around the Earth, providing communication relay services for the lander and rover.
In conclusion, the alteration in the orbit of the Chandrayaan-3 propulsion module is a fascinating example of the complex dynamics of space travel. The lunar gravity has changed the module’s orbit size and direction, requiring adjustments to be made to the spacecraft’s trajectory in order to ensure a successful landing on the lunar surface. The Chandrayaan-3 mission is a significant milestone in India’s space program, and the ISRO will need to carefully plan and execute a series of maneuvers to ensure the success of the mission.