Title: Gold & Platinum created through Neutron Stars’ Explosions: Study
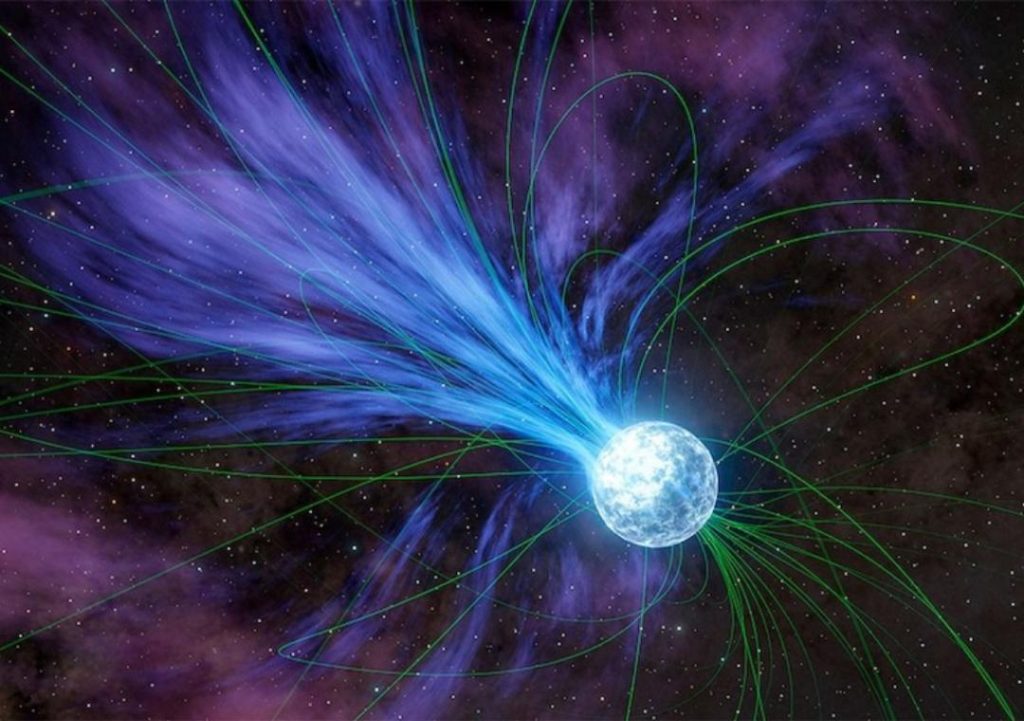
The origin of precious metals like gold and platinum has long been a topic of fascination for scientists and treasure hunters alike. For a long time, the exact process by which these metals were formed has remained a mystery. However, a recent study led by Columbia University student Anirudh Patel has shed new light on the subject, revealing that magnetars, or highly magnetized neutron stars, played a crucial role in creating these valuable elements.
According to the study, magnetars underwent powerful explosions, releasing flares that contained gold and platinum. This phenomenon is not unique to one specific event, but rather, it occurs approximately once per decade in the Milky Way galaxy and annually across the observable universe.
The study, published in the journal Science, analyzed data from a cosmic event that took place over 20 years ago. By examining the light curves and spectra of the magnetar’s explosion, the researchers were able to identify the presence of these precious metals. This discovery has significant implications for our understanding of the origins of gold and platinum.
But how exactly did magnetars manage to create these valuable elements? The process is believed to have occurred through a series of complex physical and chemical reactions. During the explosion, the magnetar’s intense magnetic field and powerful radiation accelerated particles to incredible speeds, causing them to collide and merge. This collision produced a vast array of heavy elements, including gold and platinum.
The formation of these elements is thought to have occurred through a process known as rapid neutron capture, or r-process nucleosynthesis. This process involves the rapid accumulation of neutrons, which then combine with atomic nuclei to form heavier elements. In the case of gold and platinum, this process likely occurred in the intense magnetic fields surrounding the magnetar, where the conditions were ideal for the creation of these heavy elements.
The discovery of gold and platinum in magnetars’ explosions has significant implications for our understanding of the origins of these precious metals. For decades, scientists have been searching for answers to the question of how these metals came to be. While there have been several theories, none have been able to fully explain the process by which gold and platinum were formed.
The study’s findings have also sparked renewed interest in the study of magnetars, which are a type of neutron star with an incredibly strong magnetic field. These objects are thought to be responsible for many of the most powerful explosions in the universe, and their study has the potential to reveal new insights into the fundamental laws of physics.
The discovery of gold and platinum in magnetars’ explosions also has implications for our understanding of the origins of the elements themselves. The presence of these elements in the universe is thought to have been created through a series of complex processes, involving the fusion of lighter elements in the hearts of stars.
However, the study’s findings suggest that magnetars may have played a crucial role in the creation of these elements, particularly in the formation of heavier elements like gold and platinum. This challenges our current understanding of the origins of the elements and highlights the importance of further research into the mysteries of the universe.
In conclusion, the study’s findings have significant implications for our understanding of the origins of gold and platinum. The discovery of these precious metals in magnetars’ explosions provides new insights into the process by which they were formed, and highlights the importance of further research into the mysteries of the universe.
As scientists continue to study the universe and its many wonders, we may yet uncover even more secrets about the origins of gold and platinum. Perhaps one day, we will discover that other celestial bodies, such as black holes or supernovae, also played a role in the creation of these valuable elements.
For now, the study’s findings provide a fascinating glimpse into the workings of the universe, and remind us of the awe-inspiring beauty and complexity of the cosmos.






