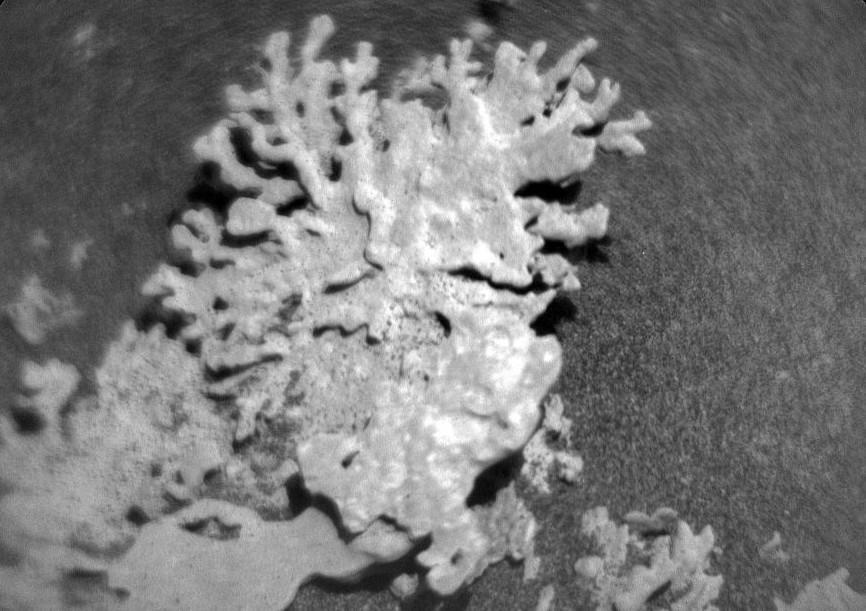
Coral-shaped rock spotted on Mars, NASA shares pic
NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover has been exploring the Martian surface for years, sending back a wealth of information and stunning images of the planet’s geology. Recently, the rover sent back black and white images of a rock on the Martian surface that looks uncannily like a piece of coral. The rock was found in the Gale Crater, a large impact basin on Mars, and according to NASA, the recently discovered coral-like rock is believed to be a billion years old.
The images were captured using the rover’s ChemCam instrument, which uses a laser to vaporize the rock’s surface and analyzes the resulting plasma to determine the chemical composition of the rock. The resulting images show a rock with a distinctive coral-like shape, with ridges and grooves that resemble the branching structure of coral reefs on Earth.
The discovery of the coral-like rock on Mars is significant because it provides new insights into the geological history of the planet. The Gale Crater, where the rock was found, is thought to have formed around 3.5 billion years ago, and the rock itself is believed to be around 1 billion years old.
The rock’s coral-like shape is thought to be the result of erosion, which has worn away the rock’s surface over time, creating the distinctive ridges and grooves. The rock’s composition is also interesting, with NASA scientists identifying the presence of minerals such as calcite, gypsum, and halite.
The discovery of the coral-like rock is just the latest in a long series of fascinating geological discoveries made by the Curiosity rover. Since its landing on Mars in 2012, the rover has explored the Martian surface, sending back thousands of images and providing valuable insights into the planet’s geology, climate, and potential habitability.
The Curiosity rover was designed to study the Martian surface and subsurface, and it has been equipped with a range of instruments designed to study the planet’s geology, climate, and potential habitability. The rover is powered by a radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG), which provides a steady source of electricity, and it is designed to operate for at least 687 days, or about 23 months.
The Curiosity rover is just one of several NASA rovers that have been sent to Mars over the years. The first rover to be sent to Mars was the Sojourner rover, which landed on the planet in 1997 as part of the Mars Pathfinder mission. Since then, NASA has sent several other rovers to Mars, including the Spirit and Opportunity rovers, which launched in 2003 and operated until 2011.
The Curiosity rover is the largest and most advanced rover to be sent to Mars, and it has been equipped with a range of instruments designed to study the planet’s geology, climate, and potential habitability. The rover is about the size of a small car, and it is equipped with a range of instruments, including cameras, spectrometers, and drilling equipment.
The Curiosity rover is also equipped with a range of scientific instruments, including a rock analyzer, a geology tool, and a weather station. The rover is designed to study the Martian surface and subsurface, and it is equipped with a range of instruments designed to study the planet’s geology, climate, and potential habitability.
The discovery of the coral-like rock on Mars is just the latest in a long series of fascinating geological discoveries made by the Curiosity rover. The rover has been exploring the Martian surface for years, and it has sent back thousands of images and provided valuable insights into the planet’s geology, climate, and potential habitability.
News Source:
https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/images/pia26634-curiositys-chemcam-views-a-rock-shaped-like-coral/






