India’s Coal Imports Slide 7.9% in FY25
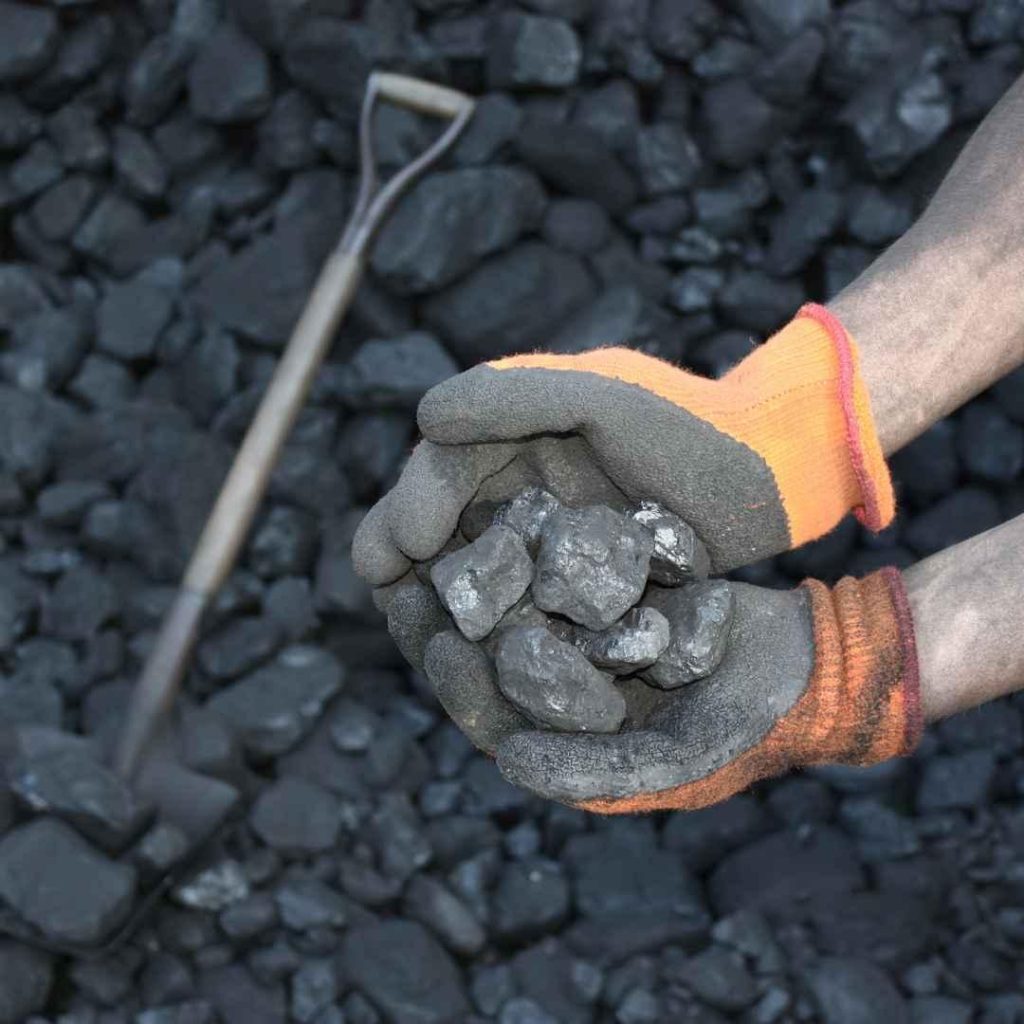
The Indian government has announced a significant reduction in coal imports during the fiscal year 2024-25. According to the latest data, India’s coal imports dropped by 7.9% year-on-year, totaling 243.62 million tonnes (MT) compared to 264.53 MT in the previous fiscal year. This reduction has resulted in foreign exchange savings of approximately $7.93 billion (₹60681.67 crore).
The decline in coal imports is a welcome development for the Indian government, which has been working towards reducing the country’s dependence on coal imports. The government has been promoting the use of domestic coal and encouraging the development of renewable energy sources to reduce the country’s carbon footprint.
The reduction in coal imports is not limited to the power sector alone. The Non-Regulated Sector, which includes industries such as cement, steel, and chemicals, also experienced a significant decline in coal imports. The imports dropped by 8.95% year-on-year in this sector, indicating a broader trend of reducing coal consumption across various industries.
The decline in coal imports can be attributed to several factors, including the increasing availability of domestic coal, the growth of renewable energy sources, and the government’s efforts to promote energy efficiency. The government has been implementing various policies and initiatives to promote the use of domestic coal and renewable energy sources, which has led to a reduction in coal imports.
One of the key factors contributing to the decline in coal imports is the increasing availability of domestic coal. India has been producing more coal domestically, which has reduced the need for imports. The country’s coal production has been increasing steadily over the years, with the government setting a target of producing 675 MT of coal by 2024-25. The increasing availability of domestic coal has not only reduced the country’s dependence on imports but also helped to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Another factor contributing to the decline in coal imports is the growth of renewable energy sources. India has been promoting the development of renewable energy sources, including solar and wind power, to reduce its dependence on fossil fuels. The country has set a target of generating 40% of its electricity from non-fossil fuels by 2030. The growth of renewable energy sources has helped to reduce the country’s coal consumption, which has in turn reduced coal imports.
The government’s efforts to promote energy efficiency have also played a significant role in reducing coal imports. The government has been implementing various policies and initiatives to promote energy efficiency, including the implementation of energy-efficient technologies and the promotion of energy-efficient practices. The government has also been working to improve the energy efficiency of industries, which has helped to reduce coal consumption.
The reduction in coal imports is not only beneficial for the Indian economy but also for the environment. Coal is one of the most polluting forms of energy, and its consumption has a significant impact on the environment. The reduction in coal imports has helped to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, which is a significant step towards mitigating climate change.
In conclusion, India’s coal imports have slid by 7.9% in FY25, totaling 243.62 MT compared to 264.53 MT in the previous fiscal year. This reduction has resulted in foreign exchange savings of approximately $7.93 billion (₹60681.67 crore). The decline in coal imports is a welcome development for the Indian government, which has been working towards reducing the country’s dependence on coal imports. The government’s efforts to promote the use of domestic coal, renewable energy sources, and energy efficiency have all contributed to the decline in coal imports. This reduction is not only beneficial for the Indian economy but also for the environment, and it is an important step towards mitigating climate change.
Source: https://www.refersms.com/indias-coal-imports-drop-by-7-9-in-fy-2024-25/