Skull reveals some ancient humans had more ‘primitive’ faces
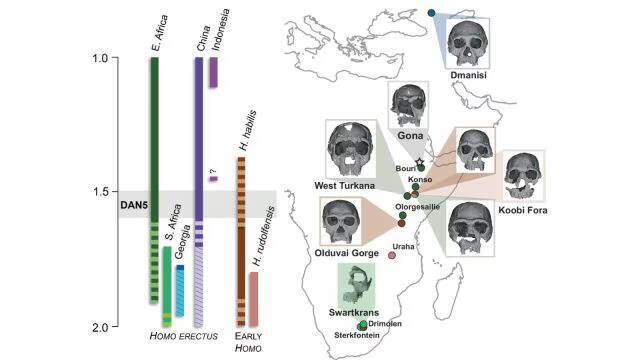
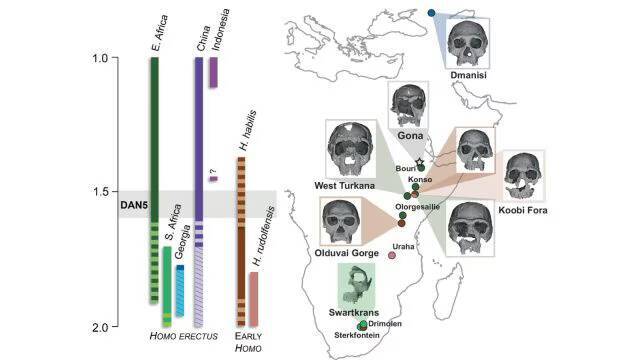
The discovery of a 1.5-1.6-million-year-old Homo erectus skull in Ethiopia has shed new light on the evolution of early humans. The skull, known as DAN5, has been reconstructed and studied using micro-CT modeling, revealing a face that is more primitive than expected. According to Dr. Baab, “The face is more archaic than we anticipated,” which has significant implications for our understanding of human evolution.
The study, which examined the DAN5 skull, found that it had a small braincase paired with ancestral features, including a flat nasal bridge and large molars. This combination of traits is surprising, as it was thought that early Homo erectus fossils would have more modern facial features. “Seeing such a primitive face on a fossil this young was surprising,” said Yousuke Kaifu, highlighting the significance of this discovery.
The Homo erectus species is thought to have evolved around 2 million years ago and is considered one of the most successful human species to have existed. They were able to adapt to a wide range of environments and were found in various parts of the world, including Africa, Asia, and Europe. However, the discovery of the DAN5 skull suggests that the evolution of Homo erectus was more complex than previously thought.
The primitive facial features of the DAN5 skull are similar to those of earlier human ancestors, such as Homo habilis. This suggests that there may have been a period of evolutionary stasis, where the facial features of early Homo erectus fossils remained relatively unchanged for a significant period. This challenges the traditional view of human evolution, which assumes a linear progression from more primitive to more modern traits.
The use of micro-CT modeling has been instrumental in the study of the DAN5 skull. This technique allows researchers to create detailed 3D models of the fossil, which can be used to examine the internal structure of the skull. This has provided valuable insights into the evolution of the human brain and the development of facial features.
The discovery of the DAN5 skull has significant implications for our understanding of human evolution. It suggests that the evolution of early Homo erectus fossils was more complex and nuanced than previously thought. The combination of primitive facial features with a small braincase is a unique characteristic of the DAN5 skull, which challenges our current understanding of human evolution.
Furthermore, the study of the DAN5 skull highlights the importance of continued exploration and discovery in the field of paleoanthropology. The discovery of new fossils and the development of new technologies, such as micro-CT modeling, are essential for advancing our understanding of human evolution.
In conclusion, the discovery of the 1.5-1.6-million-year-old Homo erectus skull DAN5 has shed new light on the evolution of early humans. The primitive facial features of the skull, including a flat nasal bridge and large molars, are surprising and challenge our current understanding of human evolution. The use of micro-CT modeling has been instrumental in the study of the DAN5 skull, providing valuable insights into the evolution of the human brain and the development of facial features. As we continue to explore and discover new fossils, our understanding of human evolution will become increasingly nuanced and complex.
The study of human evolution is an ongoing and dynamic field, with new discoveries and advancements in technology continually shaping our understanding of the past. The discovery of the DAN5 skull is a significant contribution to this field, and it will be exciting to see how future discoveries and studies build upon this finding.
As we look to the future, it is clear that the study of human evolution will continue to be an exciting and rapidly evolving field. With the continued development of new technologies and the discovery of new fossils, our understanding of the past will become increasingly detailed and nuanced. The discovery of the DAN5 skull is a significant step forward in this journey, and it will be exciting to see where future discoveries take us.
For more information on this topic, please visit: https://indianexpress.com/article/technology/science/ancient-ethiopian-skull-reshapes-understanding-early-homo-erectus-evolution-10426865/lite/