Skull reveals some ancient humans had more ‘primitive’ faces
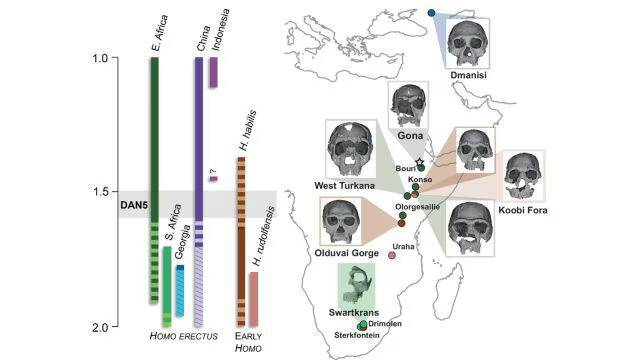
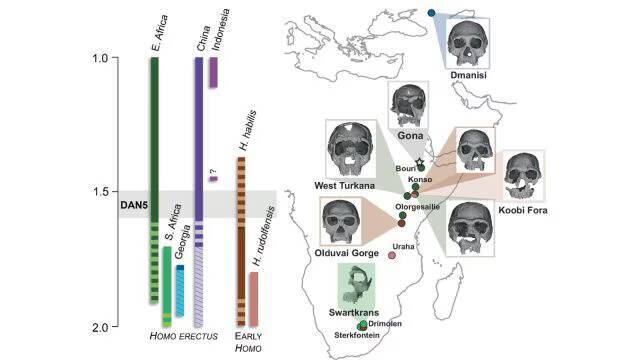
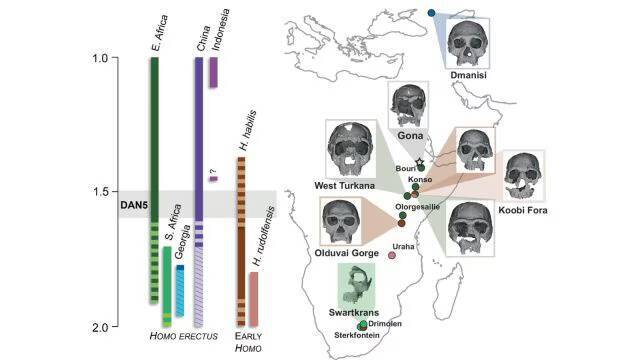
The discovery of a 1.5-1.6-million-year-old Homo erectus skull in Ethiopia has shed new light on the evolution of early humans. A recent study has revealed that this ancient skull, known as DAN5, exhibits primitive facial traits that were not expected to be found in a fossil of its age. The findings have significant implications for our understanding of human evolution and the diversity of early human populations.
The DAN5 skull was discovered in the Danakil Desert in Ethiopia, a region known for its rich fossil deposits. The skull was found to be remarkably well-preserved, with many of its original features still intact. Using micro-CT modelling, a team of researchers was able to create a detailed reconstruction of the skull, which revealed a number of surprising characteristics.
According to Dr. Baab, one of the lead researchers on the project, “The face is more archaic than we anticipated.” The skull has a small braincase, which is paired with a number of ancestral features, including a flat nasal bridge and large molars. These characteristics are more commonly associated with earlier human ancestors, such as Homo habilis, rather than the more advanced Homo erectus.
The discovery of these primitive facial traits in a fossil of this age was unexpected, as it was thought that Homo erectus had already evolved more modern facial features by this point in time. “Seeing such a primitive face on a fossil this young was surprising,” said Yousuke Kaifu, a researcher involved in the study.
The implications of this discovery are significant, as it suggests that there was more diversity in early human populations than previously thought. It appears that different human populations were evolving at different rates, with some retaining more primitive characteristics while others were developing more modern features.
The study also highlights the importance of continued exploration and discovery in the field of paleoanthropology. The DAN5 skull is just one example of the many fossils that remain to be discovered, and it is likely that future findings will continue to shed new light on the evolution of our species.
In addition to its significance for our understanding of human evolution, the discovery of the DAN5 skull also has important implications for the field of anthropology. The study of human evolution is not just about understanding the biological changes that have occurred over time, but also about understanding the cultural and social developments that have shaped our species.
The primitive facial traits exhibited by the DAN5 skull are a reminder that human evolution is a complex and multifaceted process, and that different populations have evolved in different ways. This diversity is a key aspect of the human experience, and it is essential that we continue to explore and learn more about our shared history.
In conclusion, the discovery of the DAN5 skull is a significant finding that sheds new light on the evolution of early humans. The primitive facial traits exhibited by this fossil are a reminder of the diversity and complexity of human evolution, and highlight the importance of continued exploration and discovery in the field of paleoanthropology.
As we continue to learn more about our shared history, it is essential that we approach this topic with a sense of curiosity and wonder. The study of human evolution is a fascinating field that has the power to inspire and educate us, and it is essential that we continue to support and fund research in this area.
The discovery of the DAN5 skull is just one example of the many exciting findings that are being made in the field of paleoanthropology. As we look to the future, it is likely that we will continue to uncover new and exciting information about our shared history, and it is essential that we approach this topic with a sense of excitement and curiosity.