Skull reveals some ancient humans had more ‘primitive’ faces
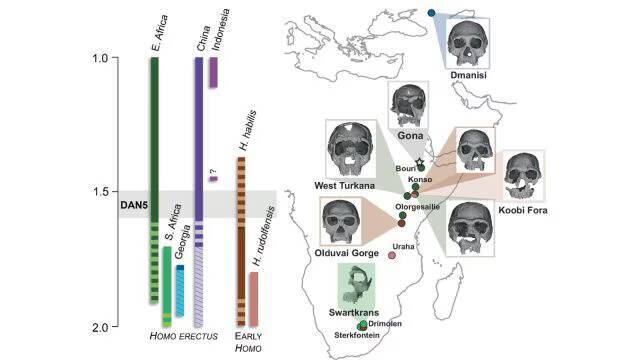
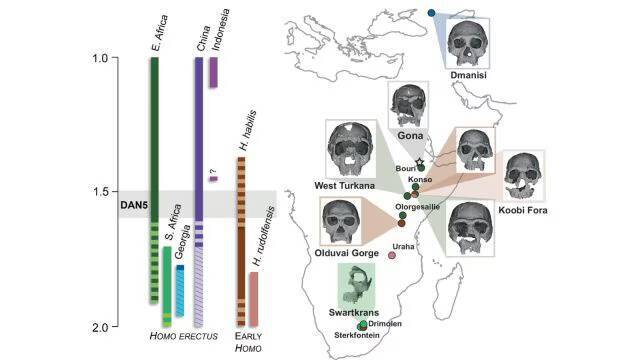
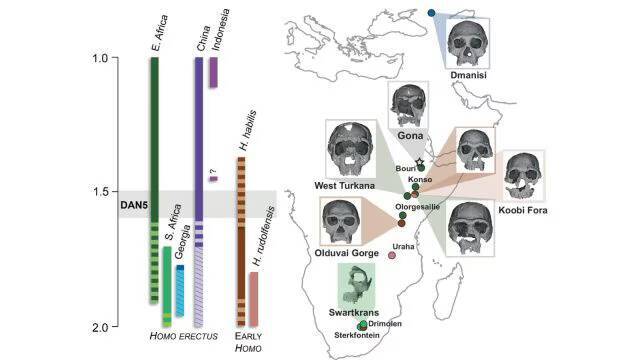
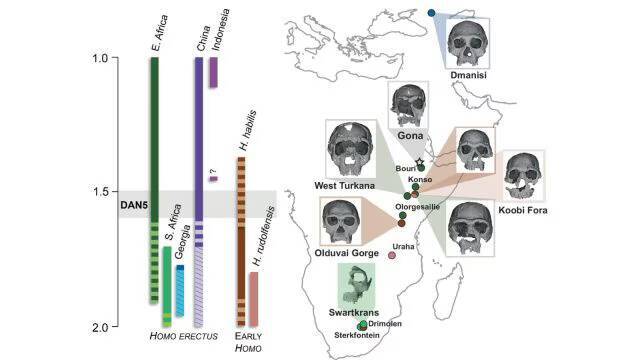
The study of human evolution has always been a fascinating and complex field, with scientists continually uncovering new evidence that helps us better understand our ancestors. Recently, a groundbreaking discovery was made in Ethiopia, where a 1.5-1.6-million-year-old Homo erectus skull, known as DAN5, was reconstructed and analyzed. The findings of this study have shed new light on the evolution of early humans, revealing that some ancient humans had more ‘primitive’ faces than previously thought.
The reconstruction of the DAN5 skull was made possible through the use of micro-CT modeling, a technique that allows researchers to create detailed, three-dimensional images of fossilized remains. This technology has revolutionized the field of paleoanthropology, enabling scientists to study fossils in unprecedented detail. The DAN5 skull, which was discovered in the Danakil Depression in Ethiopia, is one of the most well-preserved Homo erectus fossils ever found, providing a unique opportunity for researchers to learn more about this ancient human species.
According to Dr. Baab, one of the lead researchers on the study, “The face is more archaic than we anticipated.” The facial structure of the DAN5 skull is characterized by a flat nasal bridge, a pronounced jaw, and large molars. These features are more typical of earlier human ancestors, such as Homo habilis, and are not typically associated with Homo erectus, which is thought to have evolved around 1.8 million years ago. The braincase of the DAN5 skull is also relatively small, which is surprising given the age of the fossil.
The discovery of the DAN5 skull has significant implications for our understanding of human evolution. Yousuke Kaifu, a researcher involved in the study, noted, “Seeing such a primitive face on a fossil this young was surprising.” The fact that the DAN5 skull exhibits such primitive features suggests that there may have been more variation in the evolution of early humans than previously thought. It is possible that different populations of Homo erectus evolved at different rates, with some retaining more archaic traits than others.
The study of the DAN5 skull also highlights the importance of considering the complexity of human evolution. For a long time, scientists have thought of human evolution as a linear process, with each species evolving into the next in a straightforward manner. However, the discovery of the DAN5 skull suggests that the reality may be more nuanced. Human evolution is likely to have been a more complex and multifaceted process, with different populations evolving at different rates and in different ways.
The implications of this study extend beyond the field of paleoanthropology, with potential relevance to our understanding of human biology and behavior. The fact that some ancient humans had more ‘primitive’ faces than others raises interesting questions about the evolution of human cognition and social behavior. Did the physical characteristics of early humans influence their behavior and social interactions? How did the evolution of the human face and brain shape our ancestors’ ability to communicate and interact with each other?
The discovery of the DAN5 skull is a significant reminder of the importance of continued research and exploration in the field of human evolution. As scientists, we are constantly learning more about our ancestors and the complex processes that shaped the course of human history. The study of the DAN5 skull is a testament to the power of interdisciplinary research, combining cutting-edge technology with rigorous scientific inquiry to shed new light on the mysteries of human evolution.
In conclusion, the reconstruction of the 1.5-1.6-million-year-old Homo erectus skull DAN5 has revealed a fascinating insight into the evolution of early humans. The discovery of this primitive face on a relatively young fossil has significant implications for our understanding of human evolution, highlighting the complexity and nuance of the process. As we continue to explore and learn more about our ancestors, we are reminded of the importance of considering the multifaceted nature of human evolution and the many factors that have shaped the course of human history.