Skull reveals some ancient humans had more ‘primitive’ faces
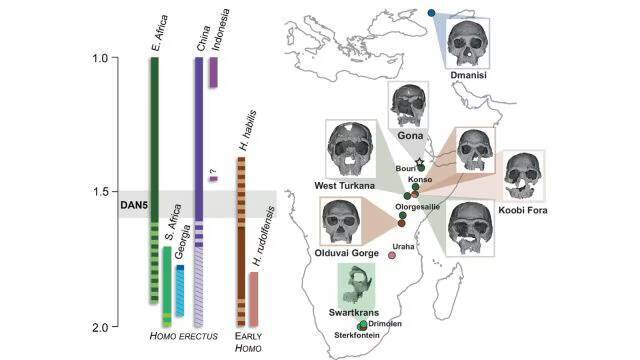
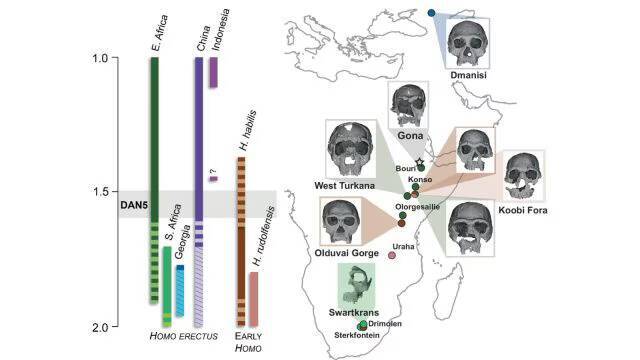
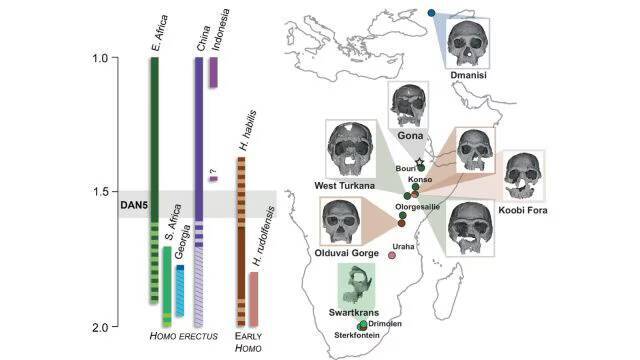
The discovery of ancient human skulls has always been a significant milestone in the field of paleoanthropology, as it provides valuable insights into the evolution of the human species. Recently, a study published on a 1.5-1.6-million-year-old Homo erectus skull, known as DAN5, has shed new light on the facial features of our ancient ancestors. The reconstruction of this ancient skull has revealed that some ancient humans had more ‘primitive’ faces than previously thought, challenging our existing understanding of human evolution.
The DAN5 skull was discovered in Ethiopia, a region known for its rich fossil record, and has been the subject of extensive study by a team of researchers. Using micro-CT modeling, a technique that allows for the creation of detailed 3D models of fossils, the team was able to reconstruct the skull and gain a better understanding of its anatomy. The results were surprising, with the skull showing a combination of primitive and modern traits.
According to Dr. Baab, one of the researchers involved in the study, “The face is more archaic than we anticipated.” The skull features a small braincase, which is a characteristic of earlier human ancestors, paired with a flat nasal bridge and large molars. These ancestral features are more typical of earlier human species, such as Homo habilis, and were not expected to be found in a Homo erectus fossil of this age.
Yousuke Kaifu, another researcher involved in the study, expressed his surprise at the discovery, stating, “Seeing such a primitive face on a fossil this young was surprising.” The age of the DAN5 skull is significant, as it suggests that the evolution of the human face was a more complex and nuanced process than previously thought. The presence of primitive features in a fossil of this age challenges the idea that human evolution was a linear process, with each species exhibiting a clear set of characteristics.
The discovery of the DAN5 skull has significant implications for our understanding of human evolution. It suggests that the evolution of the human face was a gradual process, with different species exhibiting a range of characteristics. The presence of primitive features in a Homo erectus fossil of this age also highlights the complexity of the human evolutionary tree, with different species coexisting and interacting in complex ways.
The study of ancient human skulls like DAN5 is essential for our understanding of human evolution. By analyzing the anatomy of these fossils, researchers can gain insights into the lives of our ancient ancestors, including their diet, behavior, and environment. The discovery of the DAN5 skull is a significant milestone in the field of paleoanthropology, and its implications will be felt for years to come.
The reconstruction of the DAN5 skull is a testament to the power of modern technology in the field of paleoanthropology. The use of micro-CT modeling has allowed researchers to create detailed 3D models of fossils, which can be used to analyze the anatomy of ancient human species. This technology has revolutionized the field of paleoanthropology, allowing researchers to gain insights into the lives of our ancient ancestors that were previously impossible.
In conclusion, the discovery of the DAN5 skull has shed new light on the evolution of the human face. The presence of primitive features in a Homo erectus fossil of this age challenges our existing understanding of human evolution and highlights the complexity of the human evolutionary tree. The study of ancient human skulls like DAN5 is essential for our understanding of human evolution, and the use of modern technology like micro-CT modeling has revolutionized the field of paleoanthropology.
As we continue to study the DAN5 skull and other ancient human fossils, we may uncover even more surprises about the evolution of our species. The discovery of this skull is a reminder that there is still much to be learned about our ancient ancestors and the processes that shaped the human species. By continuing to explore and study the fossil record, we can gain a deeper understanding of our place in the natural world and the complex history of our species.
The study of human evolution is an ongoing process, with new discoveries and advancements in technology continually shedding new light on our understanding of the past. The discovery of the DAN5 skull is a significant milestone in this process, and its implications will be felt for years to come. As we continue to explore and study the fossil record, we may uncover even more surprises about the evolution of our species, and gain a deeper understanding of the complex and nuanced process that has shaped the human face.