Skull reveals some ancient humans had more ‘primitive’ faces
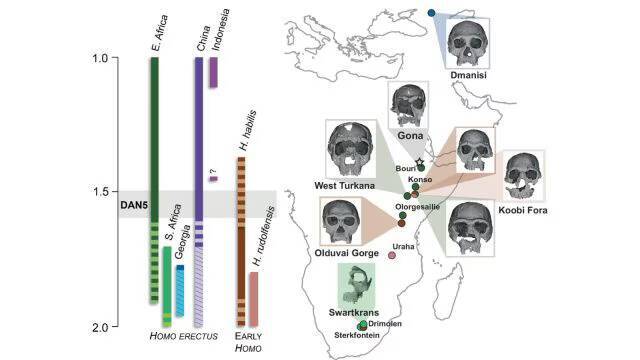
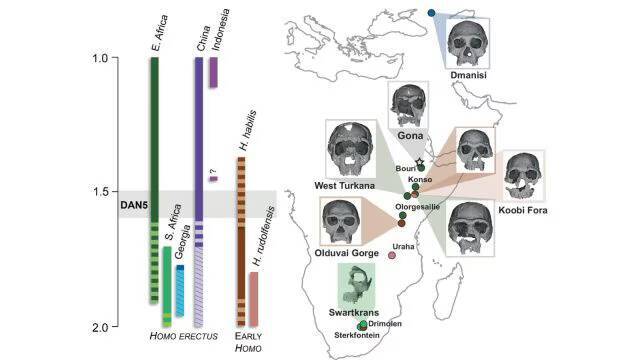
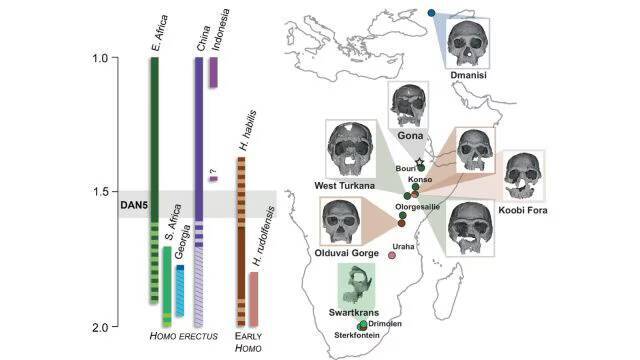
The study of human evolution has always been a fascinating field, with new discoveries constantly shedding light on our ancient ancestors. A recent study has revealed that some ancient humans had more ‘primitive’ faces, challenging our previous understanding of human evolution. The discovery was made possible by the reconstruction of a 1.5-1.6 million-year-old Homo erectus skull, known as DAN5.
The reconstruction of the DAN5 skull was a significant undertaking, requiring the use of advanced technologies such as micro-CT modeling. This technique allowed researchers to create a detailed and accurate model of the skull, revealing its unique characteristics. According to Dr. Baab, one of the researchers involved in the study, “The face is more archaic than we anticipated.” The skull’s facial traits were found to be more primitive than expected, with a flat nasal bridge and large molars.
The discovery of the DAN5 skull has significant implications for our understanding of human evolution. The skull’s primitive facial features suggest that some ancient humans may have retained more ancestral characteristics than previously thought. As Yousuke Kaifu, another researcher involved in the study, noted, “Seeing such a primitive face on a fossil this young was surprising.” The fact that the skull is relatively young, dating back to 1.5-1.6 million years ago, makes the discovery even more significant.
The study of the DAN5 skull has also provided valuable insights into the evolution of the human brain. The skull’s small braincase, paired with its primitive facial features, suggests that the development of the human brain may have occurred at a slower pace than previously thought. This challenges the traditional view of human evolution, which suggests that the development of the human brain was a rapid and dramatic process.
The discovery of the DAN5 skull is also significant because it highlights the diversity of human evolution. The fact that some ancient humans had more primitive faces suggests that there may have been multiple paths to modern human evolution. This challenges the traditional view of human evolution, which suggests that there was a single, linear path to modern humans.
The study of human evolution is a complex and multifaceted field, with many different factors at play. The discovery of the DAN5 skull is a significant addition to our understanding of human evolution, and highlights the importance of continued research and discovery in this field. As our understanding of human evolution continues to grow and evolve, we may uncover even more surprising and significant discoveries.
In conclusion, the reconstruction of the 1.5-1.6 million-year-old Homo erectus skull DAN5 has revealed that some ancient humans had more ‘primitive’ faces. The skull’s primitive facial traits, including a flat nasal bridge and large molars, suggest that some ancient humans may have retained more ancestral characteristics than previously thought. The discovery of the DAN5 skull has significant implications for our understanding of human evolution, and highlights the diversity and complexity of the human evolutionary process.
The study of human evolution is an ongoing and dynamic field, with new discoveries constantly shedding light on our ancient ancestors. The discovery of the DAN5 skull is a significant addition to this field, and highlights the importance of continued research and discovery. As we continue to explore and learn more about human evolution, we may uncover even more surprising and significant discoveries.
The discovery of the DAN5 skull is also a testament to the power of advanced technologies such as micro-CT modeling. These technologies have allowed researchers to create detailed and accurate models of ancient skulls, revealing their unique characteristics and providing valuable insights into human evolution.
In the end, the study of human evolution is a fascinating and complex field, with many different factors at play. The discovery of the DAN5 skull is a significant addition to this field, and highlights the importance of continued research and discovery. As we continue to explore and learn more about human evolution, we may uncover even more surprising and significant discoveries.