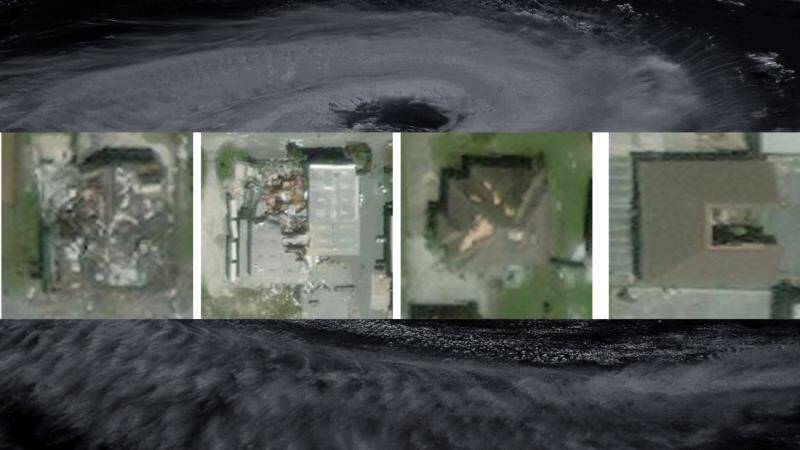
IIT Bombay’s AI speeds up hurricane damage assessment
Hurricanes are one of the most destructive natural disasters, causing widespread damage and loss of life. The aftermath of a hurricane is a critical period, where quick and accurate assessment of the damage is essential for effective disaster response and relief efforts. However, traditional methods of damage assessment can be time-consuming, labor-intensive, and often inaccurate. To address this challenge, researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Bombay have developed an innovative AI model called SpADANet, which can quickly and accurately identify building damage from aerial images.
SpADANet is a spatially aware AI model that uses deep learning techniques to analyze aerial images and identify damaged buildings. The model is designed to overcome the “domain gap” problem, which refers to the difference in appearance between images taken during different storms. This allows SpADANet to adapt to different storms with minimal data, making it a highly versatile and effective tool for damage assessment.
One of the key features of SpADANet is its ability to use spatial context to improve its accuracy. The model takes into account the spatial relationships between different objects in the image, such as buildings, roads, and vegetation, to better understand the extent of the damage. This approach enables SpADANet to outperform existing methods, which often rely on simple image classification techniques.
Another significant advantage of SpADANet is its optimization for mobile devices. This means that the model can be deployed on smartphones and other mobile devices, allowing damage assessment to be conducted quickly and efficiently in the field. This is particularly important in disaster response situations, where access to desktop computers or other specialized equipment may be limited.
The development of SpADANet has significant implications for disaster response and relief efforts. By providing quick and accurate damage assessments, SpADANet can help emergency responders to prioritize their efforts, allocate resources more effectively, and ultimately save lives. The model can also be used to identify areas that are most in need of assistance, allowing aid to be targeted more effectively.
The potential applications of SpADANet extend beyond hurricane damage assessment. The model can be used to assess damage from other types of natural disasters, such as earthquakes, floods, and wildfires. It can also be used in other fields, such as urban planning and infrastructure management, where accurate assessments of building damage are essential.
The researchers at IIT Bombay who developed SpADANet are excited about the potential of their model to make a positive impact on disaster response and relief efforts. “Our goal is to provide a tool that can help emergency responders to quickly and accurately assess damage, so that they can respond more effectively to disasters,” said one of the researchers. “We believe that SpADANet has the potential to make a significant difference in this area, and we are eager to see it being used in real-world applications.”
In conclusion, the development of SpADANet by IIT Bombay researchers is a significant breakthrough in the field of disaster response and relief efforts. The model’s ability to quickly and accurately identify building damage from aerial images, using spatial context and deep learning techniques, makes it a powerful tool for damage assessment. Its optimization for mobile devices and ability to adapt to different storms with minimal data make it a highly versatile and effective tool for disaster response. As the world becomes increasingly vulnerable to natural disasters, the development of innovative technologies like SpADANet is crucial for saving lives and reducing the impact of disasters.
The use of AI and machine learning in disaster response and relief efforts is a rapidly growing field, with many researchers and organizations exploring new technologies and approaches. The development of SpADANet is an important contribution to this field, and it has the potential to make a significant impact on the way that disaster response and relief efforts are conducted.
As the frequency and severity of natural disasters continue to increase, the need for effective and efficient damage assessment tools is becoming more pressing. SpADANet is an important step towards addressing this need, and it has the potential to save lives and reduce the impact of disasters. The researchers at IIT Bombay who developed SpADANet are to be commended for their innovative work, and their contribution to the field of disaster response and relief efforts.
In the future, it is likely that we will see even more innovative technologies being developed to support disaster response and relief efforts. The use of AI, machine learning, and other advanced technologies will continue to play an increasingly important role in this field, and it is exciting to think about the potential applications and benefits that these technologies may bring.
For now, the development of SpADANet is an important milestone in the development of more effective and efficient damage assessment tools. It has the potential to make a significant impact on disaster response and relief efforts, and it is an important contribution to the field of disaster response and relief efforts.
News Source: https://researchmatters.in/news/novel-spatially-aware-ai-model-makes-hurricane-damage-assessment-more-accurate