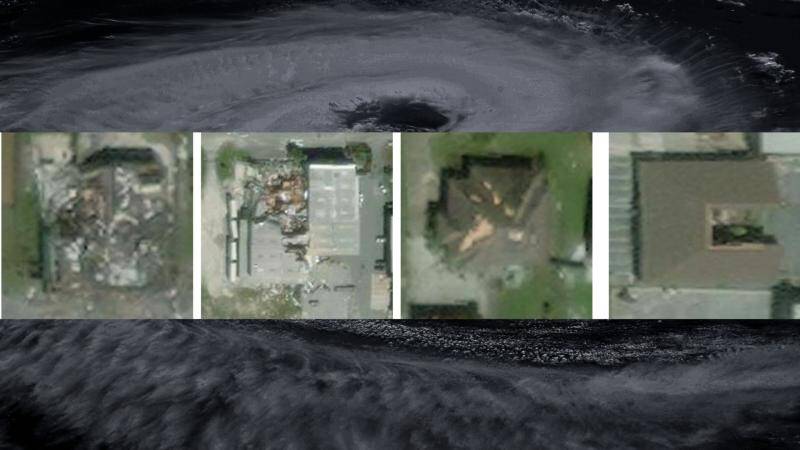
IIT Bombay’s AI speeds up hurricane damage assessment
Hurricanes are one of the most destructive natural disasters, causing widespread damage to infrastructure, properties, and human life. The aftermath of a hurricane is a critical period where timely assessment and response are crucial to mitigate the effects of the disaster. However, assessing the extent of damage caused by a hurricane is a challenging task, especially in areas with limited access. Traditionally, damage assessment is done through manual surveys, which are time-consuming, labor-intensive, and often inaccurate. With the advent of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), researchers have been exploring ways to leverage these technologies to improve the efficiency and accuracy of damage assessment.
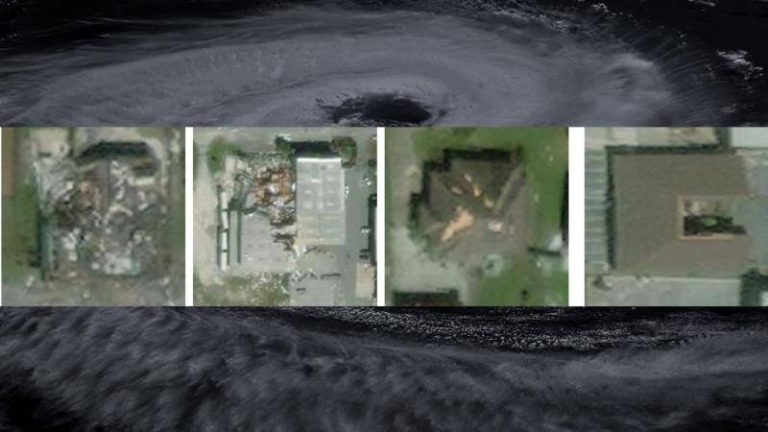
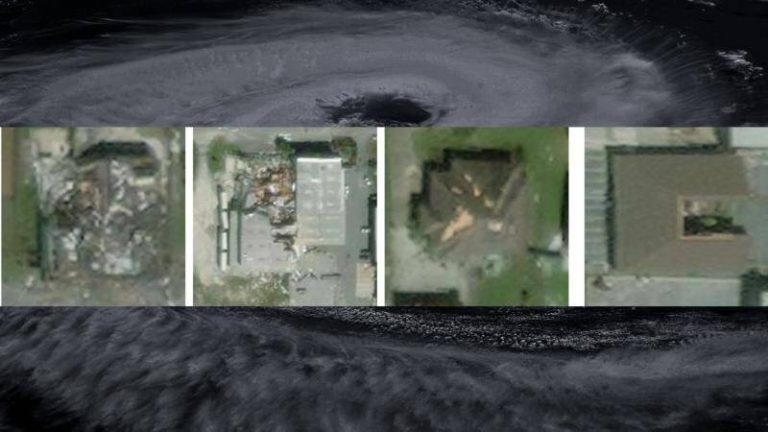
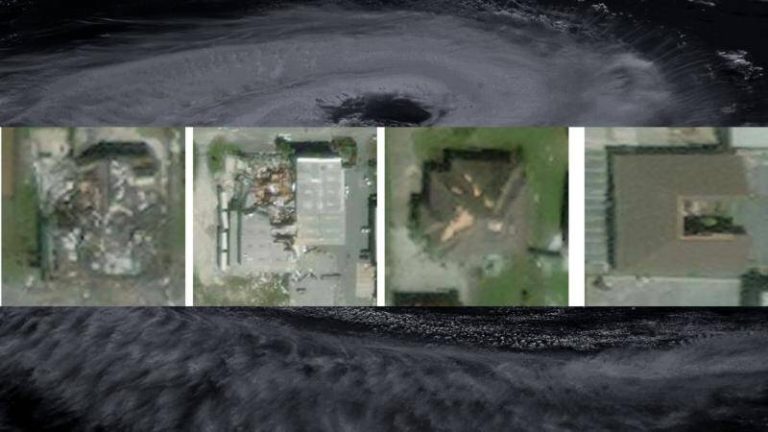
Recently, researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Bombay have developed an AI model called SpADANet, which can identify building damage from aerial images. This innovative tool has the potential to revolutionize the way damage assessment is done, making it faster, more accurate, and more efficient. In this blog post, we will delve into the details of SpADANet, its features, and its potential impact on disaster response and relief efforts.
The Challenge of Domain Gap
One of the significant challenges in developing AI models for damage assessment is the “domain gap.” The domain gap refers to the difference in characteristics between the training data and the real-world data. In the context of damage assessment, the domain gap arises because the aerial images of different storms have distinct characteristics, such as varying lighting conditions, angles, and resolutions. This makes it challenging to develop an AI model that can adapt to different storms with minimal data.
SpADANet overcomes this challenge by using a novel approach that takes into account the spatial context of the aerial images. The model is designed to learn the spatial relationships between different objects in the image, such as buildings, roads, and trees. This allows SpADANet to adapt to different storms with minimal data, making it a more robust and reliable tool for damage assessment.
Optimized for Mobile Devices
Another significant feature of SpADANet is that it is optimized for mobile devices. This means that the model can be deployed on mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, making it more accessible and user-friendly. The optimized version of SpADANet can process aerial images in real-time, providing quick and accurate damage assessments.
The optimization of SpADANet for mobile devices is crucial for disaster response and relief efforts. In the aftermath of a hurricane, access to affected areas may be limited, and communication infrastructure may be disrupted. Mobile devices can provide a reliable means of communication and data collection, enabling responders to quickly assess the damage and prioritize their efforts.
Outperforming Existing Methods
SpADANet has been tested on various datasets and has outperformed existing methods for damage assessment. The model’s ability to learn spatial relationships between objects and adapt to different storms with minimal data makes it a more accurate and reliable tool. The results of the tests demonstrate that SpADANet can identify building damage with high accuracy, even in areas with complex infrastructure and varying environmental conditions.
The outperformance of SpADANet over existing methods is significant, as it highlights the potential of AI and ML in improving damage assessment. The use of SpADANet can reduce the time and resources required for damage assessment, enabling responders to focus on relief efforts and mitigate the effects of the disaster.
Real-Time Disaster Response and Relief Efforts
The development of SpADANet has significant implications for real-time disaster response and relief efforts. The model’s ability to provide quick and accurate damage assessments can help responders prioritize their efforts, allocate resources more effectively, and save lives.
In the aftermath of a hurricane, every minute counts. The use of SpADANet can provide responders with critical information about the extent of damage, enabling them to make informed decisions about relief efforts. The model can also help identify areas that are most in need of assistance, ensuring that resources are allocated effectively.
Global Impact
The impact of SpADANet is not limited to India or any specific region. The model has the potential to be used globally, in any area affected by hurricanes or other natural disasters. The use of SpADANet can improve disaster response and relief efforts worldwide, saving lives and reducing the economic impact of disasters.
The development of SpADANet is a testament to the power of AI and ML in improving disaster response and relief efforts. The model’s ability to adapt to different storms with minimal data, optimize for mobile devices, and outperform existing methods makes it a valuable tool for responders and relief organizations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the development of SpADANet by IIT Bombay researchers is a significant breakthrough in the field of disaster response and relief efforts. The model’s ability to identify building damage from aerial images, adapt to different storms with minimal data, and optimize for mobile devices makes it a powerful tool for responders. The use of SpADANet can improve the efficiency and accuracy of damage assessment, enabling responders to prioritize their efforts, allocate resources more effectively, and save lives.
As the world becomes increasingly vulnerable to natural disasters, the development of innovative tools like SpADANet is crucial. The model has the potential to be used globally, improving disaster response and relief efforts worldwide. We look forward to seeing the impact of SpADANet in the years to come and exploring its potential applications in other areas of disaster response and relief efforts.
News Source: https://researchmatters.in/news/novel-spatially-aware-ai-model-makes-hurricane-damage-assessment-more-accurate