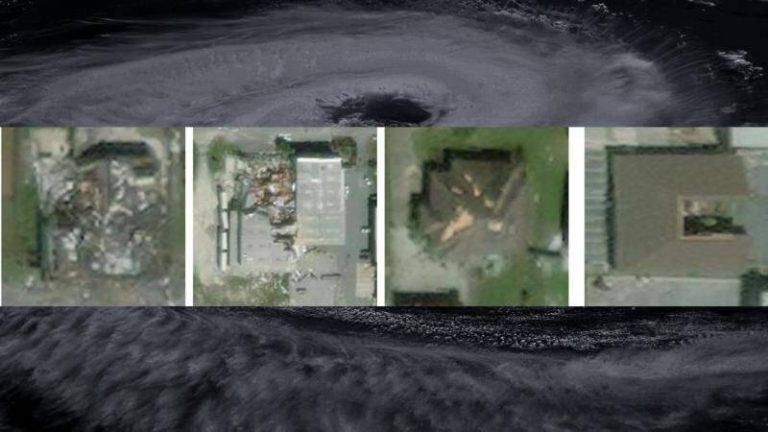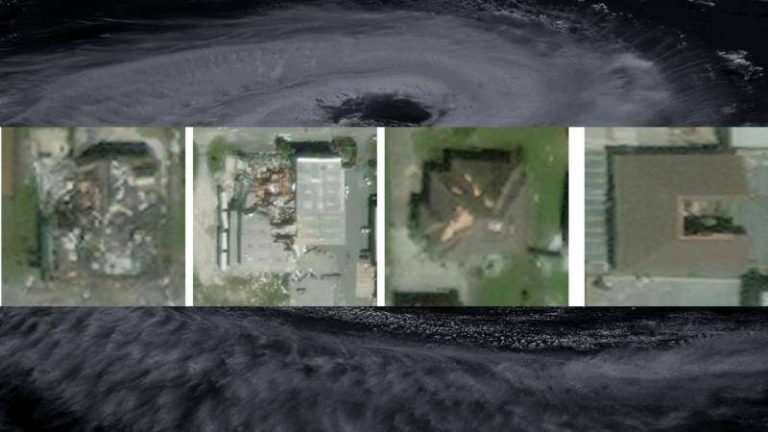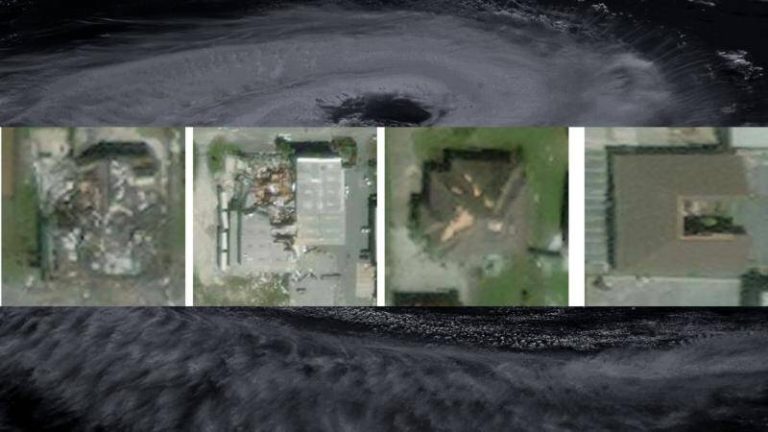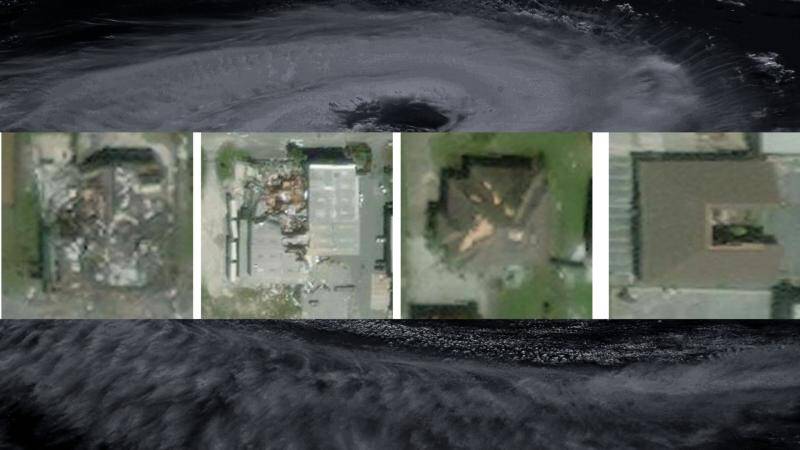
IIT Bombay’s AI speeds up hurricane damage assessment
Hurricanes are one of the most destructive natural disasters, causing widespread damage to infrastructure, properties, and human lives. The aftermath of a hurricane is a critical period where rapid assessment of damage is essential for effective disaster response and relief efforts. However, traditional methods of damage assessment can be time-consuming, labor-intensive, and often inaccurate. To address this challenge, researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Bombay have developed an innovative artificial intelligence (AI) model called SpADANet, which can quickly and accurately identify building damage from aerial images.
The SpADANet model is a significant breakthrough in the field of disaster response and relief, as it overcomes the “domain gap” that has limited the effectiveness of existing AI models. The domain gap refers to the difference in characteristics between the training data and the actual data collected during a disaster. This gap can lead to inaccurate results, as the AI model may not be able to adapt to the unique conditions of a specific storm. SpADANet, on the other hand, can adapt to different storms with minimal data, making it a highly versatile and effective tool for damage assessment.
One of the key features of SpADANet is its ability to use spatial context to identify building damage. The model takes into account the spatial relationships between different objects in an image, such as buildings, roads, and vegetation, to determine the extent of damage. This approach allows SpADANet to outperform existing methods, which often rely on individual image features rather than spatial context. The model is also optimized for mobile devices, making it accessible to a wide range of users, including disaster response teams and relief workers.
The development of SpADANet has significant implications for real-time disaster response and relief efforts globally. By providing rapid and accurate damage assessments, SpADANet can help emergency responders to prioritize their efforts, allocate resources more effectively, and ultimately save lives. The model can also be used to identify areas that are most in need of assistance, allowing relief workers to target their efforts more efficiently.
The potential applications of SpADANet extend beyond hurricane damage assessment. The model can be used to assess damage from other types of natural disasters, such as earthquakes, floods, and wildfires. It can also be used to monitor infrastructure conditions, such as road damage and bridge integrity, allowing for more effective maintenance and repair.
The researchers at IIT Bombay who developed SpADANet are part of a growing community of scientists and engineers who are using AI and machine learning to address some of the world’s most pressing challenges. Their work demonstrates the potential of AI to drive innovation and improve outcomes in a wide range of fields, from disaster response and relief to healthcare and education.
In conclusion, the SpADANet model developed by IIT Bombay researchers is a significant breakthrough in the field of disaster response and relief. By providing rapid and accurate damage assessments, SpADANet can help to improve real-time disaster response and relief efforts globally. Its ability to adapt to different storms with minimal data and its use of spatial context to identify building damage make it a highly effective tool for damage assessment. As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of natural disasters, the development of innovative AI models like SpADANet offers new hope for more effective and efficient disaster response and relief efforts.
The development of SpADANet is a testament to the power of innovation and collaboration in addressing some of the world’s most pressing challenges. As researchers and scientists continue to push the boundaries of what is possible with AI and machine learning, we can expect to see even more innovative solutions to real-world problems. The future of disaster response and relief is likely to be shaped by technologies like SpADANet, which have the potential to save lives, reduce damage, and improve outcomes for communities around the world.
For more information on this topic, please visit: https://researchmatters.in/news/novel-spatially-aware-ai-model-makes-hurricane-damage-assessment-more-accurate