How does a stage-gate model cut product-launch failures?
The excitement of launching a new product can be thrilling, but the reality is that many product launches fail to meet expectations. In fact, it’s estimated that up to 80% of new products fail to achieve their intended goals. One of the primary reasons for this high failure rate is the lack of a structured approach to product development. This is where the stage-gate model comes in – a proven methodology that helps organizations de-risk launches, speed up execution, and ensure only validated concepts reach the market.
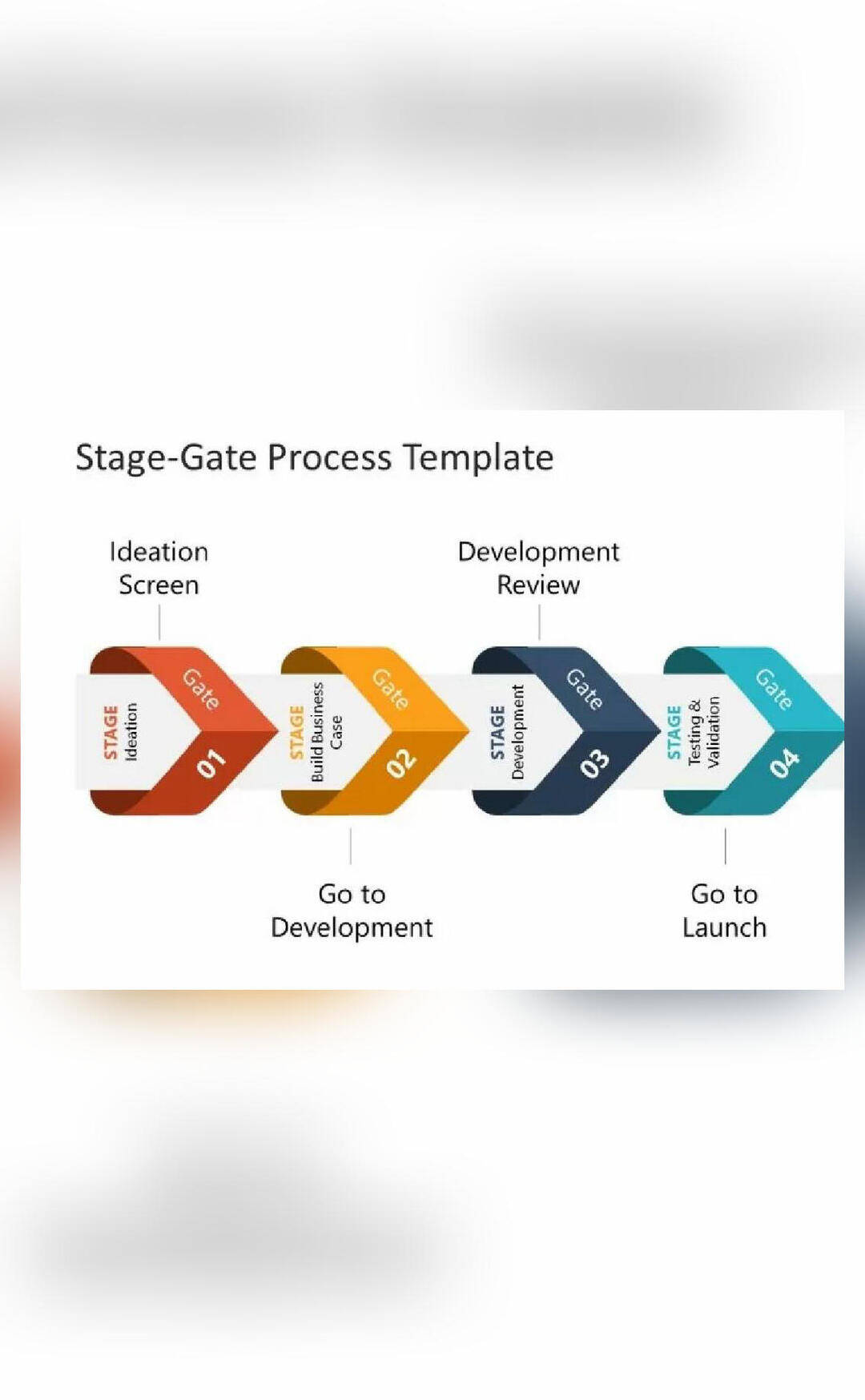
The stage-gate model is a phased approach to product development, where each phase is designed to build on the previous one, with a series of gates or checkpoints that ensure the project is on track and worthy of continued investment. The model typically consists of five stages: idea, scoping, feasibility, development, validation, and launch. Each stage has a specific set of activities, deliverables, and criteria for progression to the next stage.
Stage 1: Idea
The idea stage is where the product development process begins. This stage involves generating and capturing ideas, often through brainstorming sessions, customer feedback, or market research. The goal is to identify potential opportunities and concepts that align with the organization’s strategic objectives. During this stage, teams should focus on high-level ideas, without getting too bogged down in details.
Stage 2: Scoping
The scoping stage involves defining the project’s scope, objectives, and key performance indicators (KPIs). This stage helps to clarify the project’s goals, timelines, and resource requirements. Teams should develop a preliminary business case, including market size, competitive analysis, and financial projections. The scoping stage is critical in ensuring that the project is aligned with the organization’s overall strategy and that the team has a clear understanding of what needs to be achieved.
Stage 3: Feasibility
The feasibility stage is where the team conducts a thorough analysis of the project’s technical, financial, and operational feasibility. This stage involves assessing the project’s risks, evaluating alternative solutions, and identifying potential roadblocks. The goal is to determine whether the project is viable and whether it’s worth proceeding to the next stage. During this stage, teams should engage with stakeholders, including customers, suppliers, and partners, to validate assumptions and gather feedback.
Stage 4: Development
The development stage is where the product is designed, developed, and tested. This stage involves creating prototypes, conducting usability testing, and refining the product based on feedback. The goal is to create a product that meets the customer’s needs and expectations. During this stage, teams should focus on agile development methodologies, such as iterative and incremental development, to ensure that the product is developed quickly and efficiently.
Stage 5: Validation
The validation stage is where the product is tested with a larger audience, often through pilots or beta launches. This stage involves gathering feedback, assessing the product’s performance, and identifying areas for improvement. The goal is to validate the product’s assumptions and ensure that it meets the customer’s needs and expectations. During this stage, teams should engage with customers, gather feedback, and make any necessary adjustments to the product before launch.
Stage 6: Launch
The launch stage is where the product is released to the market. This stage involves executing the launch plan, including marketing, sales, and distribution. The goal is to create a successful launch that meets the organization’s objectives and delivers a strong return on investment. During this stage, teams should focus on executing the launch plan, monitoring progress, and making any necessary adjustments to ensure a successful launch.
The Benefits of the Stage-Gate Model
The stage-gate model offers several benefits, including:
- De-risking launches: By conducting thorough analysis and validation at each stage, organizations can de-risk launches and reduce the likelihood of product failure.
- Speeding up execution: The stage-gate model enables teams to work efficiently and effectively, with a clear understanding of what needs to be achieved at each stage.
- Ensuring validated concepts: The model ensures that only validated concepts reach the market, reducing the risk of launching a product that doesn’t meet customer needs.
- Aligning resources: The stage-gate model helps organizations align resources with strategic objectives, ensuring that the right people, skills, and budget are allocated to the project.
Conclusion
The stage-gate model is a proven methodology that helps organizations de-risk launches, speed up execution, and ensure only validated concepts reach the market. By dividing development into structured phases, each with a go/no-go review, teams can prevent over-investing in weak ideas and force early market checks, risk analysis, and resource alignment. Organizations that adopt the stage-gate model can reduce the risk of product failure, improve time-to-market, and increase the likelihood of launching successful products that meet customer needs and deliver a strong return on investment.
News Source: https://www.growthjockey.com/blogs/stage-gate-model






