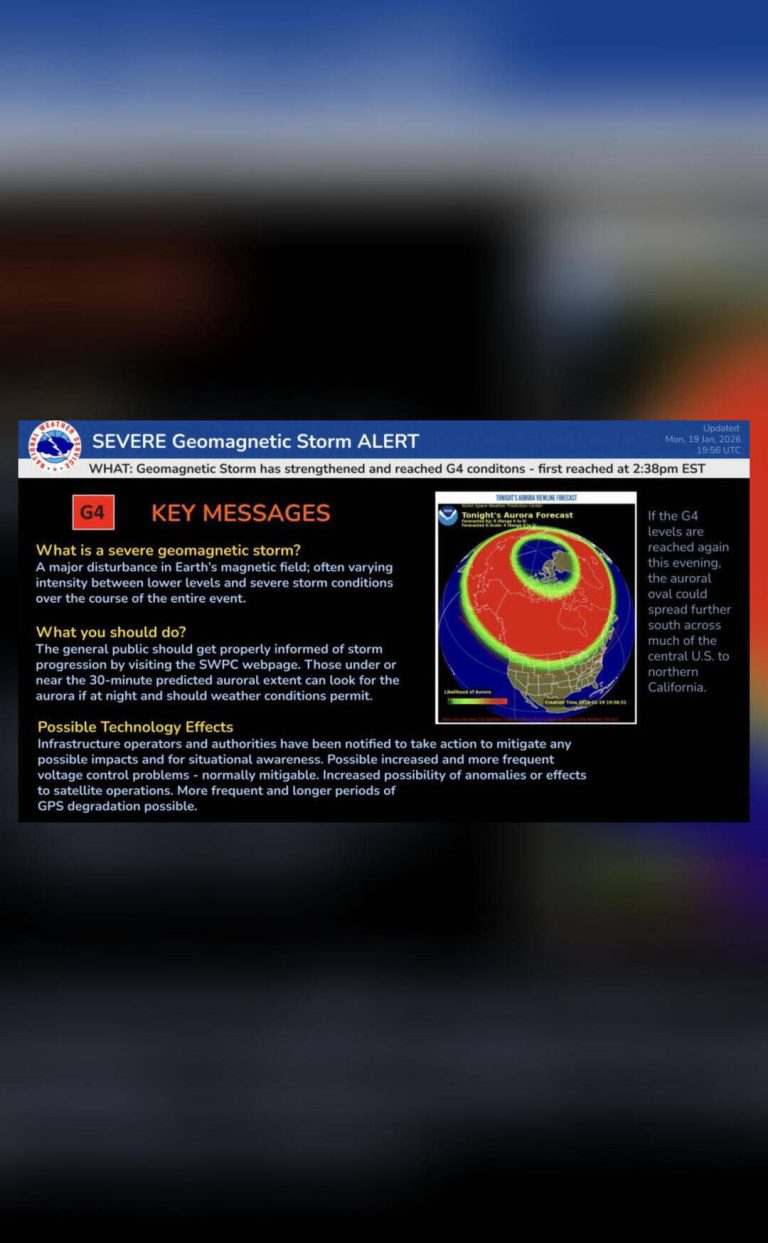
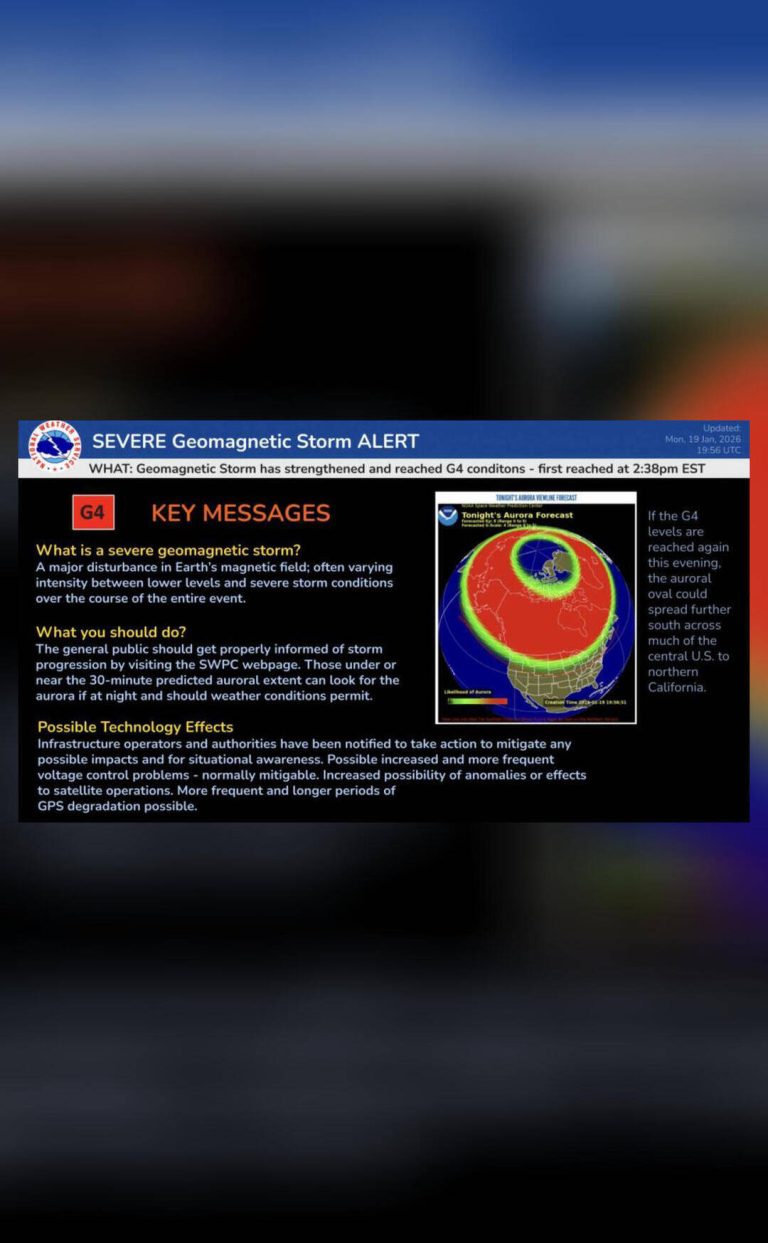
Comet C/2025 K1 (ATLAS) breaks into 3 after coming close to Sun
In a stunning celestial event, Comet C/2025 K1 (ATLAS) has broken into three pieces after swinging too close to the Sun. This rare phenomenon was captured by astronomers using Italy’s Copernicus telescope, providing a unique glimpse into the fragile nature of comets. The comet’s nucleus became unstable after it passed close to the Sun on October 8, resulting in a spectacular breakup that has left scientists and astronomy enthusiasts alike in awe.
Comet C/2025 K1 (ATLAS) was first discovered in May 2025 by the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) survey. Initially, it was thought to be a single, intact comet, but as it approached the Sun, its behavior became increasingly erratic. As the comet drew closer to the Sun, its ices began to vaporize, creating a bright tail of gas and dust that stretched millions of kilometers into space.
However, it was not until the comet made its closest approach to the Sun, known as perihelion, that the true extent of its instability became apparent. On October 8, Comet C/2025 K1 (ATLAS) passed within 1.2 astronomical units (AU) of the Sun, where 1 AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun. This close encounter caused the comet’s nucleus to break apart, resulting in three distinct pieces.
The two largest fragments, which are estimated to be around 1-2 kilometers in diameter, have drifted approximately 2,000 kilometers apart from each other. A smaller, third piece can be seen to the left of the pair, highlighting the violent nature of the comet’s breakup. The images captured by the Copernicus telescope provide a fascinating insight into the comet’s disintegration, with the two main fragments appearing as bright, diffuse blobs surrounded by a halo of gas and dust.
The breakup of Comet C/2025 K1 (ATLAS) is not an isolated event. Many comets have been known to fragment as they approach the Sun, with some even disintegrating completely. This is often due to the intense heat and radiation emitted by the Sun, which causes the comet’s ices to vaporize and its structure to become unstable. In some cases, the breakup of a comet can even lead to spectacular meteor showers, as the resulting fragments burn up in the Earth’s atmosphere.
The study of comets like C/2025 K1 (ATLAS) provides valuable insights into the formation and evolution of our solar system. Comets are thought to be remnants from the early days of the solar system, when the planets were still forming and the Sun was much more active. By studying the composition and behavior of comets, scientists can gain a better understanding of the conditions that existed during this period and how they may have influenced the development of our planet.
In addition to their scientific significance, comets have also played an important role in human culture and history. Many ancient civilizations believed that comets were omens or signs from the gods, and their appearance was often seen as a harbinger of change or disaster. Today, comets continue to captivate our imagination, inspiring new generations of astronomers and space enthusiasts.
The breakup of Comet C/2025 K1 (ATLAS) is a reminder of the dynamic and unpredictable nature of our universe. As we continue to explore and study the cosmos, we are constantly reminded of the awe-inspiring beauty and complexity of the stars and planets that surround us. Whether you are a professional astronomer or simply someone who appreciates the beauty of the night sky, the sight of a comet breaking apart is a truly unforgettable experience.
In conclusion, the breakup of Comet C/2025 K1 (ATLAS) is a significant event that highlights the fragile nature of comets and the intense forces that shape our solar system. As we continue to study and explore the universe, we may uncover even more secrets about the formation and evolution of our cosmos. For now, the stunning images of Comet C/2025 K1 (ATLAS) will remain a reminder of the beauty and wonder that awaits us in the vast expanse of space.