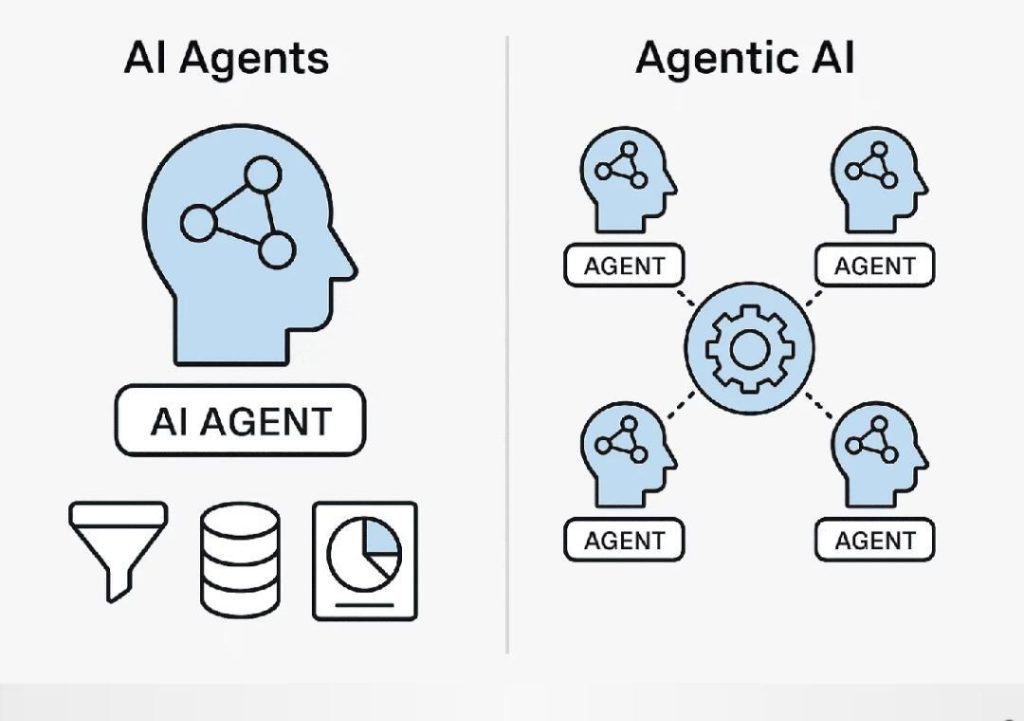
Agentic AI vs AI Agents: What’s the Difference?
In the realm of artificial intelligence (AI), the terms “agentic AI” and “AI agents” are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings. Understanding the difference between these two concepts is crucial for designing and developing autonomous systems that can operate efficiently and reliably.
In this blog post, we will delve into the world of AI agents and agentic AI, exploring their definitions, characteristics, and applications. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of what sets these two concepts apart and how to choose the right architecture for your AI project.
What is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is a program that acts on behalf of a user or organization to achieve a specific goal. AI agents can be thought of as software robots that perform tasks, make decisions, and interact with users or other systems. They are designed to follow predefined rules, protocols, and guidelines set by their developers.
Chatbots are a classic example of AI agents. They are programmed to respond to user queries, provide information, and perform simple tasks like booking appointments or sending notifications. AI agents can also be used in applications such as customer service, data processing, and research.
Characteristics of AI Agents:
- Rule-based: AI agents operate based on predefined rules, protocols, and guidelines.
- Deterministic: AI agents make decisions based on predefined conditions and outcomes.
- Limited autonomy: AI agents require constant oversight and control from their developers or users.
- Focused on a specific task: AI agents are designed to perform a specific task or set of tasks.
What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI, on the other hand, is a type of AI that is self-directed and capable of setting its own goals, planning its actions, and adapting to new situations without constant oversight. Agentic AI is designed to operate autonomously, making decisions and taking actions based on its own understanding of the environment and its goals.
Autonomous legal researchers and document processors with feedback loops are examples of agentic AI. These systems can analyze large amounts of data, identify patterns, and draw conclusions without human intervention. Agentic AI can also be used in applications such as decision-making, planning, and problem-solving.
Characteristics of Agentic AI:
- Self-directed: Agentic AI sets its own goals and plans its actions.
- Adaptive: Agentic AI can adapt to new situations and learn from its experiences.
- Autonomous: Agentic AI operates independently, without constant oversight.
- Focused on achieving goals: Agentic AI is designed to achieve specific goals and objectives.
Key Differences:
The key differences between AI agents and agentic AI are:
- Autonomy: AI agents require constant oversight, while agentic AI operates autonomously.
- Decision-making: AI agents make decisions based on predefined rules, while agentic AI makes decisions based on its own understanding of the environment and its goals.
- Adaptability: AI agents are limited in their ability to adapt to new situations, while agentic AI can adapt and learn from its experiences.
Choosing the Right Architecture:
When designing and developing AI systems, it is essential to choose the right architecture based on the specific requirements of the application. Here are some guidelines to help you choose between AI agents and agentic AI:
- AI agents: Use AI agents when you need a system that follows predefined rules and protocols, such as chatbots or customer service applications.
- Agentic AI: Use agentic AI when you need a system that can operate autonomously, set its own goals, and adapt to new situations, such as decision-making or problem-solving applications.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, AI agents and agentic AI are two distinct concepts in the field of artificial intelligence. AI agents are programmed to follow predefined rules and operate under constant oversight, while agentic AI is self-directed and capable of setting its own goals and adapting to new situations.
Understanding the difference between these two concepts is crucial for designing and developing autonomous systems that can operate efficiently and reliably. By choosing the right architecture for your AI project, you can ensure that your system meets the specific requirements of your application.
Source:






