Are More Young People Getting Type 2 Diabetes?
In recent years, there has been a growing concern about the rising incidence of type 2 diabetes among young people. According to recent reports, the number of individuals under the age of 40 being diagnosed with type 2 diabetes is increasing at an alarming rate. This trend is not only worrying but also raises serious questions about the future health of our younger generation.
Type 2 diabetes, once considered a disease of older adults, is now affecting people of all ages, including children and young adults. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that over 422 million people worldwide have diabetes, and this number is expected to rise to 643 million by 2030. The alarming rate at which this disease is spreading is largely attributed to the growing prevalence of obesity, physical inactivity, and unhealthy diets.
The Rise of Early-Onset Diabetes
In the past, type 2 diabetes was typically associated with older adults, often over the age of 40. However, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that the number of people under 40 being diagnosed with type 2 diabetes has increased significantly over the past decade. In the United States alone, the prevalence of youth-onset diabetes has risen by 21% between 2002 and 2012.
The rising incidence of early-onset diabetes is not limited to developed countries. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism found that the prevalence of type 2 diabetes in young people aged 10-19 increased by 46% between 2001 and 2013 in the United Kingdom.
Why is Early-Onset Diabetes a Concern?
Early-onset diabetes can have serious consequences for young people, increasing their risk of developing complications such as:
- Cardiovascular disease: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease.
- Kidney damage: Diabetes can cause kidney damage, leading to kidney failure and the need for dialysis or transplantation.
- Nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can damage nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet.
- Blindness: Diabetes can cause vision loss and blindness if left untreated or poorly managed.
Early-onset diabetes also increases the risk of developing other health problems, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and depression.
The Causes of Early-Onset Diabetes
The rising incidence of early-onset diabetes is largely attributed to lifestyle factors, including:
- Poor diet: Consuming high amounts of sugar, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Low physical activity: A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to weight gain and insulin resistance, increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Weight gain: Excessive weight gain, particularly around the midsection, can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Genetic factors: Having a family history of type 2 diabetes can increase an individual’s risk of developing the disease.
What Can Be Done to Prevent Early-Onset Diabetes?
Preventing early-onset diabetes requires a combination of healthy lifestyle habits and regular health check-ups. The following steps can help reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Engage in regular physical activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week.
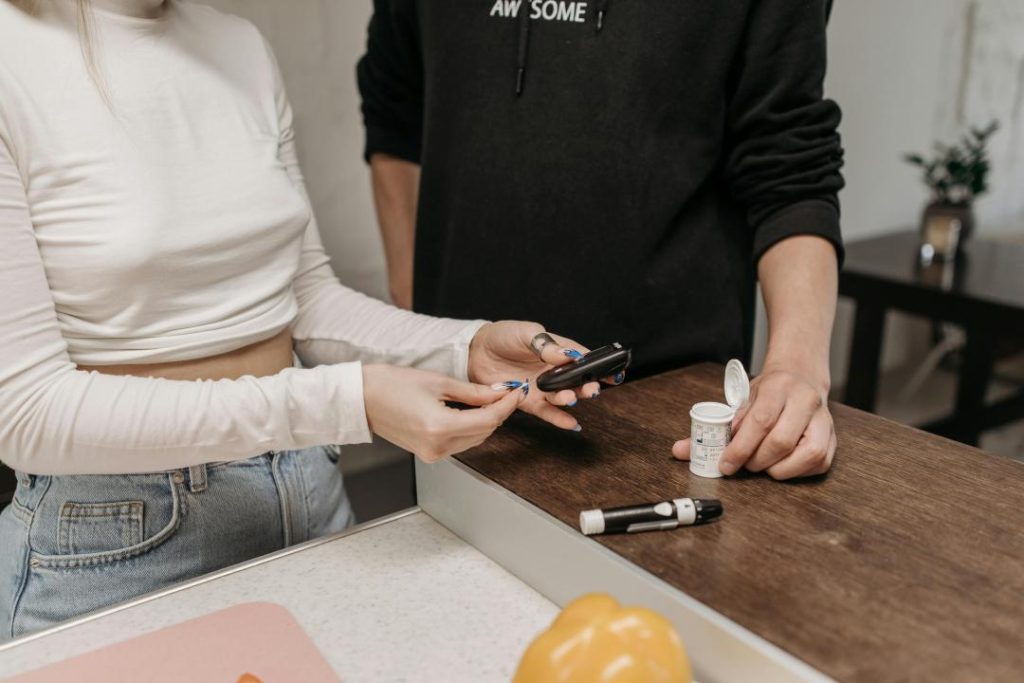
- Monitor blood sugar levels: Regularly monitor blood sugar levels to detect any abnormalities early on.
- Get regular health check-ups: Visit your healthcare provider regularly to monitor your health and catch any potential health problems early.
Conclusion
Early-onset diabetes is a growing concern, and it is essential that we take steps to prevent this disease from affecting our younger generation. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits and staying informed about the risks and consequences of type 2 diabetes, we can help reduce the incidence of this disease and promote overall health and well-being.
News Source:
https://thepfc.club/blogs/news/why-early-onset-type-2-diabetes-needs-special-attention