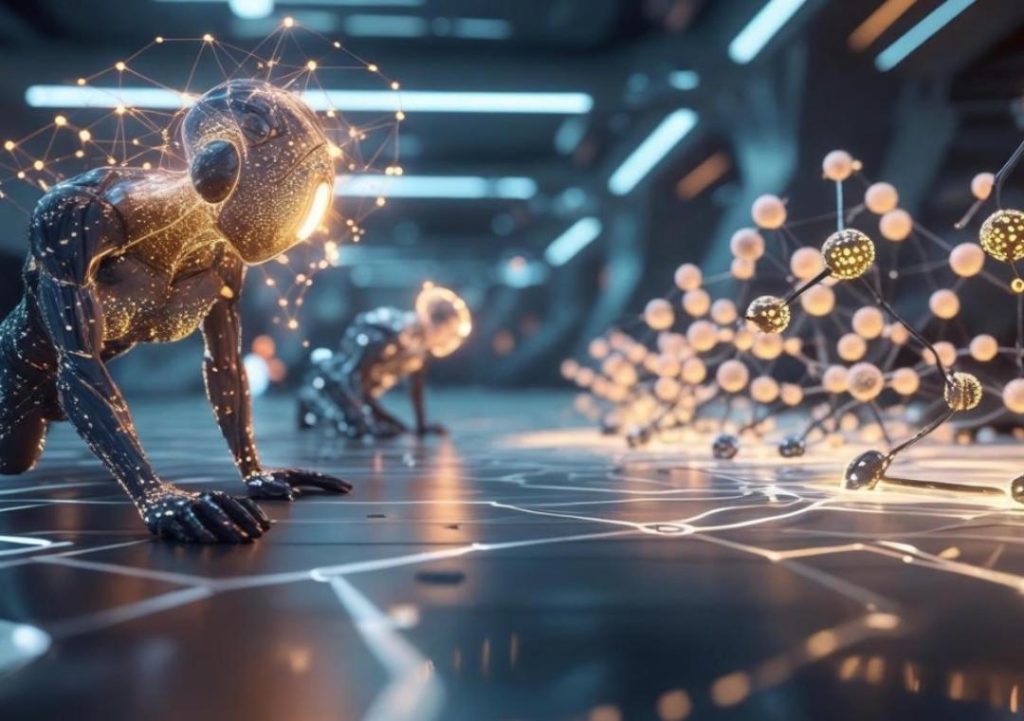
From Solo Intelligence to Swarm Thinking: MAS Gains Momentum
In a world where artificial intelligence (AI) has become the norm, we’ve grown accustomed to the idea of solo algorithms working independently to solve complex problems. However, the AI landscape is undergoing a significant shift towards more collaborative and dynamic approaches. Enter Multi-Agent Systems (MAS), where multiple bots learn and adapt through interaction, mimicking real-world social dynamics.
Imagine a fleet of delivery drones optimising their routes in real-time, working together to ensure the most efficient delivery possible. Envision financial agents dynamically trading with each other, adapting to market fluctuations and making collective decisions in sync. This is the power of MAS, and it’s gaining momentum rapidly.
The Rise of Multi-Agent Systems
In traditional AI, a single algorithm or agent is designed to perform a specific task. While this approach has been successful in many areas, it has its limitations. For instance, a single agent may not be able to adapt to changing environments or respond to unexpected events in real-time.
MAS, on the other hand, brings a new level of intelligence and resilience to the table. By incorporating multiple agents that interact and collaborate with each other, MAS can tackle complex problems that would be impossible for a single agent to solve.
Real-World Applications of MAS
The potential applications of MAS are vast and varied. Here are a few examples:
- Autonomous Transportation: Imagine a fleet of self-driving cars, trucks, and drones working together to navigate complex traffic scenarios. MAS could enable them to communicate and adapt to changing conditions in real-time, reducing congestion and improving safety.
- Financial Markets: MAS could be used to create dynamic trading systems, where multiple agents adapt to market fluctuations and make collective decisions in sync. This could lead to more efficient and stable financial markets.
- Healthcare: In healthcare, MAS could be used to coordinate patient care, where multiple agents work together to develop personalized treatment plans and respond to changing patient conditions.
- Environmental Monitoring: MAS could be used to monitor and respond to environmental changes, such as tracking wildlife populations, monitoring water quality, and predicting natural disasters.
Benefits of MAS
So, what are the benefits of MAS over traditional AI approaches?
- Resilience: MAS can adapt to changing environments and respond to unexpected events in real-time, making it more resilient than traditional AI.
- Flexibility: MAS can be applied to a wide range of domains and scenarios, making it a highly flexible approach.
- Real-time Responsiveness: MAS can respond to changing conditions in real-time, making it ideal for applications where speed and agility are critical.
- Scalability: MAS can be easily scaled up or down depending on the requirements of the application, making it a highly scalable approach.
Challenges and Limitations
While MAS holds tremendous promise, there are still challenges and limitations to overcome:
- Complexity: MAS can be complex to design and implement, requiring significant expertise and resources.
- Communication: Agents in a MAS must be able to communicate effectively with each other, which can be a challenge in complex or distributed systems.
- Trust: In a MAS, agents must be able to trust each other to work collaboratively, which can be a challenge in environments where trust is low.
Conclusion
As we move forward in the world of AI, it’s clear that MAS is gaining momentum. By mimicking real-world social dynamics and allowing multiple agents to learn and adapt through interaction, MAS brings a new level of intelligence and resilience to the table. Whether it’s optimizing delivery routes, dynamically trading in financial markets, or responding to environmental changes, MAS has the potential to revolutionize many areas of our lives.
Source:
https://www.growthjockey.com/blogs/multi-agent-systems