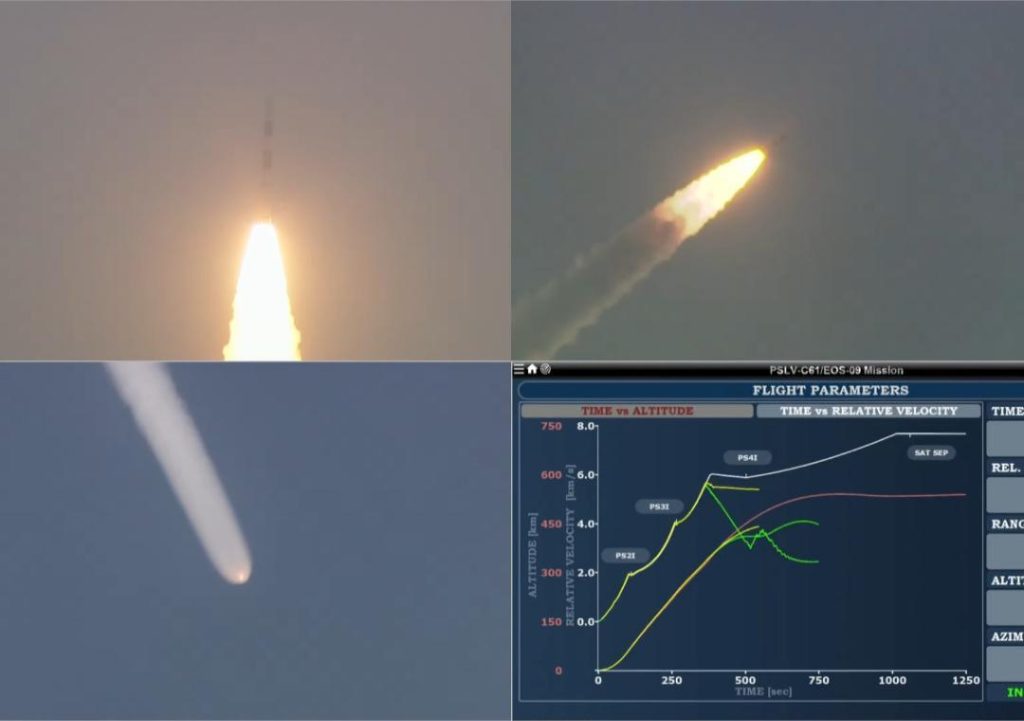
ISRO’s 1,696-kg Earth-Observation Satellite Mission Fails Minutes After Launch
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has suffered a setback with the failure of its PSLV-C61/EOS-09 satellite mission just minutes after launch. The satellite, designed to provide high-quality earth observation services, was launched from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota at 5:59 am on [Date]. However, despite the successful launch, the mission unfortunately ended in disappointment as the satellite could not be deployed as planned.
According to ISRO, the problem arose in the third stage of the launch vehicle, which resulted in the failure of the mission. The 1,696-kg earth-observation satellite, EOS-09, was designed to provide high-resolution imagery of the Earth’s surface, even through clouds and darkness. Its failure means that India will not be able to utilize its capabilities, which were intended to support various applications such as disaster management, urban planning, and environmental monitoring.
The PSLV-C61/EOS-09 mission was a significant one for ISRO, as it marked the organization’s 54th launch of the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV). The PSLV is a reliable and versatile launch vehicle that has successfully launched numerous satellites into orbit over the years. However, this mission’s failure is a setback for ISRO, which had high hopes for the EOS-09 satellite.
The EOS-09 satellite was designed to operate in the visible, near-infrared, and short-wave infrared spectral bands, allowing it to capture high-quality images of the Earth’s surface. Its advanced sensors were capable of detecting changes in land cover, monitoring atmospheric conditions, and providing critical data for various applications.
ISRO’s failure to deploy the EOS-09 satellite may have significant implications for various industries and users who were expecting to utilize its services. The satellite was intended to provide critical data for disaster management, urban planning, and environmental monitoring, among other applications. Its failure means that these users will have to rely on other sources of data, which may not be as high-quality or reliable.
Despite the setback, ISRO remains committed to its mission of advancing India’s space program and providing critical services to the nation. The organization has a robust launch schedule, with several missions planned for the coming months. ISRO’s next major mission is the Chandrayaan-3, which is scheduled to launch in [Date]. The Chandrayaan-3 mission aims to soft-land a rover on the lunar surface, marking India’s maiden attempt to achieve a soft landing on the Moon.
ISRO’s failure to deploy the EOS-09 satellite is a reminder of the challenges and risks involved in space exploration. Despite advances in technology and launch vehicles, failures can and do occur. However, ISRO’s commitment to learning from its mistakes and improving its capabilities is evident in its continued investment in research and development.
In conclusion, ISRO’s failure to deploy the EOS-09 satellite is a setback for the organization and its users. However, it is also an opportunity for ISRO to learn from its mistakes and improve its capabilities. As India continues to advance its space program, it is essential to remember that failures are an essential part of the learning process. With its commitment to innovation and excellence, ISRO is likely to bounce back from this setback and continue to make significant contributions to India’s space program.
Source:
https://www.isro.gov.in/Mission_PSLV_C61_EOS_09.html






