Gold & Platinum Created through Neutron Stars’ Explosions: Study
For centuries, humans have been fascinated by the origins of precious metals like gold and platinum. While we have long known that these metals are formed through natural processes, the exact mechanisms behind their creation have remained a mystery. However, a recent study led by Columbia University student Anirudh Patel has shed new light on the origins of these valuable elements. According to the study, magnetars – highly magnetized neutron stars – played a crucial role in creating gold and platinum through a cosmic event that occurred over 20 years ago.
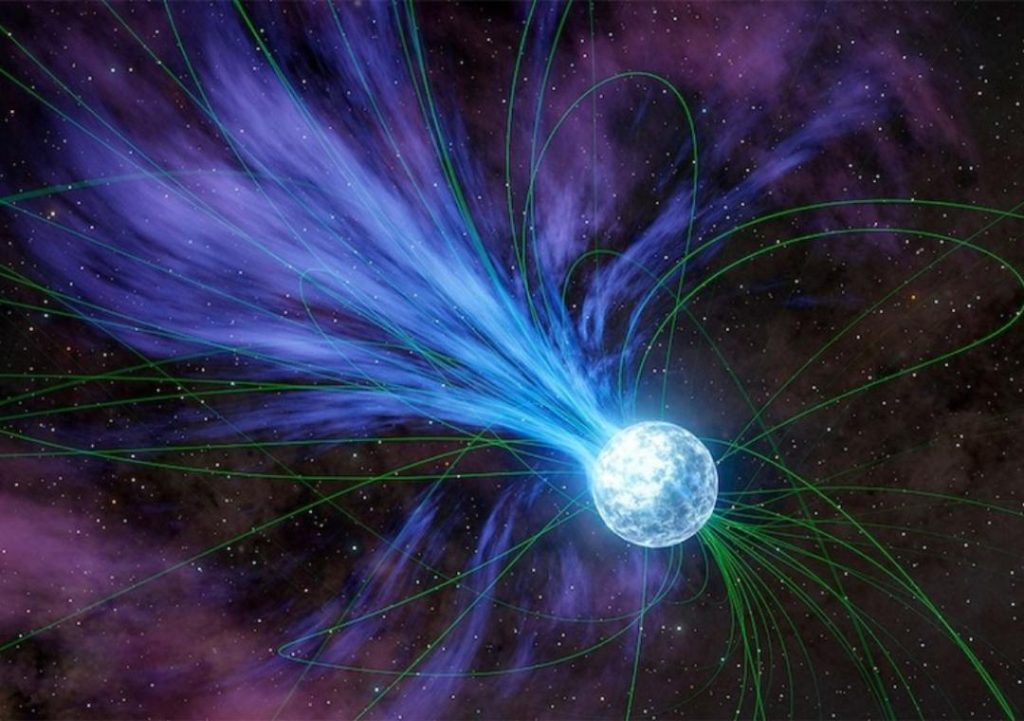
Magnetars, as their name suggests, are stars that are incredibly magnetic. They are formed when a massive star undergoes a supernova explosion, leaving behind a dense core of neutrons. This core is so dense that it creates an incredibly strong magnetic field, making the star a magnetar. While magnetars are not uncommon in the universe, their magnetic fields are so powerful that they can have a profound impact on the surrounding environment.
In the case of the study, researchers discovered that a magnetar exploded approximately 20 years ago, releasing a flare that contained gold and platinum. This flare was so powerful that it was detectable from Earth, allowing scientists to study its composition and determine its origins. The study, published in the journal Nature Astronomy, found that the magnetar’s explosion was responsible for creating the precious metals through a process known as nucleosynthesis.
Nucleosynthesis is the process by which atomic nuclei are formed from the fusion of smaller nuclei. In the case of gold and platinum, nucleosynthesis occurs when high-energy particles collide and fuse together to form heavier elements. This process is only possible in extreme environments, such as those found in the heart of a magnetar.
The study’s findings have significant implications for our understanding of the origins of gold and platinum. For centuries, humans have believed that these metals were created through the natural processes of geological formation. However, the study suggests that they may have been created through a more dramatic and catastrophic event – the explosion of a magnetar.
But how often do magnetars explode, and what are the implications for the creation of gold and platinum? According to the study, magnetars explode approximately once every decade in the Milky Way galaxy. This means that every 10 years or so, a magnetar will explode, releasing a flare that contains gold and platinum.
But the study also suggests that this is not a unique event. In fact, magnetars explode annually across the observable universe. This means that every year, numerous magnetars will explode, releasing flares that contain gold and platinum. While these flares may be difficult to detect, they could potentially provide scientists with valuable insights into the origins of these precious metals.
The study’s findings have significant implications for our understanding of the universe and the creation of gold and platinum. For centuries, humans have believed that these metals were rare and valuable because of their natural scarcity. However, the study suggests that they may be more common than previously thought, created through the explosions of magnetars that occur regularly throughout the universe.
In conclusion, the study led by Anirudh Patel has shed new light on the origins of gold and platinum. According to the study, magnetars – highly magnetized neutron stars – played a crucial role in creating these precious metals through a cosmic event that occurred over 20 years ago. The study’s findings have significant implications for our understanding of the universe and the creation of gold and platinum, and could potentially provide scientists with valuable insights into the origins of these valuable elements.






