How does Sentinel-2 protect India’s biodiversity?
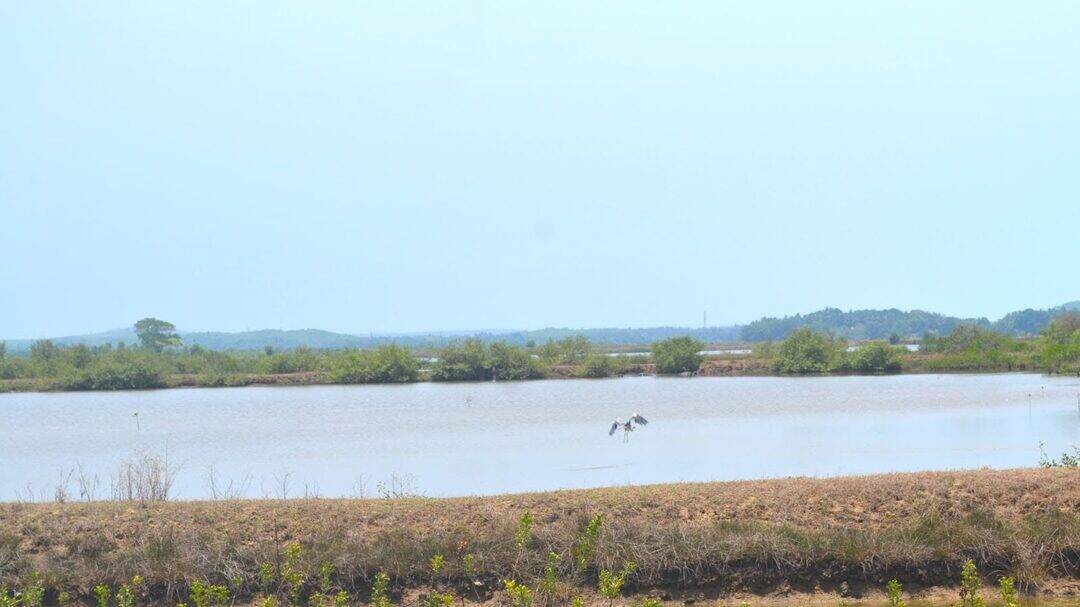
India is a country with rich and diverse biodiversity, ranging from the Himalayan mountains to the Western Ghats, and from the Indo-Gangetic Plain to the Eastern Ghats. The country is home to a wide variety of flora and fauna, and its wetlands are an essential part of its ecosystem. Wetlands are not only crucial for maintaining the water cycle, but they also provide habitat to numerous plant and animal species. However, India’s wetlands are facing a significant threat due to climate change, human activities, and other environmental factors. To monitor and protect these vital ecosystems, scientists at the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), Indian Institute of Space Technology (IIST), and Gujarat University have developed a new satellite mapping system, Sentinel-2.
The Sentinel-2 satellite is a game-changer in the field of environmental monitoring. Equipped with advanced sensors, it can identify submerged plants with an impressive 94% accuracy. This technology has been used to monitor 500 of India’s largest wetlands, and the results are alarming. The study has revealed that nearly 100 lakes, mostly in central and southern India, are experiencing a significant decline in vital plant life. This decline is a clear indication of the devastating impact of climate change and human activities on India’s wetlands.
The Sentinel-2 satellite mapping system uses advanced spectral bands to identify and classify different types of vegetation. The satellite’s sensors can detect even the slightest changes in the reflectance of light from the Earth’s surface, allowing scientists to monitor the health and distribution of plant species. This technology has revolutionized the field of environmental monitoring, enabling scientists to track changes in ecosystems over time and identify areas that require urgent conservation efforts.
The study, which used Sentinel-2 data to monitor India’s wetlands, has provided valuable insights into the state of the country’s biodiversity. The results show that many of India’s lakes are experiencing a decline in plant life, which is essential for maintaining the health of these ecosystems. Plants play a crucial role in wetlands, providing food and shelter to numerous animal species, regulating the water cycle, and maintaining water quality. The decline of plant life in India’s wetlands is a clear indication of the need for urgent climate action.
The Sentinel-2 satellite mapping system has also revealed that the decline of plant life in India’s wetlands is not uniform. While some lakes are experiencing a significant decline in plant life, others are still thriving. This variation is likely due to a range of factors, including differences in climate, geology, and human activities. For example, lakes in areas with high levels of pollution or human disturbance are more likely to experience a decline in plant life.
The study’s findings have significant implications for conservation efforts in India. The results highlight the need for urgent action to protect the country’s wetlands and the plant species that inhabit them. This can be achieved through a range of measures, including the restoration of degraded habitats, the reduction of pollution, and the implementation of sustainable land-use practices. The Sentinel-2 satellite mapping system can play a crucial role in these efforts, providing scientists and conservationists with the data they need to monitor and manage India’s wetlands effectively.
In addition to its implications for conservation, the study also highlights the importance of satellite technology in environmental monitoring. The Sentinel-2 satellite mapping system is just one example of the many satellite-based technologies that are being used to monitor the Earth’s environment. These technologies have revolutionized the field of environmental monitoring, enabling scientists to track changes in ecosystems over time and identify areas that require urgent conservation efforts.
In conclusion, the Sentinel-2 satellite mapping system is a powerful tool for protecting India’s biodiversity. The technology has revealed a significant decline in plant life in many of the country’s wetlands, highlighting the need for urgent climate action. The study’s findings have significant implications for conservation efforts in India, and the Sentinel-2 satellite mapping system can play a crucial role in these efforts. As the country continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change and environmental degradation, the use of satellite technology will become increasingly important for monitoring and managing its ecosystems.
The development of the Sentinel-2 satellite mapping system is a testament to the power of collaboration and innovation in the field of environmental science. The partnership between ISRO, IIST, and Gujarat University has resulted in a technology that has the potential to transform the way we monitor and manage the Earth’s ecosystems. As we look to the future, it is clear that satellite technology will play an increasingly important role in protecting India’s biodiversity and addressing the challenges of climate change.