Safer method boosts gas capture for clean energy
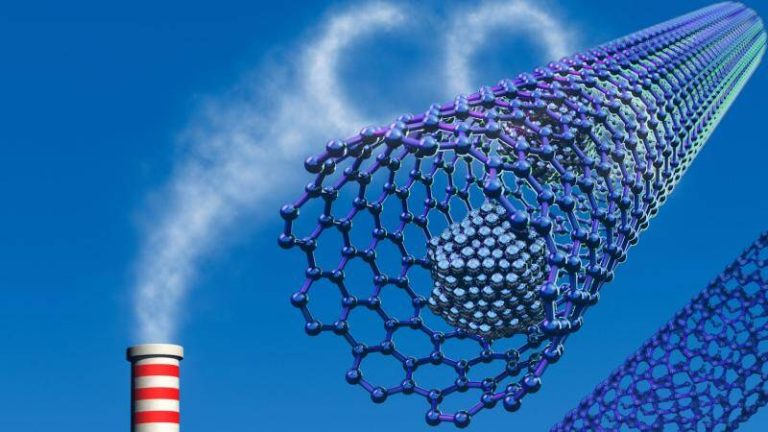
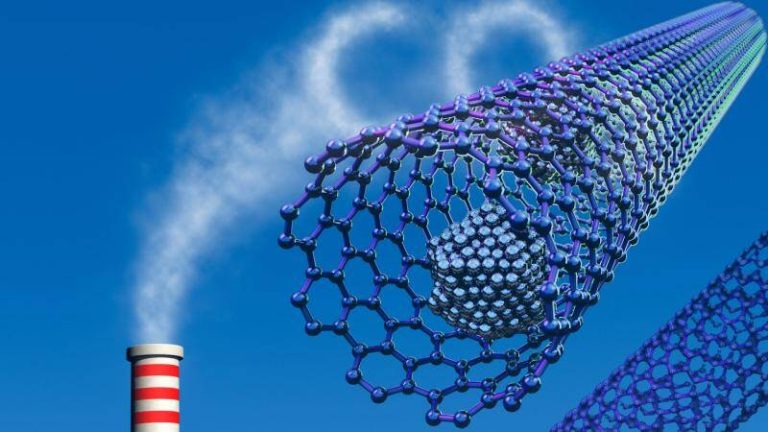
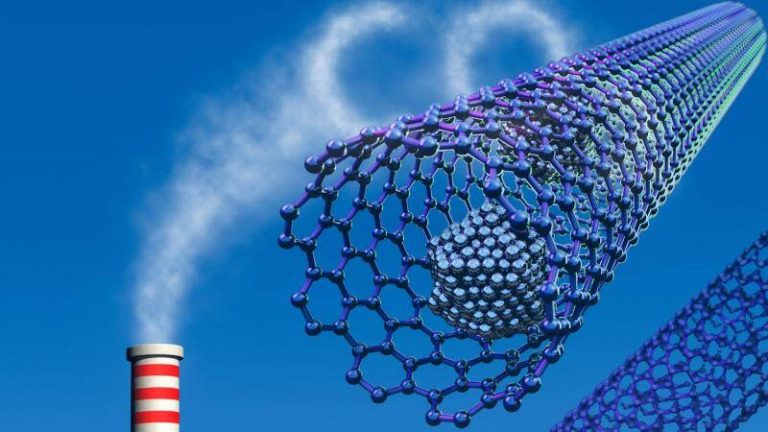
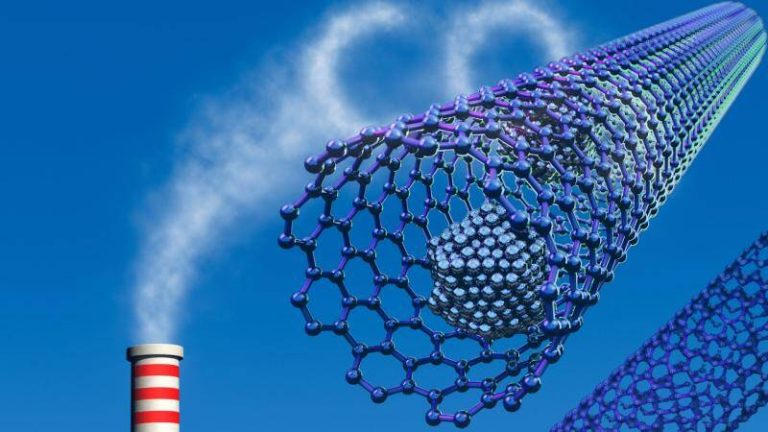
The world is grappling with the challenges of climate change, and one of the most significant contributors to this problem is the increasing levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, in particular, is a major culprit, and finding effective ways to capture and store it has become a pressing concern. Researchers have been exploring various methods to develop materials that can efficiently trap these gases, and a recent breakthrough has shown tremendous promise. A team of scientists has developed a safer and more efficient method for synthesizing metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), which are highly porous materials that can capture greenhouse gases and store hydrogen at room temperature.
The traditional method of synthesizing MOFs involves the use of hydrofluoric acid, a highly toxic and corrosive substance that poses significant risks to human health and the environment. However, the new method developed by the researchers replaces hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators, making the synthesis process much more environmentally friendly. This fluoride-free approach not only reduces the risks associated with the use of toxic chemicals but also produces superior crystals that are more efficient at trapping gases.
The new method is based on the use of modulators that control the growth of the MOF crystals, allowing for the creation of highly porous and stable structures. These structures are capable of capturing greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, with much higher efficiency than traditional methods. Furthermore, the MOFs synthesized using this method can store hydrogen at room temperature, which is a significant advantage over traditional methods that require high pressures and temperatures.
The implications of this breakthrough are far-reaching and have the potential to revolutionize the field of clean energy. The development of more efficient and safer methods for synthesizing MOFs could pave the way for the creation of affordable carbon scrubbers that can be used to capture greenhouse gases from power plants and industrial processes. Additionally, the ability to store hydrogen at room temperature could enable the widespread adoption of fuel cell technology, which has the potential to replace fossil fuels as a clean and efficient source of energy.
Another significant application of this technology is in the field of atmospheric water harvesting. MOFs can be used to capture water vapor from the air, even in arid environments, and release it as liquid water when heated. This technology has the potential to provide clean drinking water for millions of people around the world who lack access to this basic necessity. The new method for synthesizing MOFs could make this technology more efficient and cost-effective, enabling its widespread adoption in developing countries.
The fight against climate change requires a multi-faceted approach that involves reducing greenhouse gas emissions, developing clean energy sources, and protecting natural carbon sinks. The development of more efficient and safer methods for synthesizing MOFs is a significant step in this direction. By providing a more effective and environmentally friendly way to capture and store greenhouse gases, this technology has the potential to make a significant impact on the global effort to reduce carbon emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change.
Furthermore, the use of MOFs in carbon capture and storage has several advantages over traditional methods. MOFs can capture carbon dioxide at much lower concentrations than traditional methods, making them ideal for use in power plants and industrial processes where carbon emissions are a major concern. Additionally, MOFs can be designed to capture specific gases, such as carbon dioxide or methane, allowing for more targeted and efficient carbon capture.
The development of this new method for synthesizing MOFs is a testament to the power of scientific innovation in addressing some of the world’s most pressing challenges. By providing a safer and more efficient way to capture and store greenhouse gases, this technology has the potential to make a significant contribution to the global effort to reduce carbon emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change. As researchers continue to explore new applications for MOFs, it is likely that this technology will play an increasingly important role in the transition to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
In conclusion, the development of a safer and more efficient method for synthesizing MOFs is a significant breakthrough in the field of clean energy. By replacing toxic hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators, this new method produces superior crystals that can capture greenhouse gases and store hydrogen at room temperature. The implications of this technology are far-reaching, with potential applications in carbon capture and storage, fuel cell technology, and atmospheric water harvesting. As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change, innovations like this have the potential to make a significant impact and pave the way for a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
News Source: https://researchmatters.in/news/greener-path-synthesising-metal-organic-frameworks-carbon-capture-and-storage