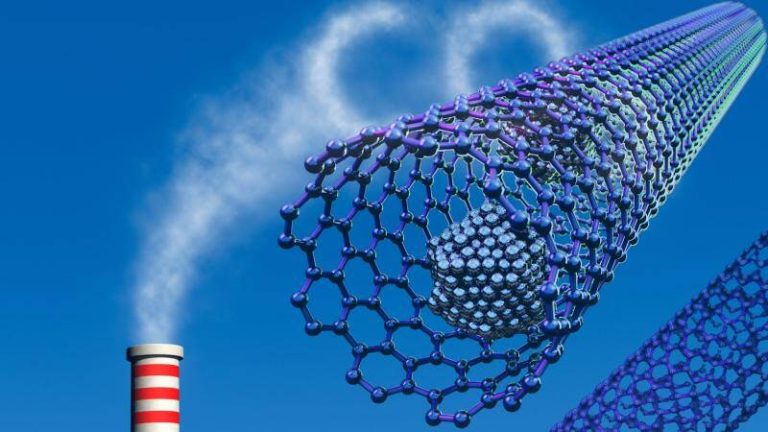
Safer method boosts gas capture for clean energy
The world is facing an unprecedented crisis in the form of climate change, and one of the primary culprits behind this crisis is the increasing levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. The burning of fossil fuels for energy has led to a significant increase in carbon dioxide emissions, which is one of the primary greenhouse gases responsible for global warming. To combat this crisis, researchers and scientists have been working tirelessly to develop new and innovative methods for capturing and storing these gases, thereby reducing their impact on the environment.
One such innovation that has shown great promise in recent years is the development of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). MOFs are a class of materials that are composed of metal ions and organic linkers, and they have been shown to be highly effective in capturing and storing gases such as carbon dioxide and hydrogen. However, the traditional methods for synthesizing MOFs have been criticized for being toxic and environmentally unfriendly, as they often involve the use of hydrofluoric acid, a highly corrosive and toxic substance.
In a breakthrough discovery, researchers have developed a fluoride-free synthesis for metal-organic frameworks, replacing toxic hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators. This simplified method produces superior crystals that trap greenhouse gases and store hydrogen more efficiently at room temperature, paving the way for affordable carbon scrubbers and advanced atmospheric water harvesting systems to fight climate change globally.
The new method, which has been hailed as a significant breakthrough in the field of clean energy, uses a combination of modulators to control the synthesis of MOFs. These modulators are able to direct the formation of the MOF crystals, allowing for the creation of materials with specific properties and structures. The resulting MOFs are not only more efficient at capturing and storing gases but are also more stable and durable, making them ideal for use in a wide range of applications.
One of the most significant advantages of the new method is its ability to produce MOFs that can capture and store gases at room temperature. This is a major breakthrough, as most traditional methods for synthesizing MOFs require high temperatures and pressures, which can be energy-intensive and expensive. The new method, on the other hand, is able to produce MOFs that can capture and store gases at ambient temperatures, making it a much more efficient and cost-effective process.
The potential applications of the new method are vast and varied. One of the most significant applications is in the development of carbon scrubbers, which are devices that can capture and remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. These devices have the potential to play a major role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the effects of climate change. The new method for synthesizing MOFs could make it possible to produce carbon scrubbers that are more efficient, more cost-effective, and more environmentally friendly.
Another potential application of the new method is in the development of advanced atmospheric water harvesting systems. These systems, which are designed to capture and condense water vapor from the air, have the potential to provide clean drinking water for millions of people around the world. The new method for synthesizing MOFs could make it possible to produce materials that are more efficient at capturing and storing water vapor, making it possible to develop more effective and sustainable water harvesting systems.
In addition to these applications, the new method for synthesizing MOFs also has the potential to play a major role in the development of more efficient and sustainable energy systems. For example, MOFs could be used to store hydrogen, which is a clean and renewable energy source. The new method for synthesizing MOFs could make it possible to produce materials that are more efficient at storing hydrogen, making it possible to develop more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy systems.
In conclusion, the development of a fluoride-free synthesis for metal-organic frameworks is a significant breakthrough in the field of clean energy. The new method, which uses safer modulators to control the synthesis of MOFs, has the potential to produce materials that are more efficient, more cost-effective, and more environmentally friendly. The potential applications of the new method are vast and varied, and it has the potential to play a major role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, mitigating the effects of climate change, and developing more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy systems.
As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change, it is innovations like this that will be crucial in helping us to develop more sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions. The development of the new method for synthesizing MOFs is a testament to the power of human ingenuity and the importance of continued investment in research and development.
News source: https://researchmatters.in/news/greener-path-synthesising-metal-organic-frameworks-carbon-capture-and-storage