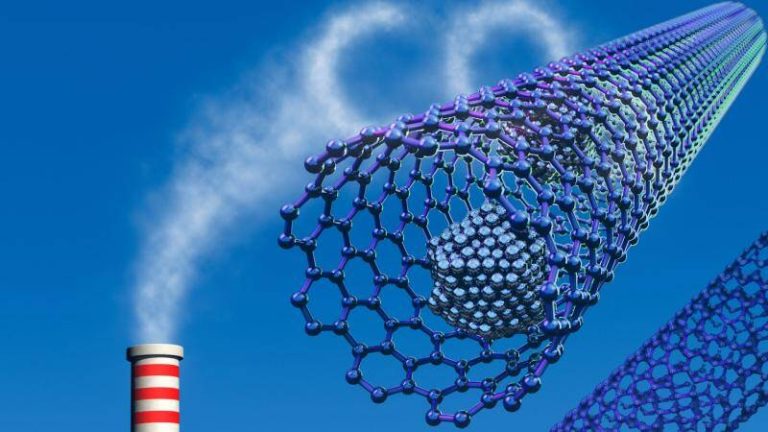
Safer method boosts gas capture for clean energy
The quest for clean energy and reducing greenhouse gas emissions has been a pressing concern globally. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change, researchers have been working tirelessly to develop innovative solutions to capture and store carbon dioxide, a major contributor to global warming. In a significant breakthrough, a team of researchers has developed a safer and more efficient method for synthesizing metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), which are porous materials that can trap greenhouse gases and store hydrogen at room temperature.
Traditionally, the synthesis of MOFs involves the use of hydrofluoric acid, a toxic and corrosive substance that poses significant health and environmental risks. However, the new method replaces hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators, making the process more environmentally friendly and reducing the risk of accidents. This fluoride-free synthesis approach not only improves the safety of the process but also produces superior crystals that are more efficient at capturing carbon dioxide and storing hydrogen.
The new method is a significant improvement over existing techniques, as it simplifies the synthesis process and reduces the cost of production. This makes it more viable for large-scale applications, such as the development of affordable carbon scrubbers and advanced atmospheric water harvesting systems. The potential impact of this breakthrough is enormous, as it could pave the way for the widespread adoption of clean energy technologies and help mitigate the effects of climate change.
The importance of metal-organic frameworks
MOFs are a class of materials that have been gaining attention in recent years due to their unique properties. They are composed of metal ions or clusters connected by organic linkers, which create a porous structure that can trap gases and other molecules. MOFs have been shown to be highly effective at capturing carbon dioxide, methane, and other greenhouse gases, making them a promising solution for carbon capture and storage.
In addition to their potential for carbon capture, MOFs also have applications in hydrogen storage, catalysis, and drug delivery. They can be designed to have specific properties, such as high surface areas, tunable pore sizes, and tailored chemical functionalities, which make them suitable for a wide range of applications.
The challenges of traditional synthesis methods
The traditional synthesis of MOFs involves the use of hydrofluoric acid, which is a highly toxic and corrosive substance. The use of hydrofluoric acid poses significant health and environmental risks, as it can cause severe burns, respiratory problems, and other health issues. Additionally, the handling and disposal of hydrofluoric acid require specialized equipment and facilities, which can be costly and logistically challenging.
The use of hydrofluoric acid also limits the scalability of MOF synthesis, as it requires specialized equipment and facilities to handle the acid safely. This can make it difficult to produce large quantities of MOFs, which is necessary for many industrial applications.
The new synthesis method
The new synthesis method developed by the researchers replaces hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators, which are less toxic and more environmentally friendly. The modulators are designed to control the growth of the MOF crystals, allowing for the formation of highly crystalline and porous materials.
The new method is also more efficient and cost-effective than traditional synthesis methods. It simplifies the synthesis process, reducing the number of steps and the amount of time required to produce high-quality MOFs. This makes it more viable for large-scale applications, such as the development of affordable carbon scrubbers and advanced atmospheric water harvesting systems.
Applications and implications
The new synthesis method has significant implications for the development of clean energy technologies and the mitigation of climate change. The production of high-quality MOFs at a lower cost and with improved safety could pave the way for the widespread adoption of carbon capture and storage technologies.
The use of MOFs for carbon capture and storage could reduce the amount of greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere, helping to mitigate the effects of climate change. Additionally, the development of advanced atmospheric water harvesting systems could provide clean water for millions of people around the world, improving public health and quality of life.
Conclusion
The development of a safer and more efficient method for synthesizing metal-organic frameworks is a significant breakthrough in the quest for clean energy and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The new method replaces toxic hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators, producing superior crystals that can trap greenhouse gases and store hydrogen at room temperature. The potential impact of this breakthrough is enormous, as it could pave the way for the widespread adoption of clean energy technologies and help mitigate the effects of climate change.
As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change, innovations like this are crucial for developing sustainable solutions. The new synthesis method is a significant step forward in the development of clean energy technologies, and it has the potential to make a major impact on the global effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change.
News Source: https://researchmatters.in/news/greener-path-synthesising-metal-organic-frameworks-carbon-capture-and-storage